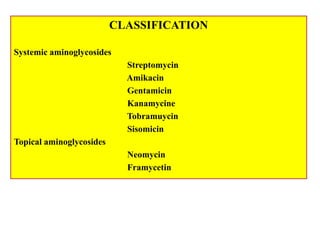
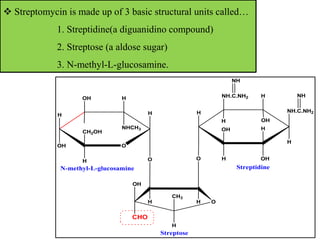
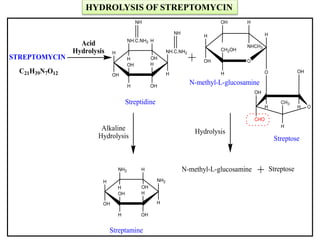
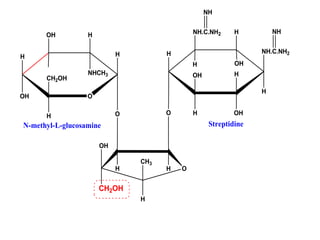
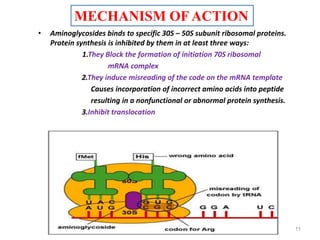
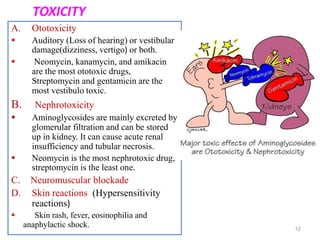
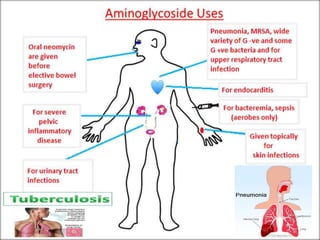
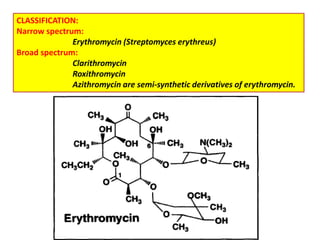
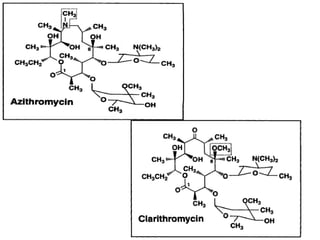
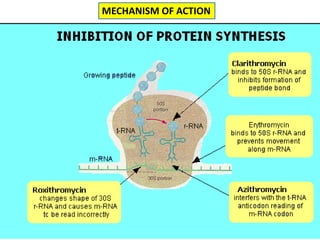
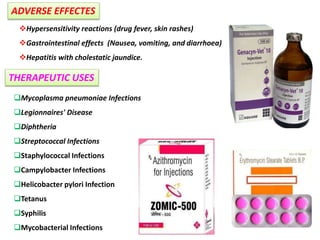
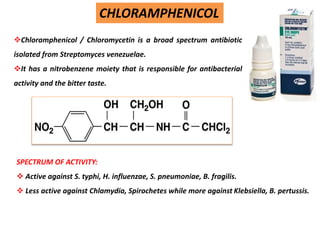
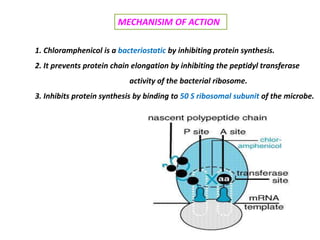
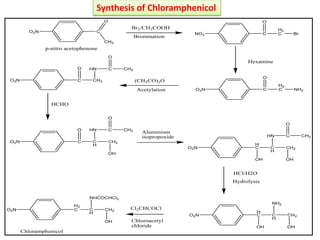
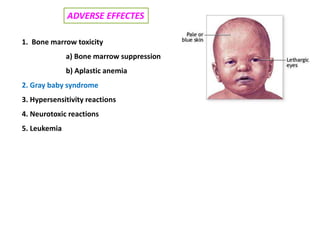
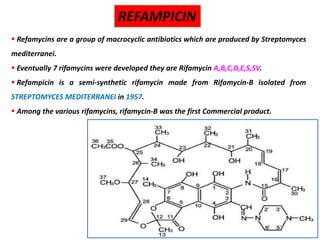
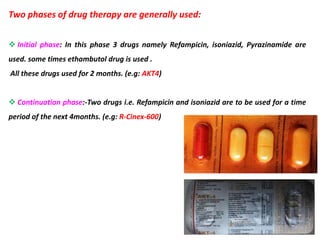
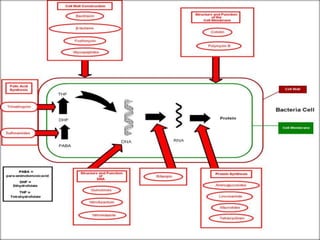
This document discusses various aminoglycoside, macrolide, and chloramphenicol antibiotics. It provides details on streptomycin, an aminoglycoside antibiotic derived from Streptomyces griseus. It describes the chemical structure and classification of aminoglycosides. Common side effects of aminoglycosides include ototoxicity and nephrotoxicity. Macrolides like erythromycin work by binding to bacterial ribosomes and inhibiting protein synthesis. Chloramphenicol is a broad-spectrum antibiotic that works by inhibiting bacterial ribosomes. Rifampicin is a semi-synthetic rifamycin antibiotic used to treat tuberculosis and leprosy by inhibiting bacterial DNA-dependent RNA polymerase.