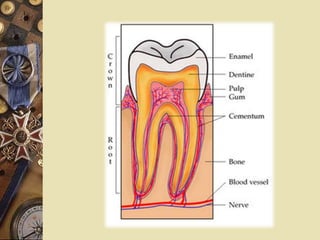
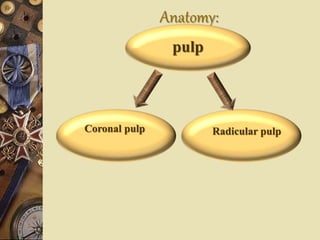
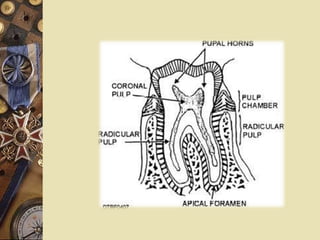
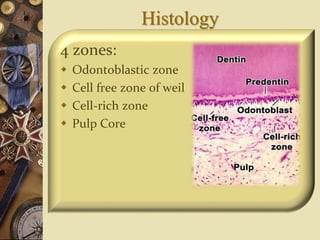
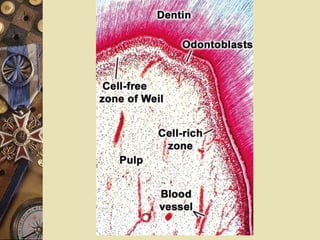
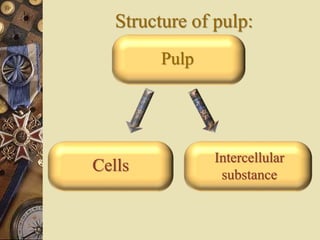
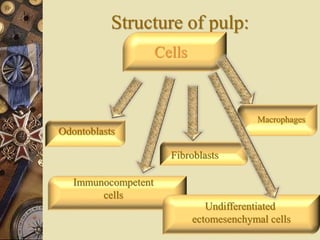
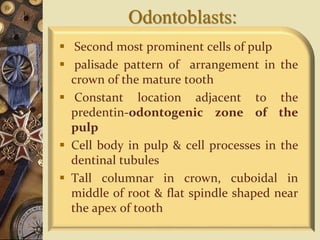
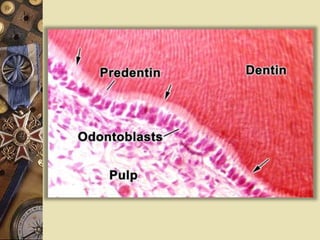
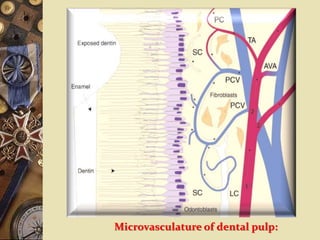
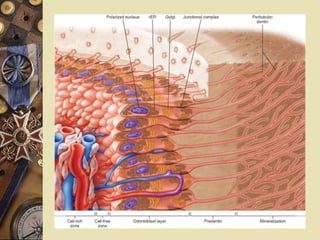
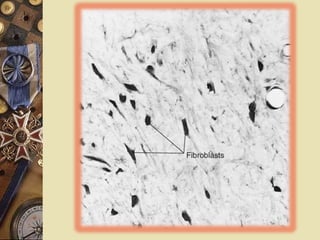
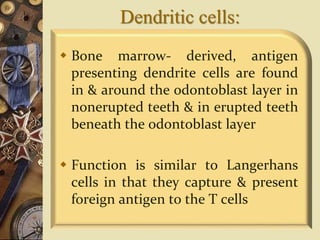
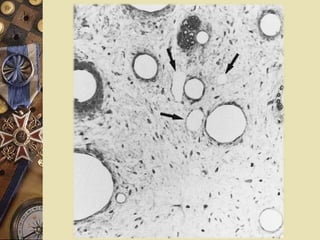
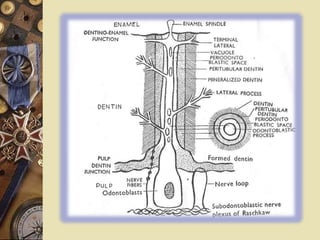
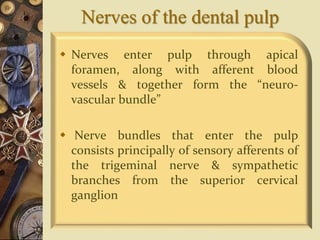
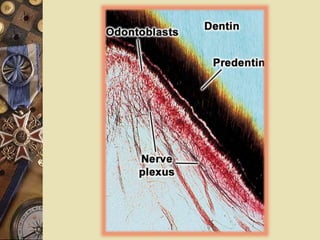
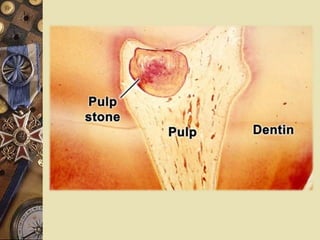
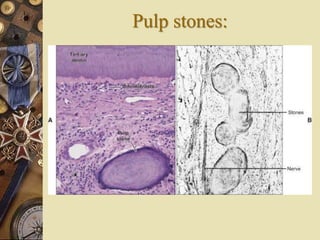
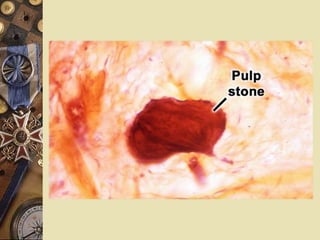
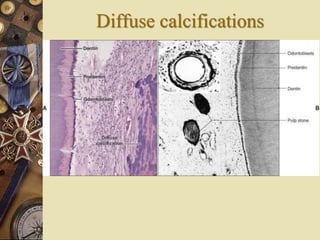
The dental pulp is the soft tissue contained within the pulp chamber and root canals of teeth. It is composed of loose connective tissue and nerves that provide sensation and nourishment to the tooth. The pulp contains cells such as odontoblasts, fibroblasts, macrophages, and stem cells embedded within an extracellular matrix. Odontoblasts are responsible for dentin formation and maintenance. With age, the pulp undergoes regressive changes like fibrosis, calcification in the form of pulp stones, and decreased cellularity. Diseases like caries, trauma, and chemical irritation can lead to inflammation of the pulp tissue.