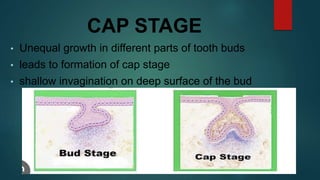
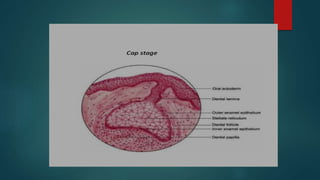
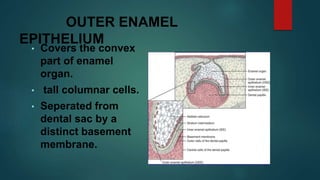
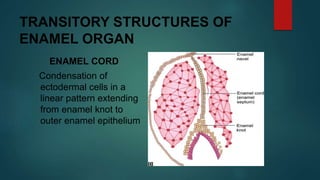
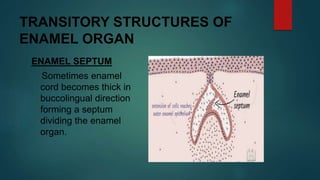
The document discusses the stages of tooth development. It focuses on the cap stage, where unequal growth of tooth buds leads to the formation of a shallow invagination. The enamel organ is composed of three cell types - inner enamel epithelium, outer enamel epithelium, and stellate reticulum. The stellate reticulum cells change shape from polygonal to star-shaped due to glycosaminoglycans pulling water into the enamel organ. There are also several transitory enamel organ structures discussed, including the enamel knot, cord, septum, navel, and niche.