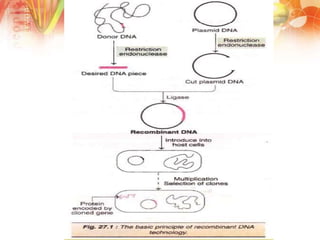
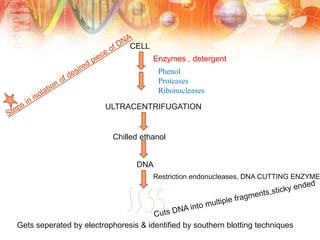
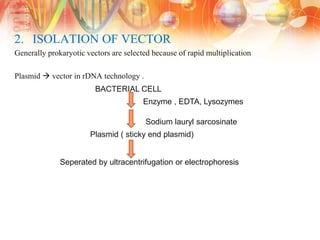
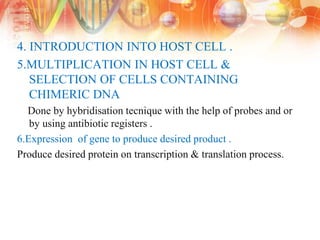
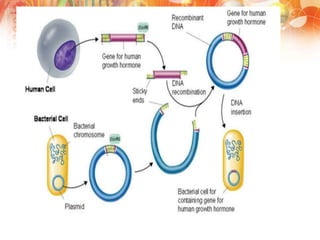
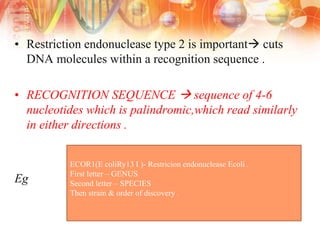
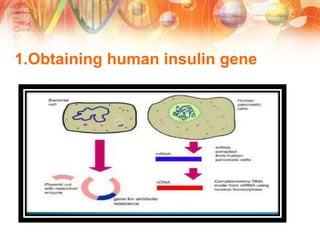
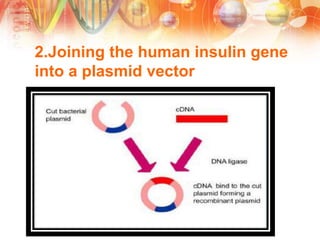
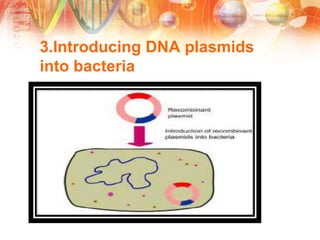
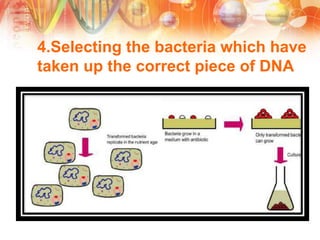
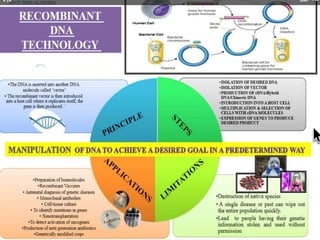
Recombinant DNA technology involves manipulating DNA from different sources to produce novel DNA molecules. It has several key steps: isolating the desired DNA and vector, joining them using enzymes to create recombinant DNA, introducing this into a host cell, and selecting cells that express the gene. This technology has many applications including producing human insulin and growth hormones through bacteria, developing vaccines by cloning genes for antigens, and creating monoclonal antibodies. It allows mass production of important biological substances that were previously difficult to obtain.