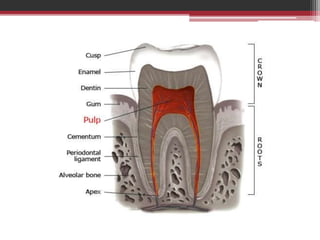
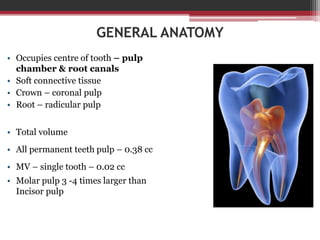
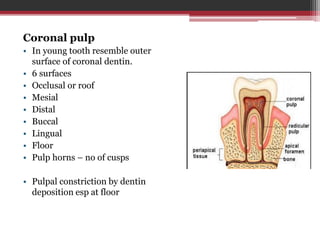
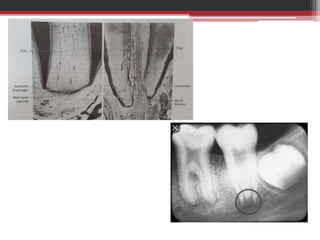
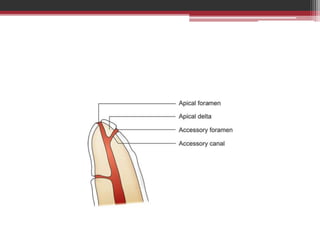
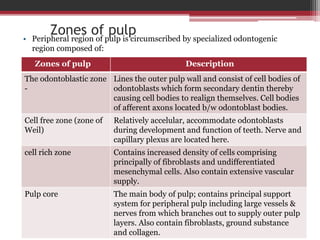
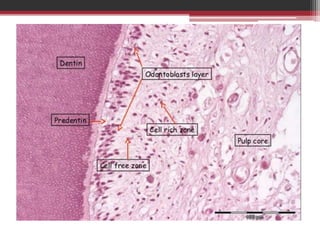
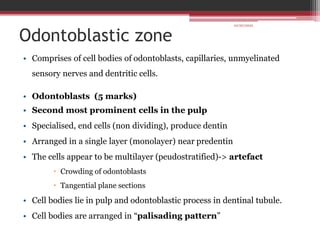
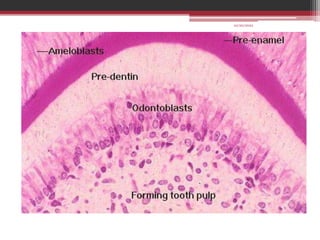
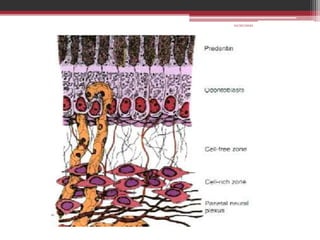
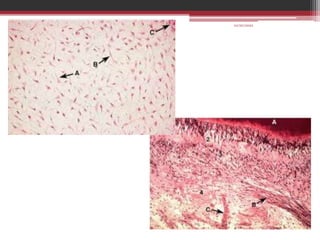
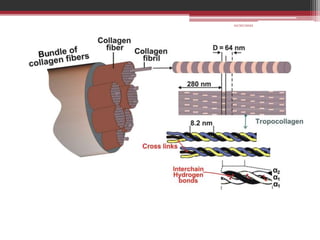
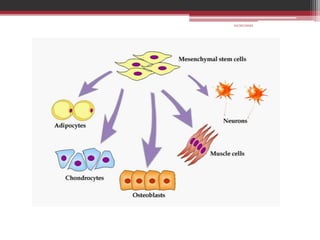
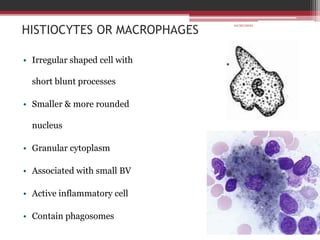
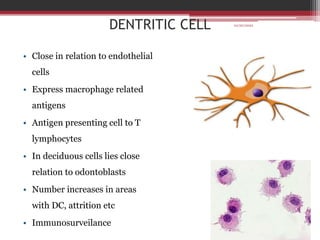
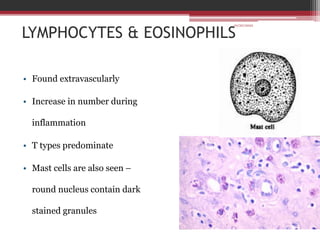
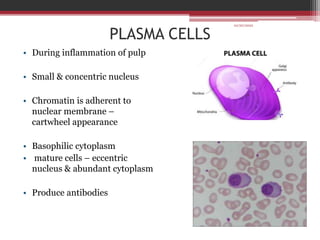
The document provides information on the structure and functions of the dental pulp. It begins with definitions and general anatomy, describing the pulp as a soft connective tissue enclosed within dentin. It then discusses the zones and structural features of the pulp in more detail. This includes the odontoblastic zone containing odontoblasts and nerve endings, the cell-free zone with capillaries and nerves, and the cell-rich zone with fibroblasts and blood vessels. Key cell types like odontoblasts, fibroblasts, and immune cells are also described. The functions of the pulp in dentin formation, nutrition, and defense are highlighted.