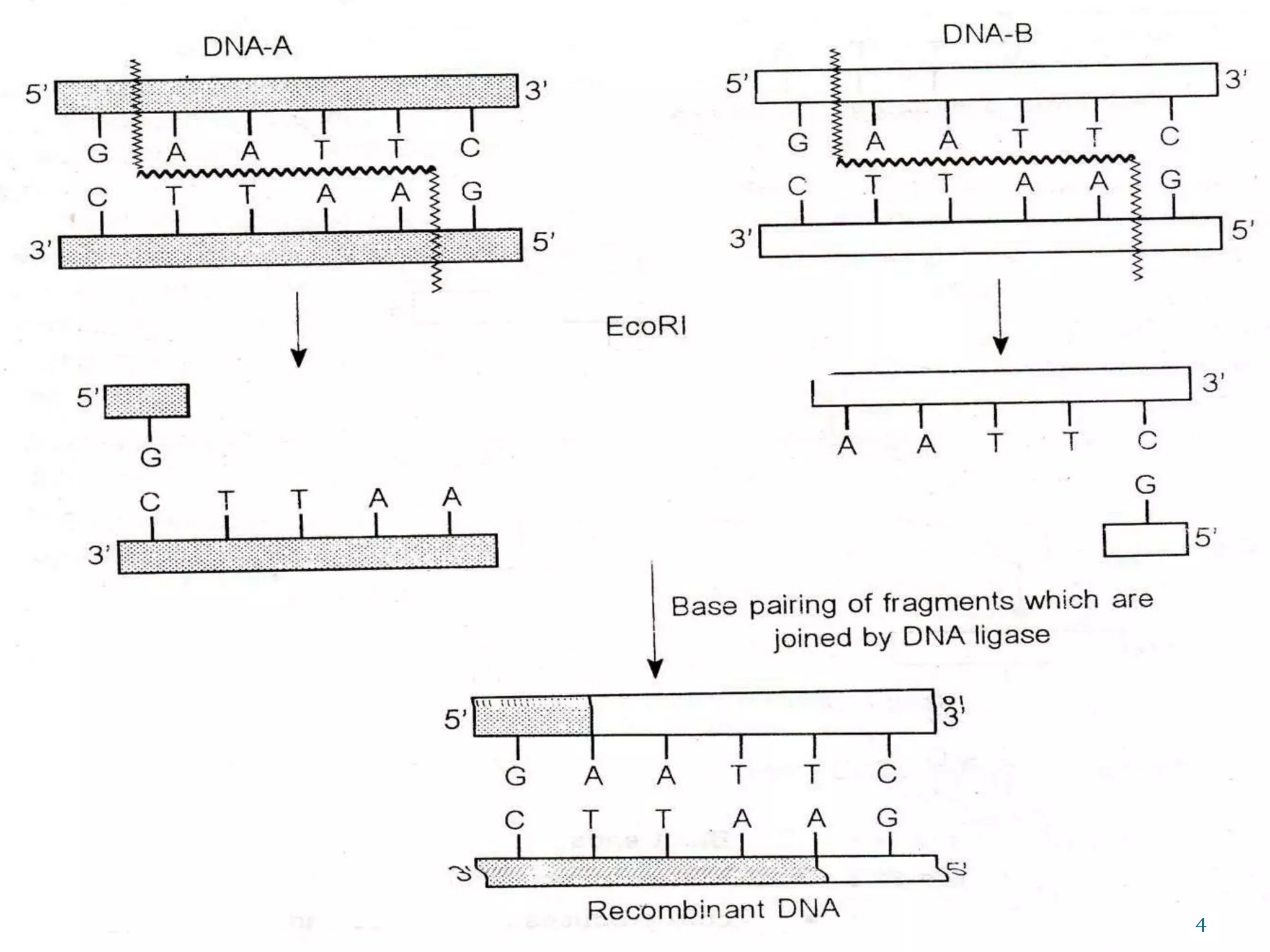
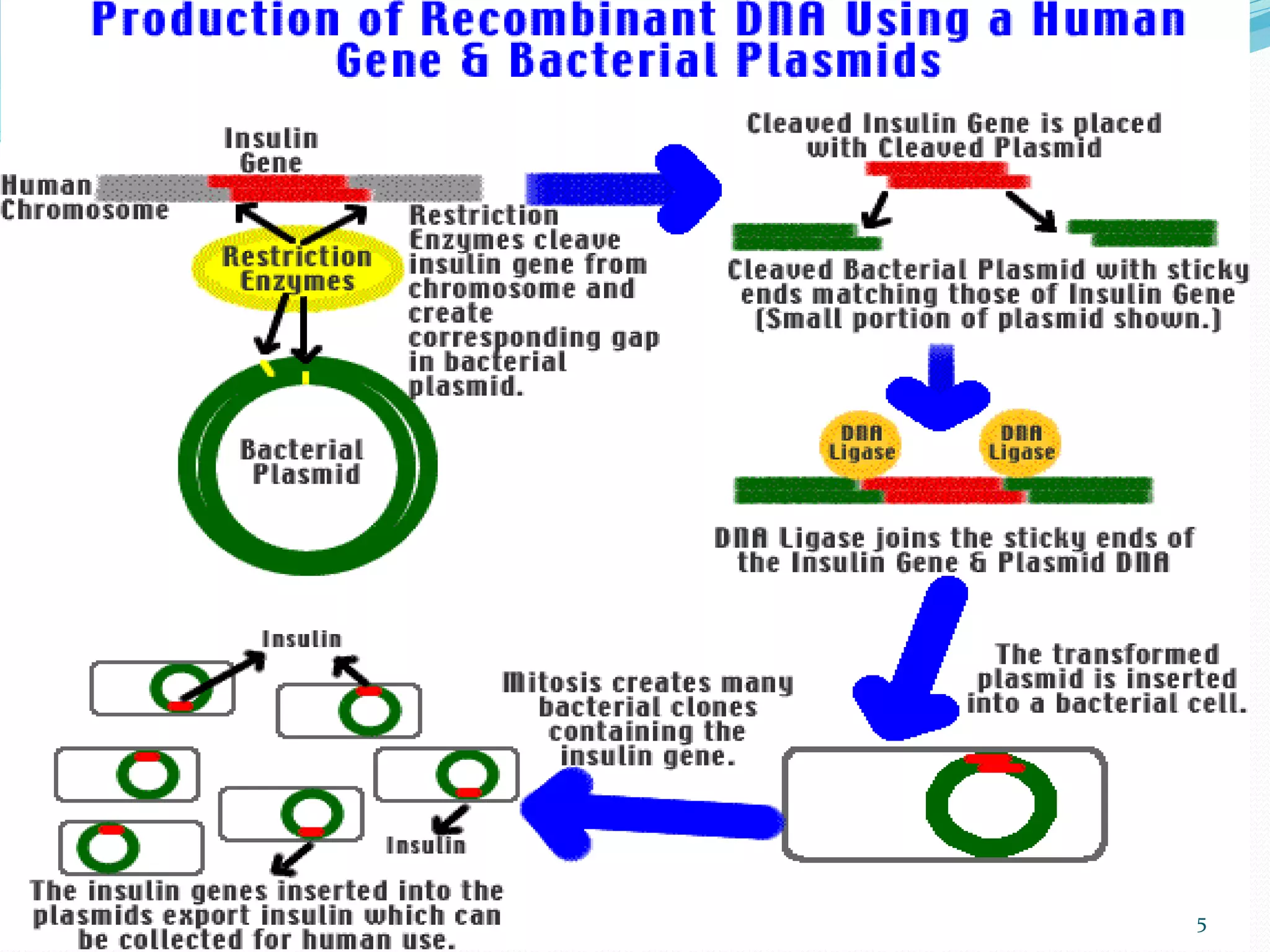
Recombinant DNA technology involves combining DNA sequences from different species that would not normally occur together to create artificial DNA and alter the genetics of living cells. There are three main methods to create recombinant DNA - transformation, phage introduction, and non-bacterial transformation. Transformation involves selecting a DNA fragment, inserting it into a vector, and introducing the vector into a host cell like E. coli. Recombinant DNA technology has many applications, including producing proteins and hormones, disease diagnosis and treatment, genetically engineering plants, and forensic analysis.