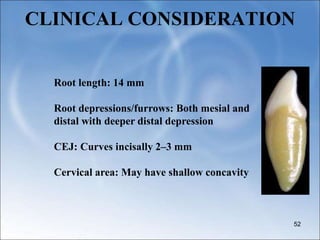
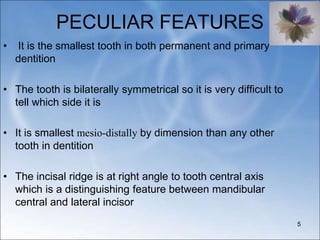
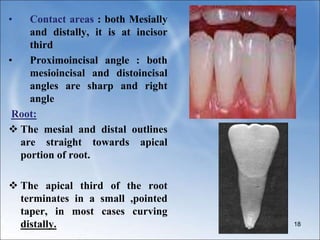
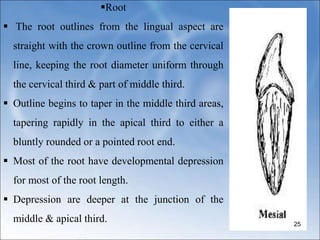
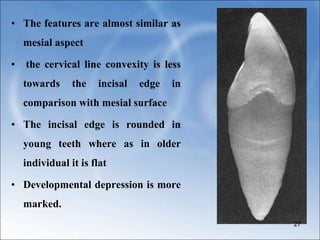
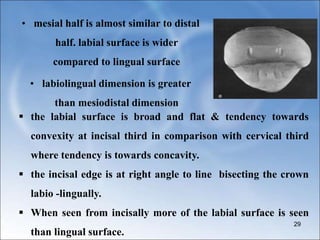
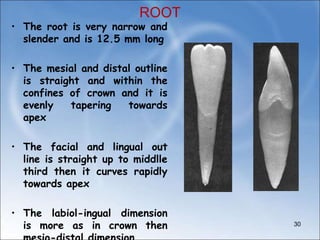
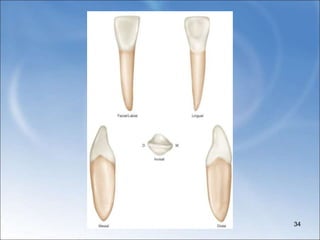
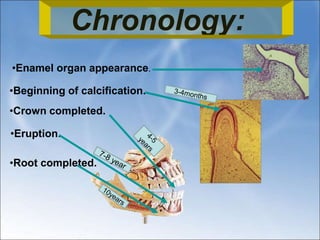
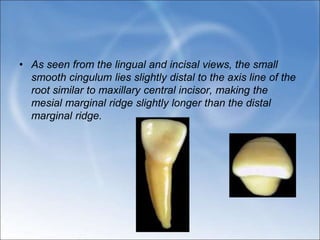
The document describes the anatomy and features of the mandibular central and lateral incisors. It discusses that the mandibular central incisor is the smallest tooth and is bilaterally symmetrical, while the lateral incisor is slightly larger with an incisal edge that declines distally. Key distinguishing features between the two incisors include the lateral having a lower distal contact point, distally tipped crown, and distolingual twist of the incisal edge. Both assist in biting and cutting food from the front view appearing as narrow teeth with a straight incisal edge and tapering sides.























![• The incisal edge is on or lingual to the mid-root axis. the
distolingual twist of the incisal ridge places the incisal distal
portion of the ridge somewhat more lingual than on the mesial.
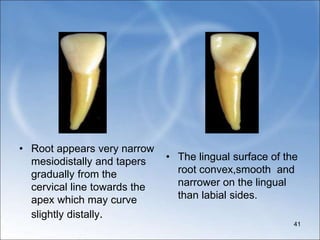
• Mesially the cervical line has deep curvature[2mm].extending
incisally over one fourth of the crown length. the curvature
averaged 0.6 mm greater on the mesial surface than distal
surface.
• The labial crest is near the cervical line in the cervical third, the
lingual crest is on the cingulum.
44](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mandibularcentralandlateralincisor-240111144534-cc6ecd50/85/MANDIBULAR-CENTRAL-AND-LATERAL-INCISOR-ppt-44-320.jpg)

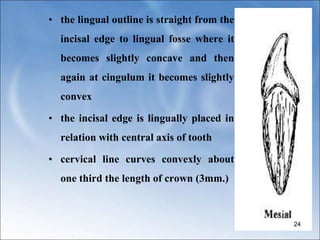
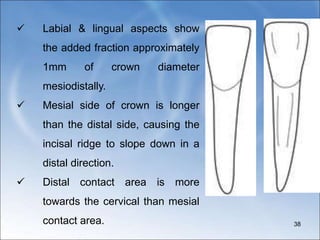
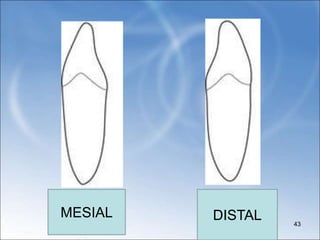
![ Crown is broader faciolingually than mesio-
distally[by 0.4mm]
Incisal edge not follow a straight line
mesiodistally , but rather it has a
distolingual twist: that is the distal half of
the incisal edge is bent lingually so that the
distolingual is more lingual in position than
the mesioincisal angle.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mandibularcentralandlateralincisor-240111144534-cc6ecd50/85/MANDIBULAR-CENTRAL-AND-LATERAL-INCISOR-ppt-47-320.jpg)

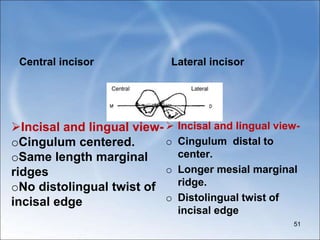
![Lateral incisor
Distinguish features between mandibular central
and lateral incisor
Central incisor
More symmetrical
Smaller overall and shorter root
Crown is 0.6mm shorter, root is
0.9 mm shorter in same mouth
.
Labial and lingual view-
o Same level contacts
o Crown not bent distally on root
o No distal side bulge on crown.
Less symmetrical[labial, lingual,
incisal views]
o Crown larger overall[especially
mesiodistallyby 0.4mm]with longer
root [0.9mm longer]
Labial and lingual view-
o Lower distal contact.
o Crown tipped distally on root.
o Distal side bulge on crown.
50](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mandibularcentralandlateralincisor-240111144534-cc6ecd50/85/MANDIBULAR-CENTRAL-AND-LATERAL-INCISOR-ppt-49-320.jpg)