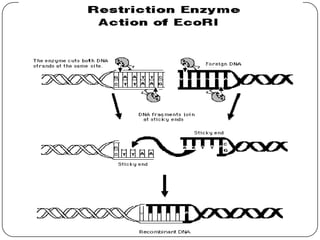
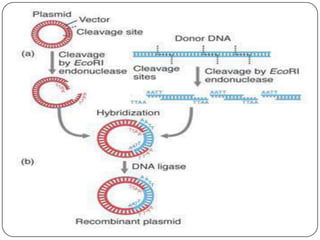
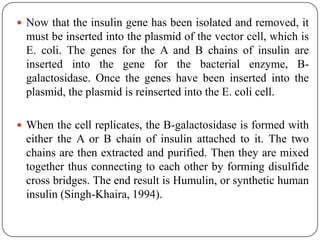
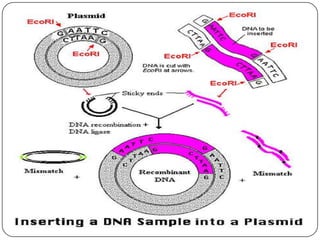
Recombinant DNA is created using molecular cloning techniques to combine DNA from multiple sources into new sequences. There are three main methods: transformation, phage introduction, and non-bacterial transformation. Transformation involves inserting DNA into bacterial host cells like E. coli, while non-bacterial transformation uses direct microinjection or biolistics in non-bacterial cells. Phage introduction uses bacteriophages to introduce DNA. Recombinant DNA technology has important applications in agriculture, medicine, and other fields.