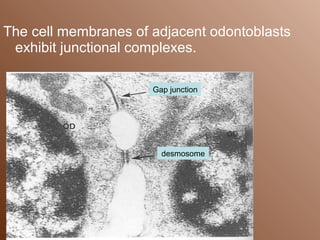
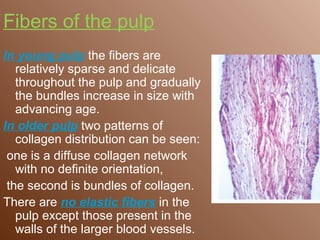
The dental pulp is loose connective tissue located within the tooth. It can be divided into the coronal pulp within the crown and radicular pulp within the root. The pulp contains cellular elements like odontoblasts, fibroblasts, and defensive cells, as well as neurovascular elements. With age, the size of the pulp decreases as secondary dentin is deposited. The number of cells and vascularity also decrease with age. Accessory canals may form due to developmental processes or resorption of tissue during aging. The pulp provides nutrients and defenses to the tooth.