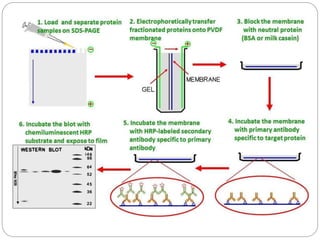
Western blotting is a technique used to detect specific proteins in a sample. It involves separating proteins by electrophoresis, transferring them to a membrane, and using antibodies to identify a target protein. There are several key steps: extraction of proteins from a sample, separation by size using gel electrophoresis, transferring proteins from the gel to a membrane, blocking the membrane to prevent nonspecific antibody binding, incubation with primary and secondary antibodies to detect the target protein, and use of a substrate to visualize the antibody-protein complex. Western blotting has applications in disease diagnosis, detecting defective proteins, and confirming the presence of viruses or bacteria.