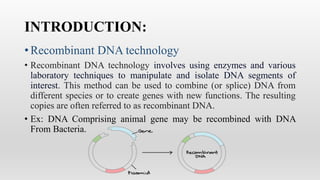
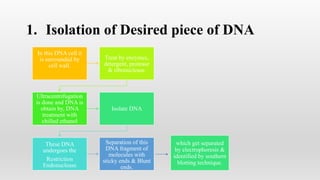
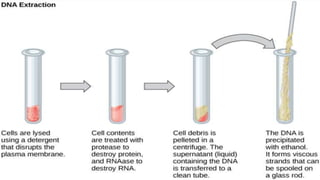
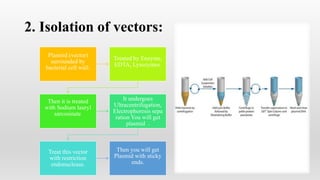
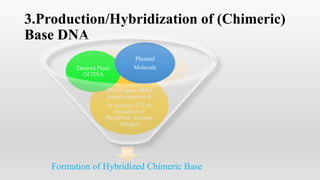
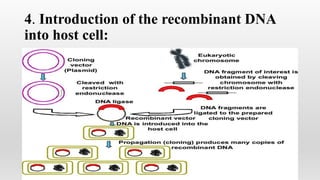
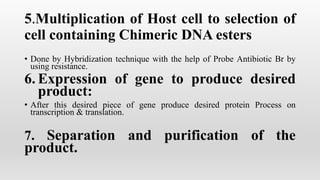
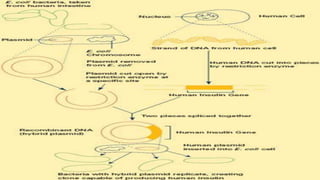
Recombinant DNA technology involves manipulating and combining DNA from different species using laboratory techniques. The resulting recombinant DNA can be used to produce large quantities of proteins encoded by genes of interest. Key steps include isolating the desired DNA and vector, combining them to form recombinant DNA, introducing this into a host cell, and causing the host cell to multiply and express the gene to produce the desired protein product. Various tools are used, including restriction enzymes to cut DNA, DNA ligase to join DNA, and polymerases for DNA replication. Common gene transfer techniques include transformation, transduction, electroporation, conjugation, and direct DNA transfer.