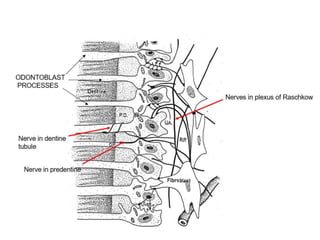
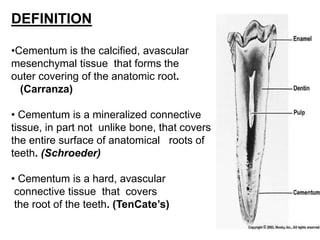
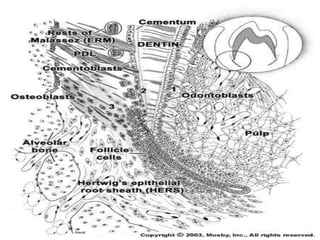
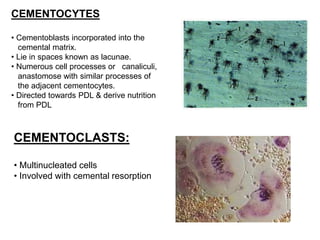
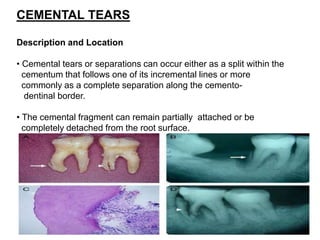
The dental pulp is the soft connective tissue contained within the tooth. It originates from neural crest cells that migrate and condense around ectomesenchymal cells to form the dental papilla during development. The pulp contains odontoblasts, fibroblasts, undifferentiated cells and defense cells. It has a histological structure with outer odontoblastic, cell-free and inner cell-rich zones. The pulp functions to provide nutrition, sensation, defense and formation/protection of dentin. In aging teeth, the pulp undergoes changes like fewer cells, fibrosis, vascular changes and calcifications that decrease its functions over time.