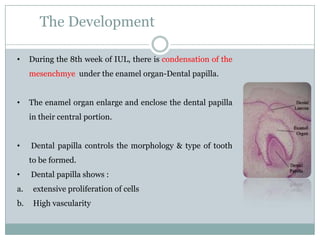
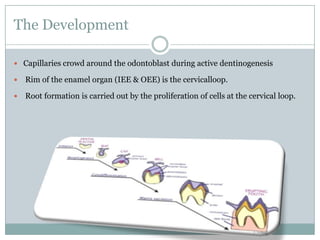
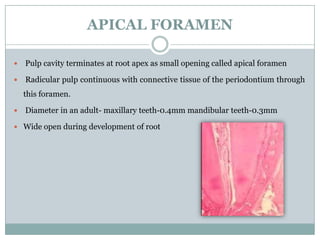
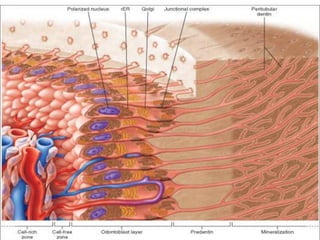
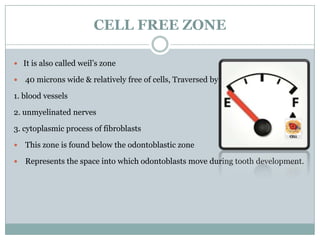
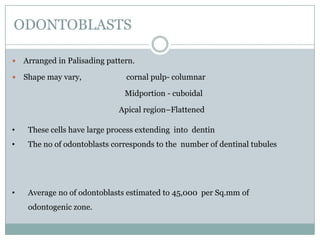
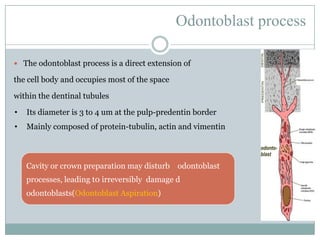
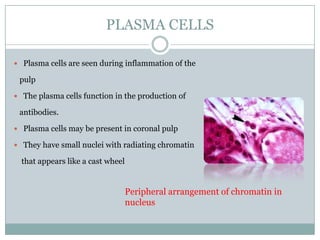
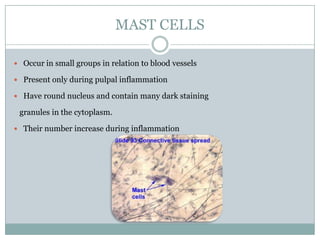
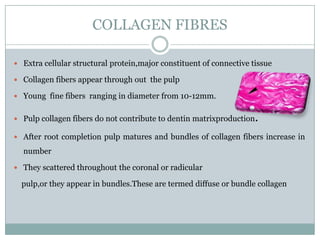
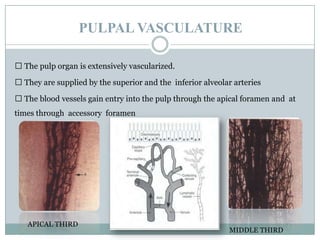
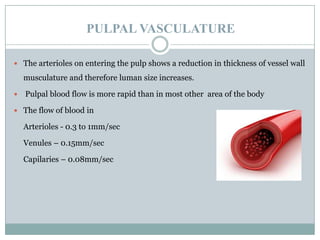
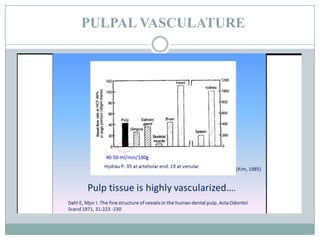
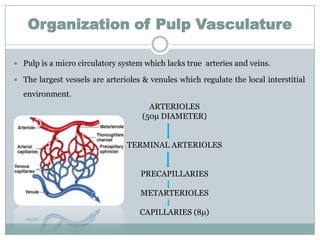
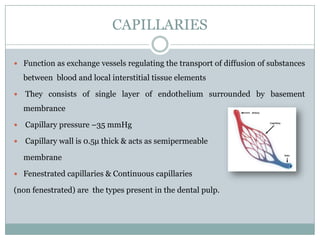
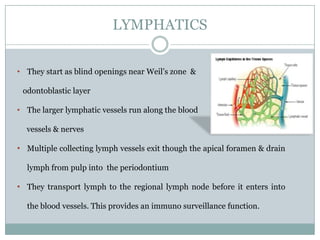
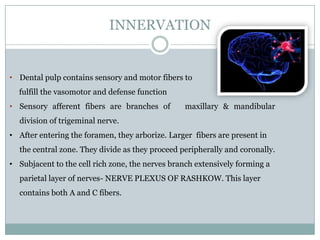
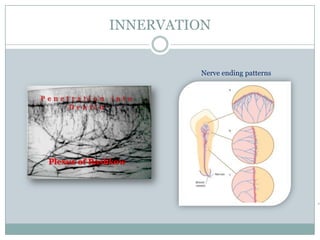
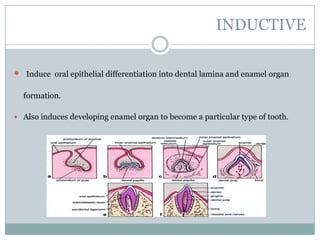
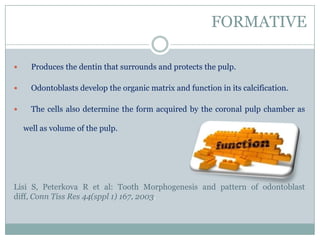
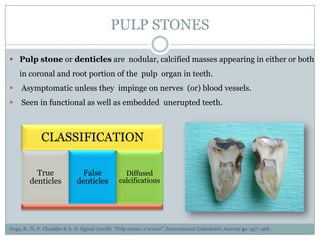
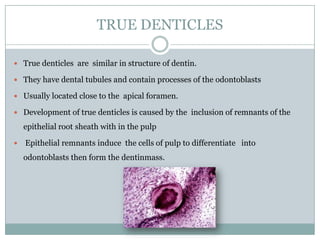
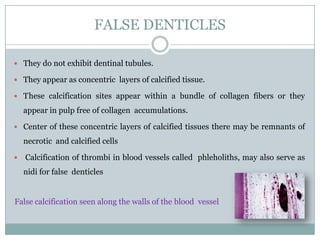
The dental pulp is a soft connective tissue located within the tooth. It develops from the dental papilla during tooth formation. The pulp has four zones - the odontoblastic zone containing cells that form dentin, the cell-free zone, cell-rich zone containing many cells, and a central zone with large blood vessels and nerves. The pulp receives blood vessels through the apical foramen and contains many cell types including odontoblasts, fibroblasts, immune cells, and undifferentiated cells. It is highly innervated with sensory fibers that detect pain and sympathetic fibers that control blood flow. The pulp plays key roles in tooth development, defense against infection, and sensitivity.