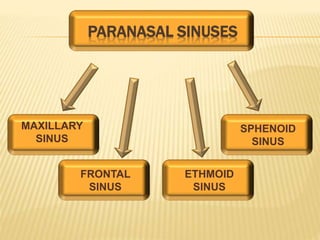
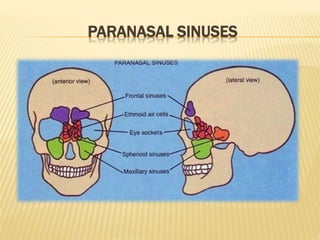
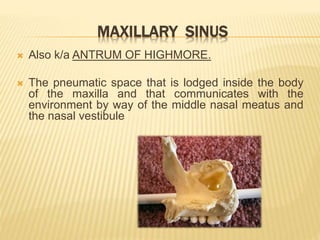
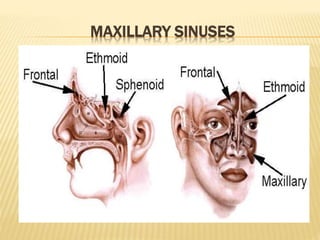
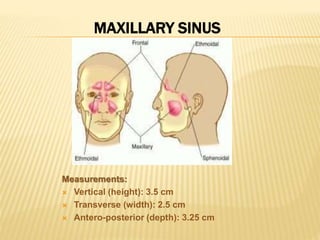
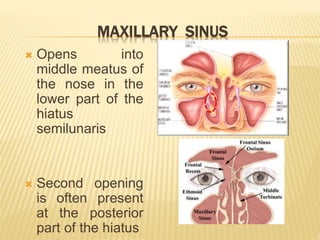
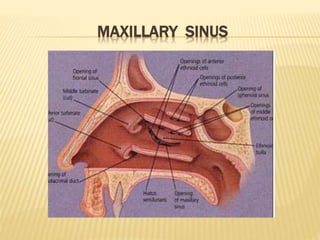
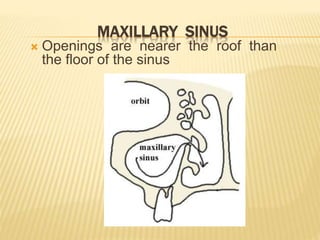
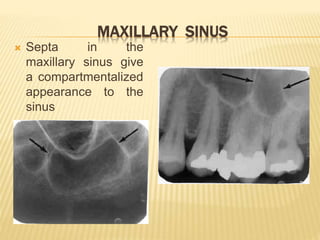
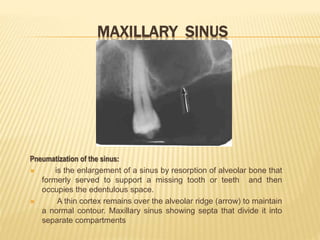
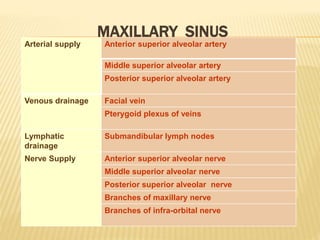
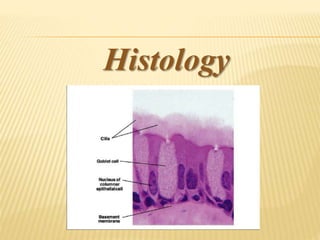
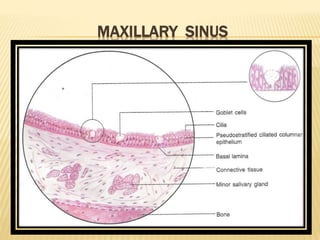
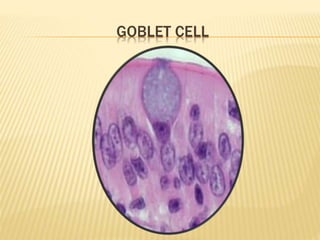
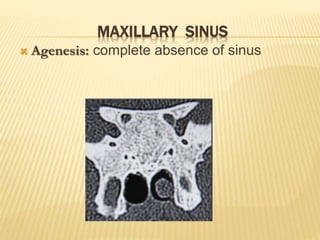
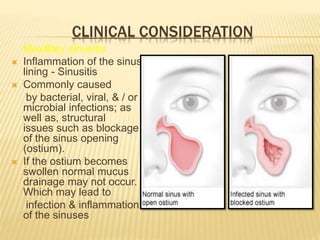
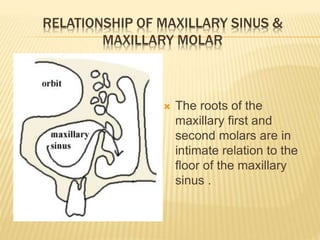
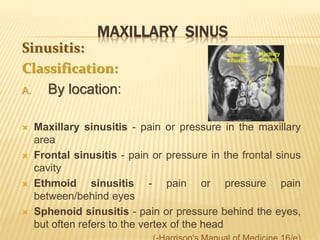
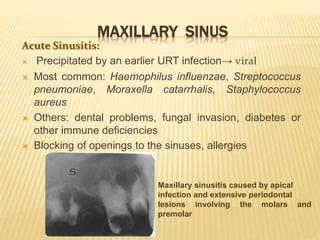
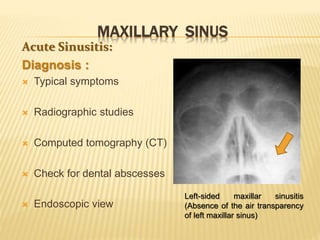
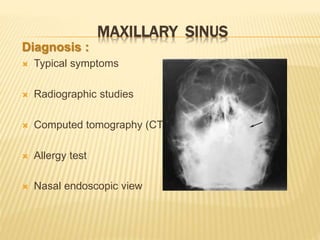
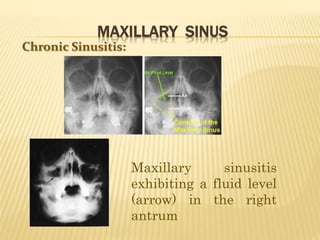
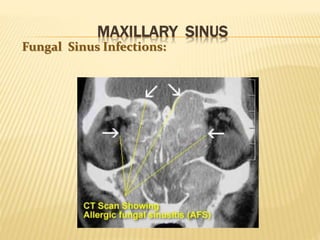
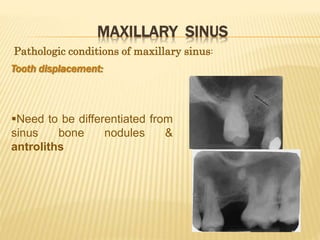
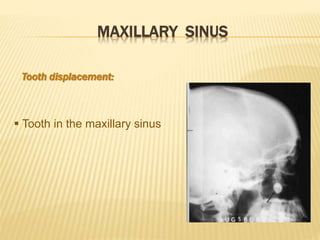
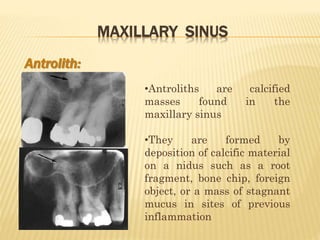
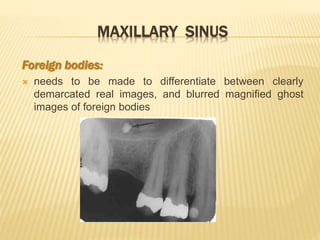
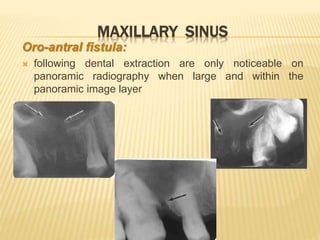
The maxillary sinus is one of the paranasal sinuses located within the body of the maxilla bone. It develops during embryological development and enlarges throughout life through resorption of surrounding bone. The maxillary sinus is lined with ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium and can be affected by developmental anomalies, infections like acute or chronic sinusitis, and fungal infections. Maxillary sinusitis presents with pain and tenderness and is diagnosed through symptoms, imaging, and endoscopy.