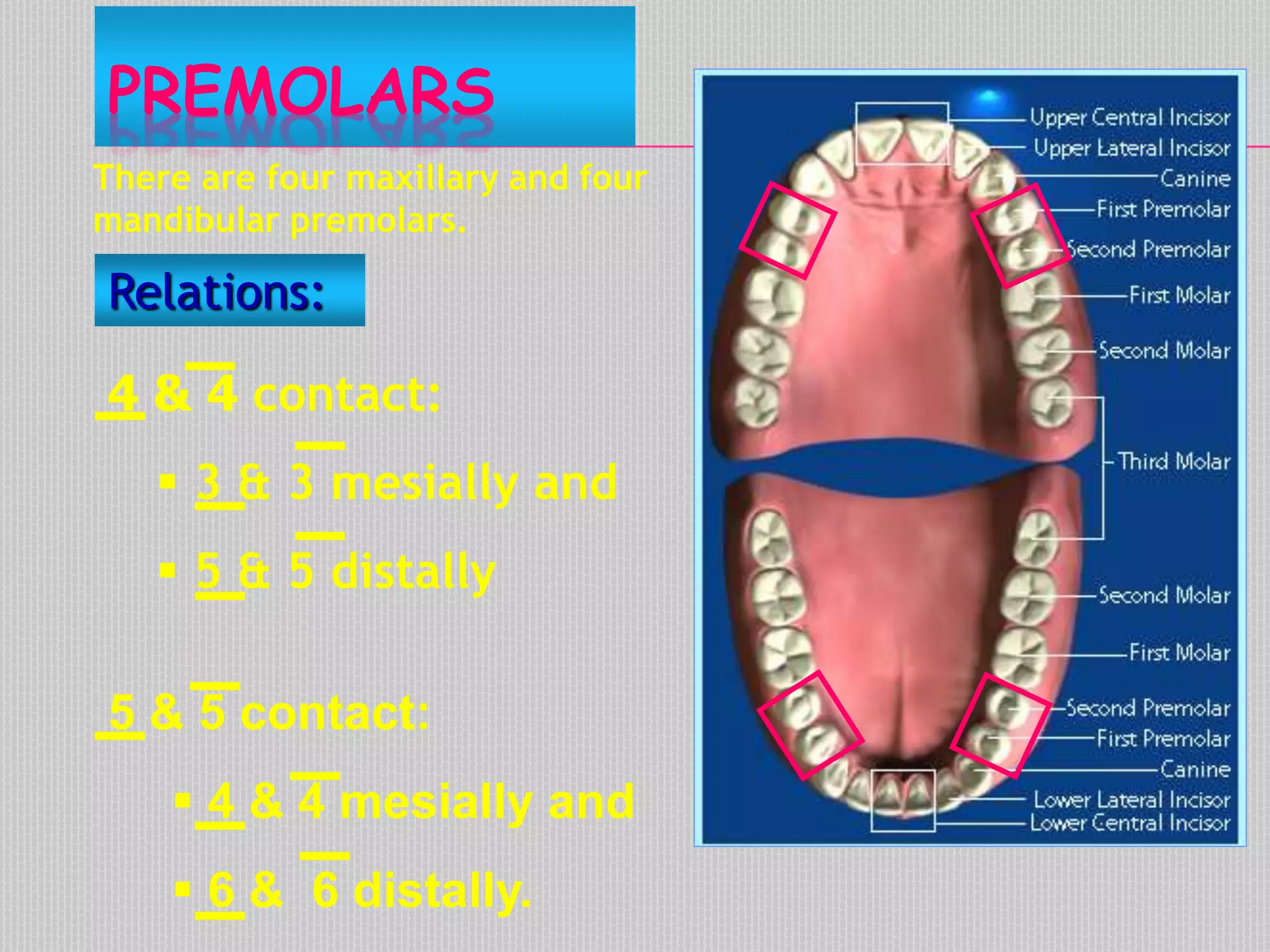
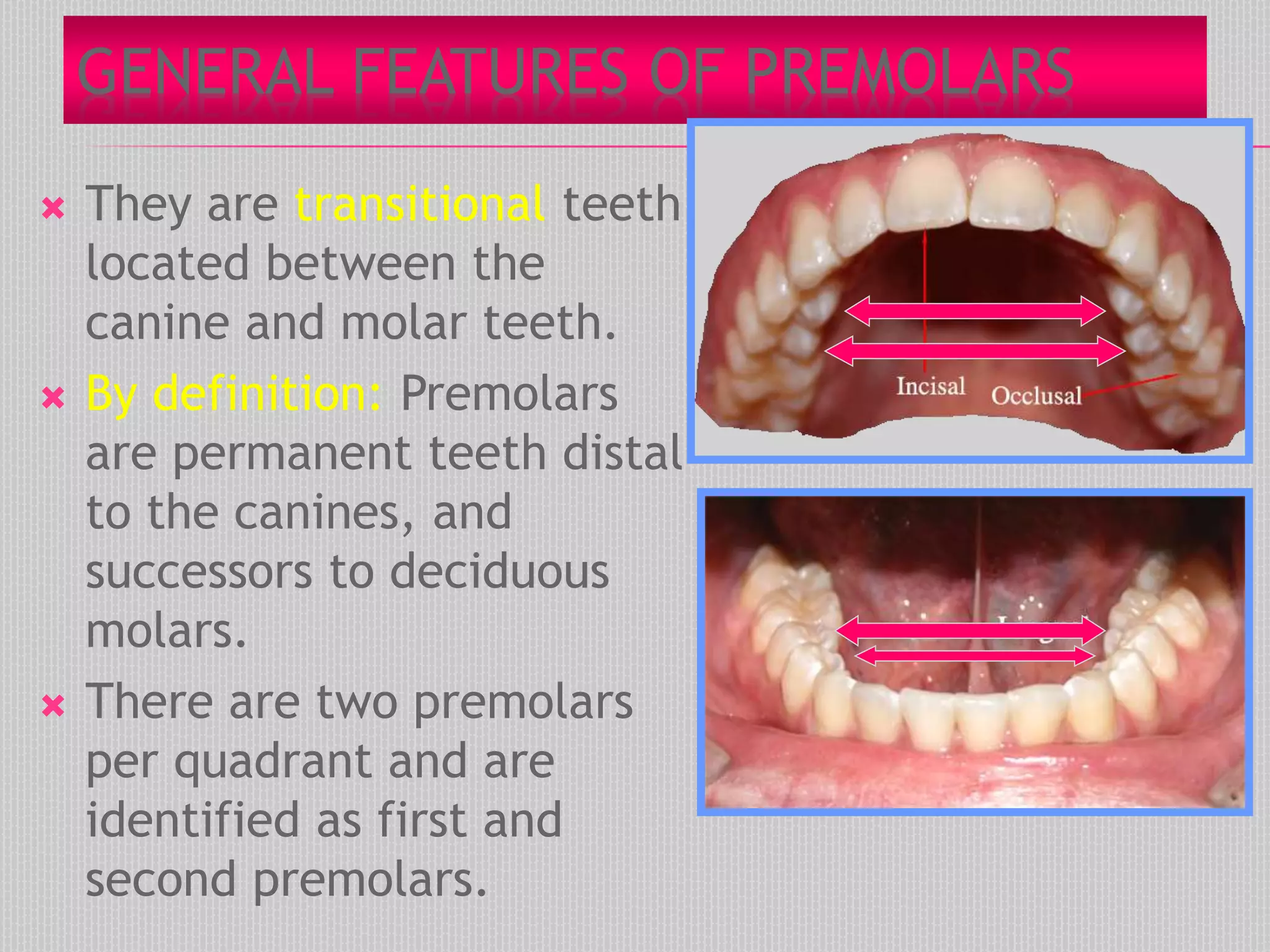
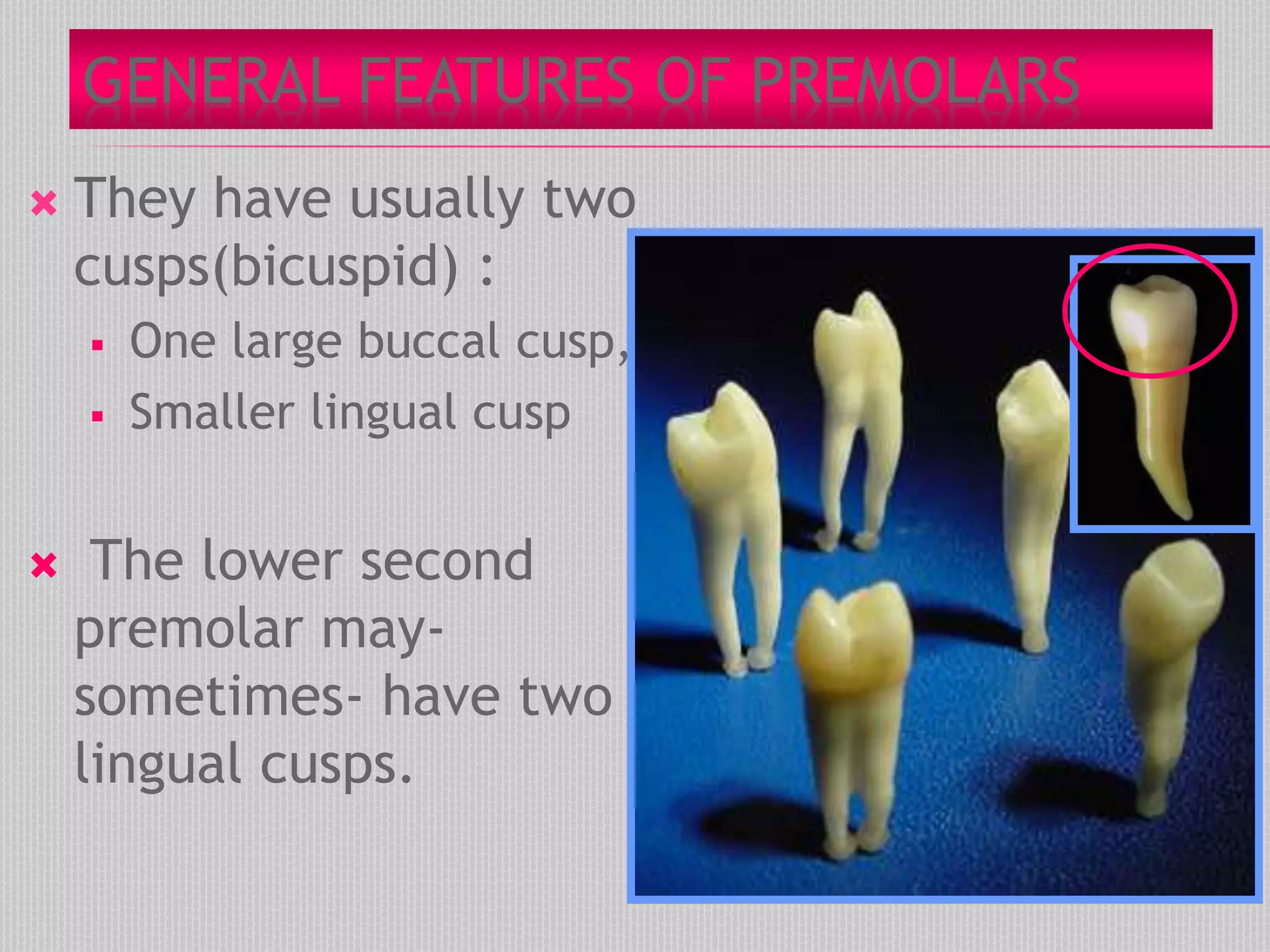
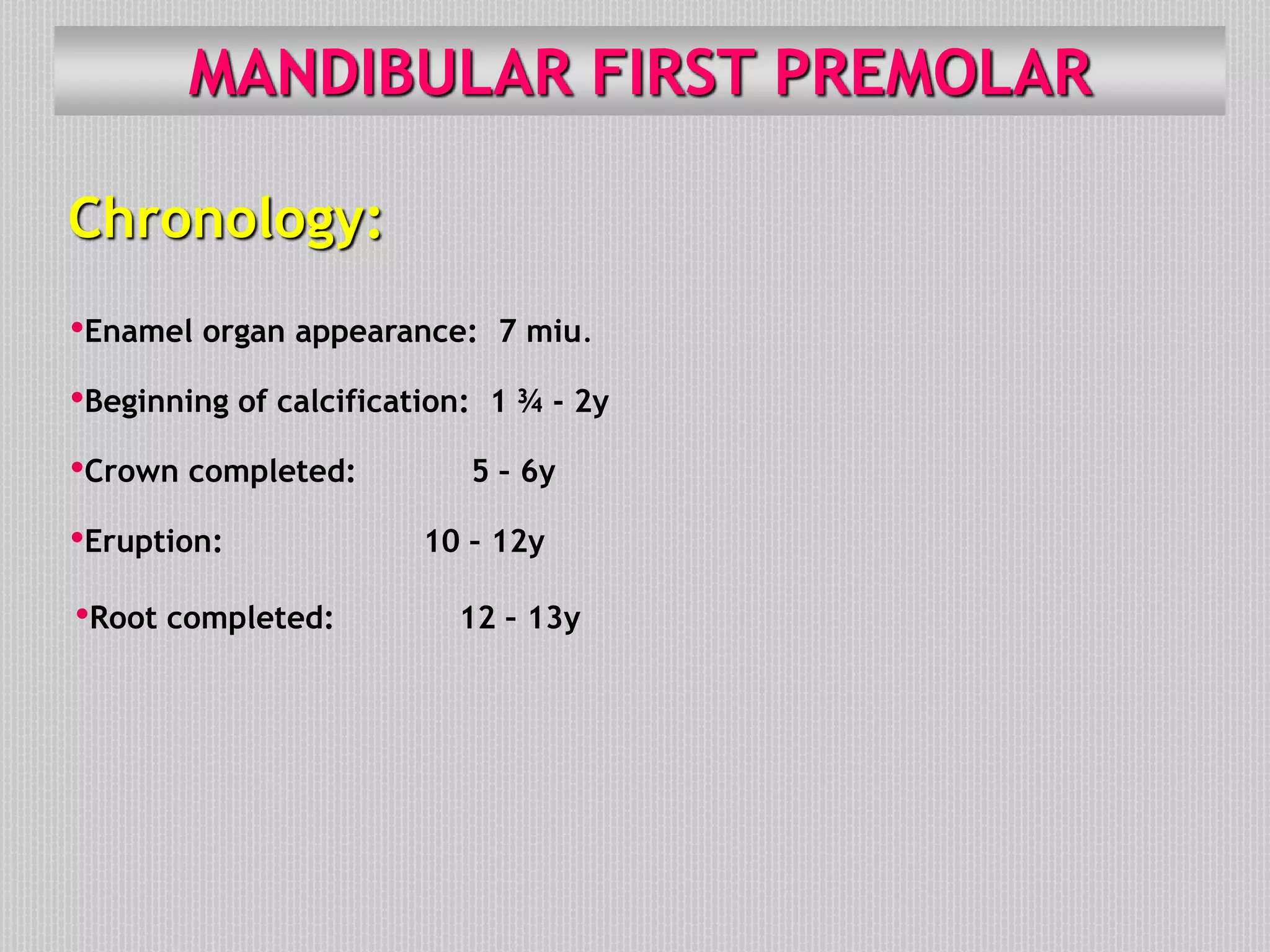
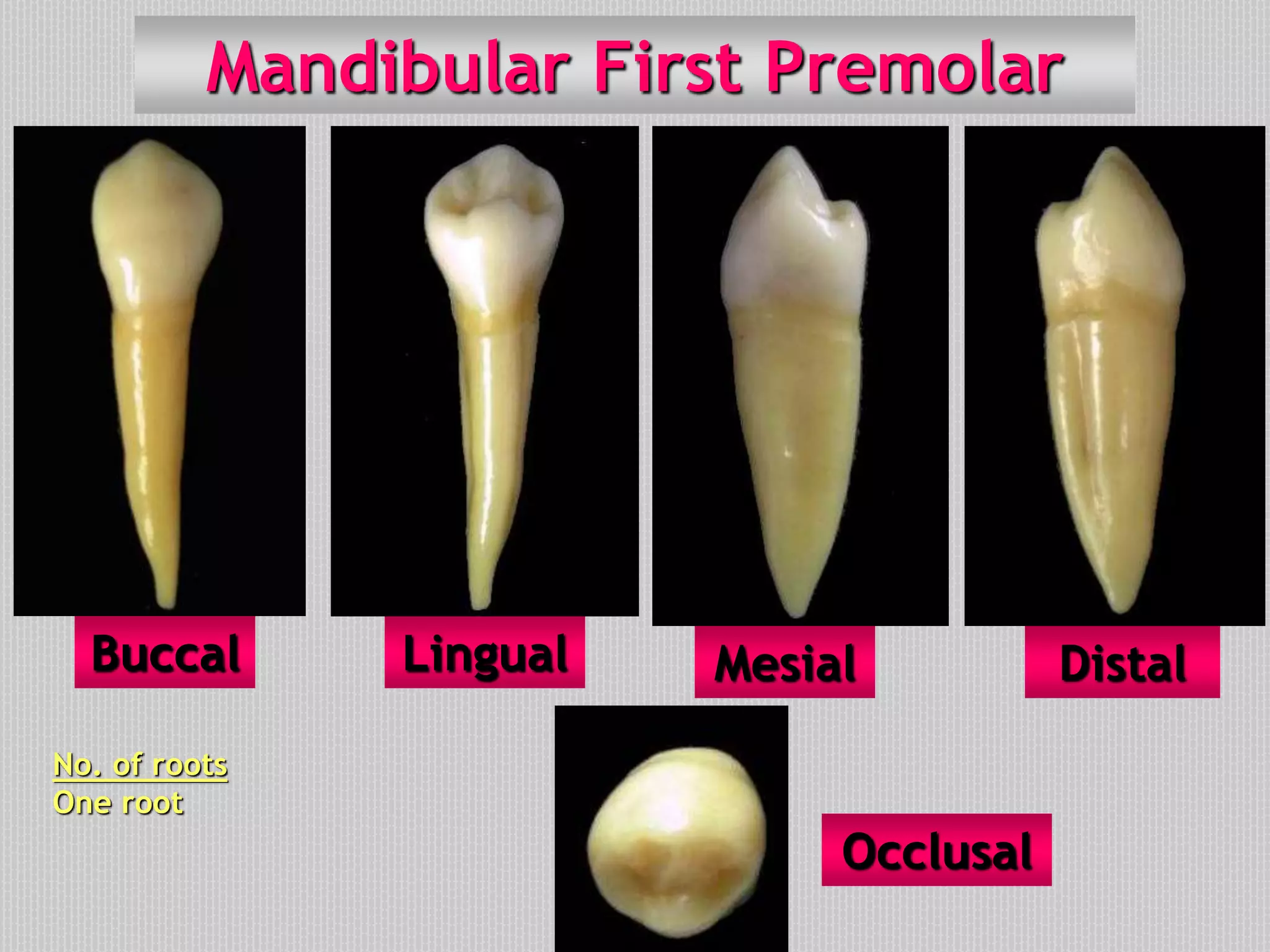
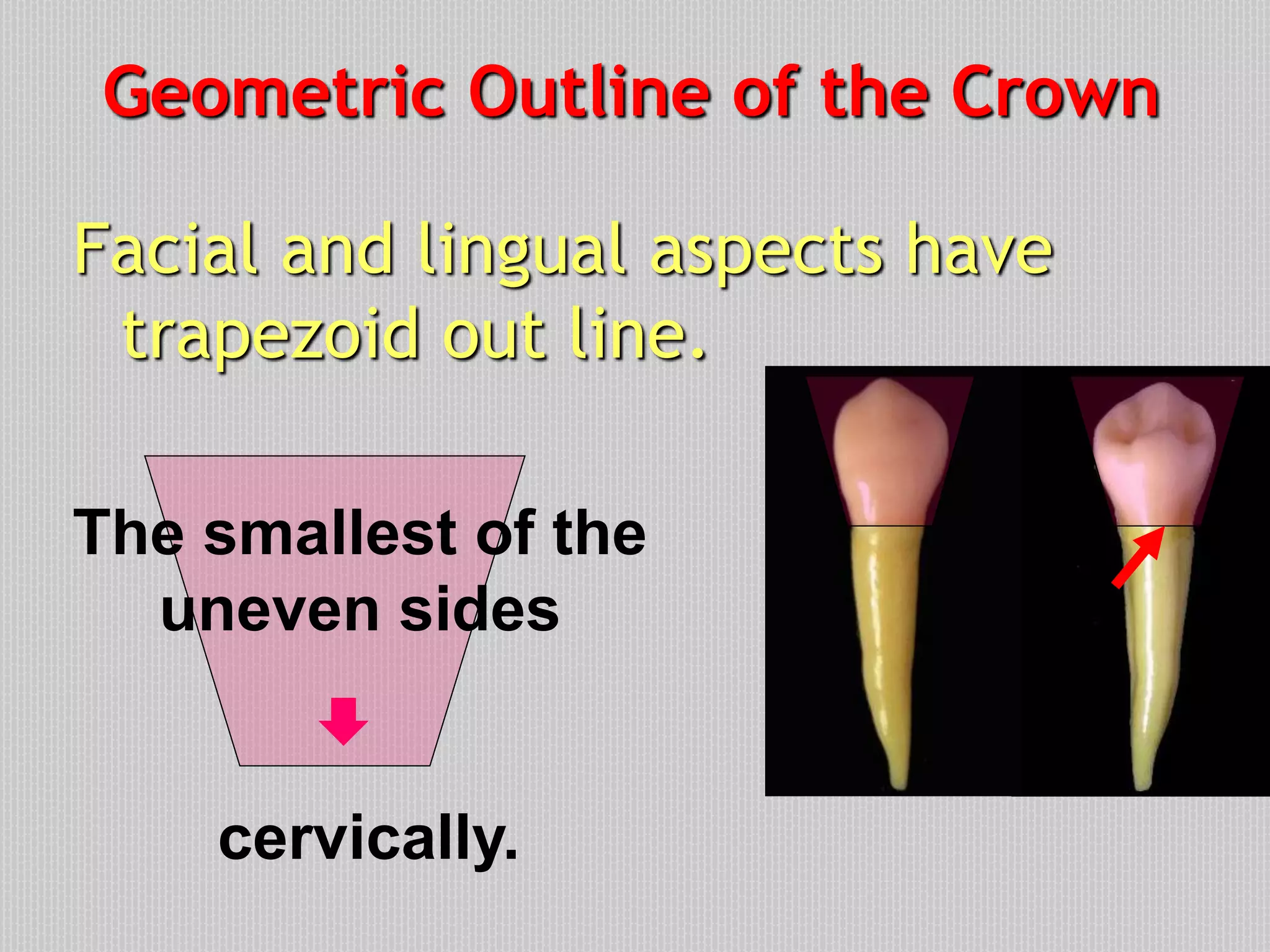
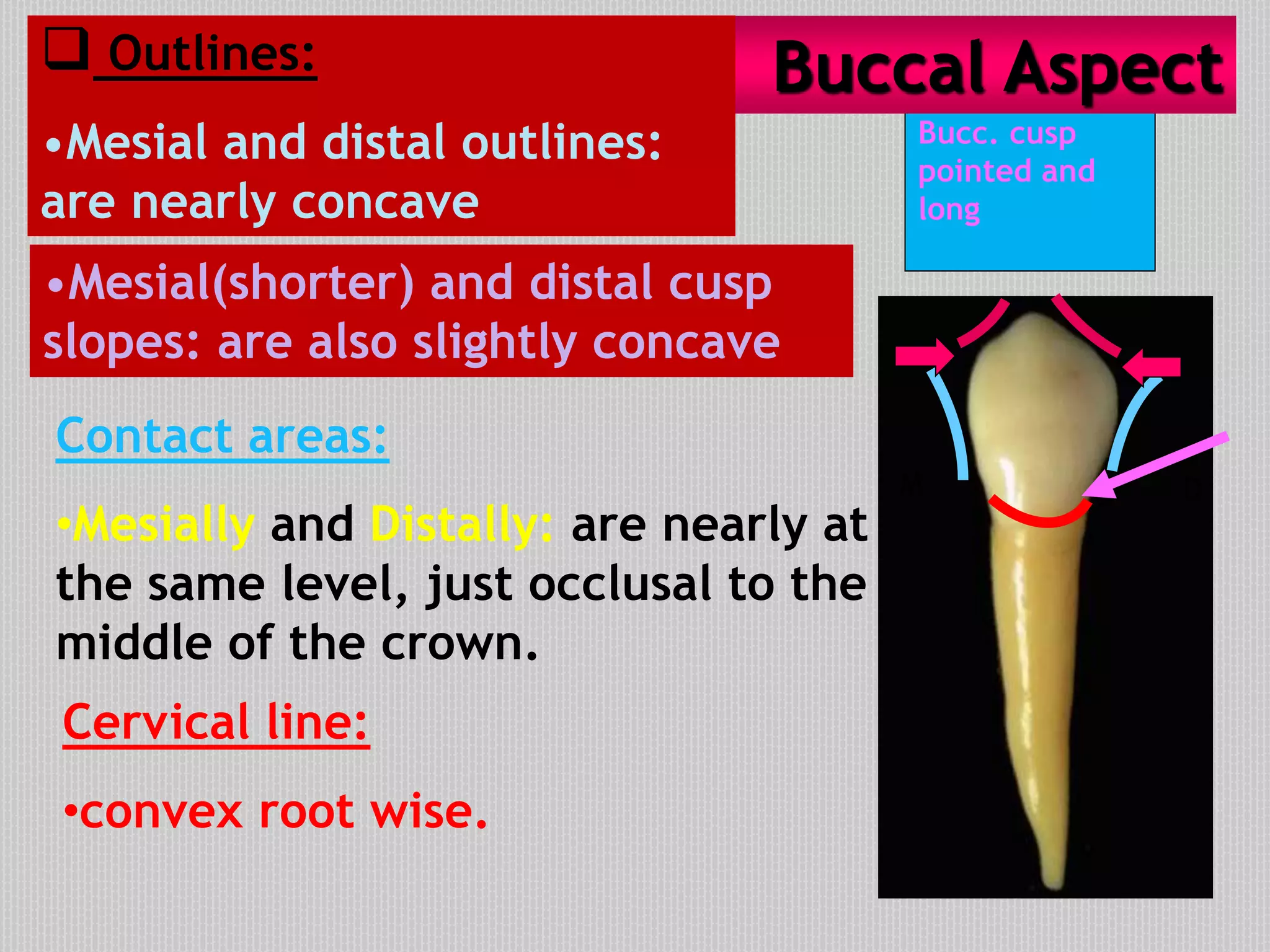
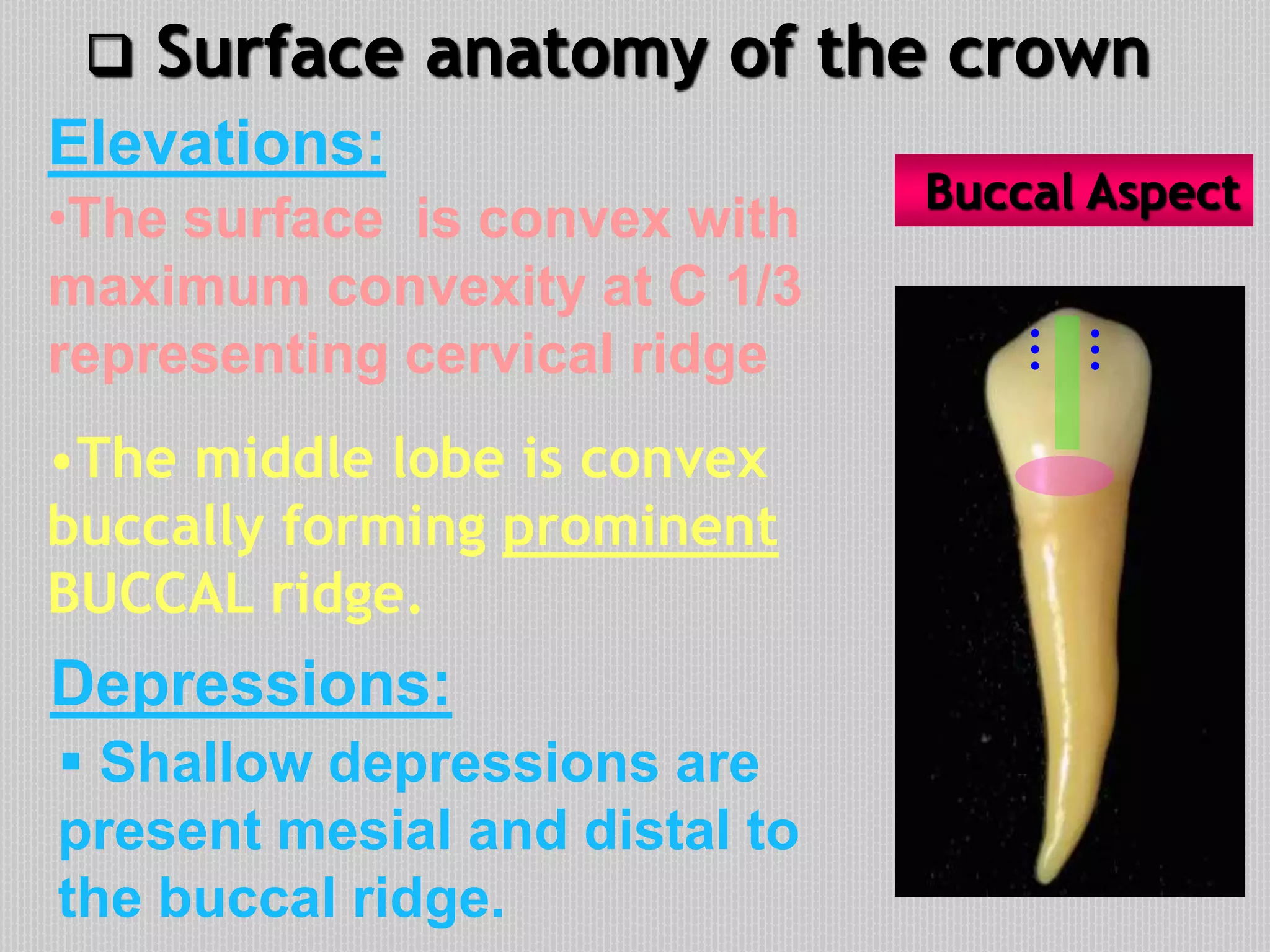
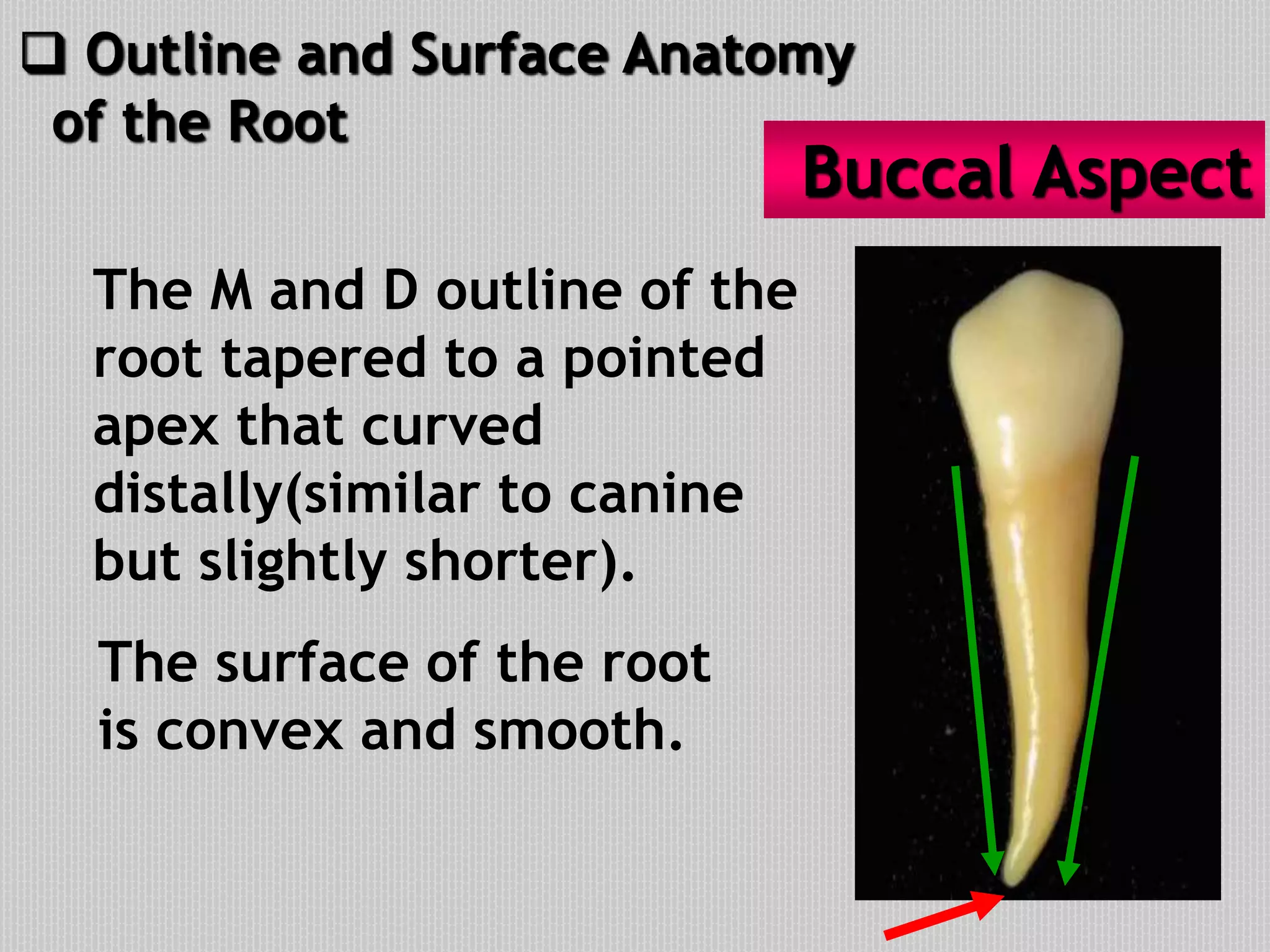
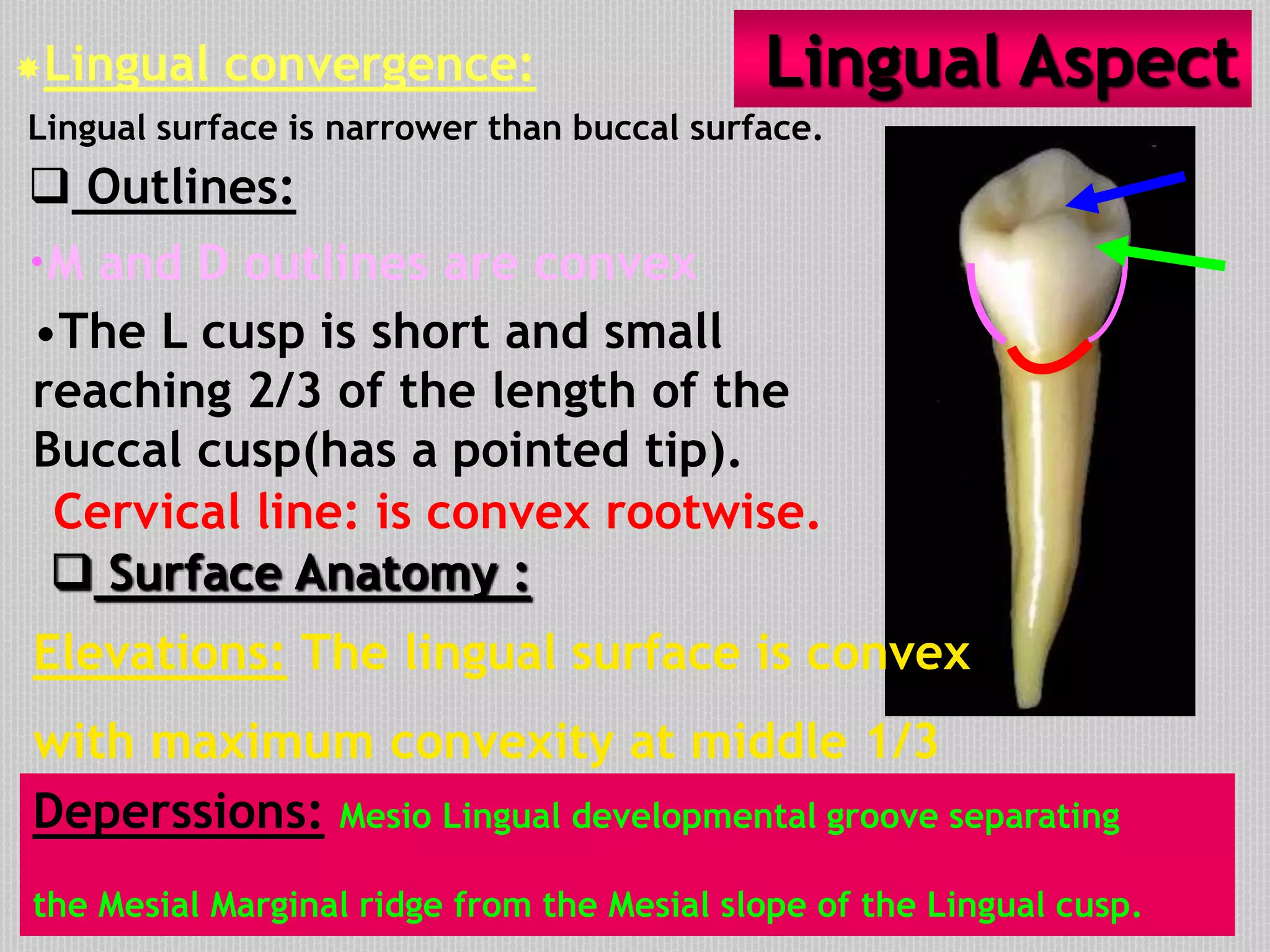
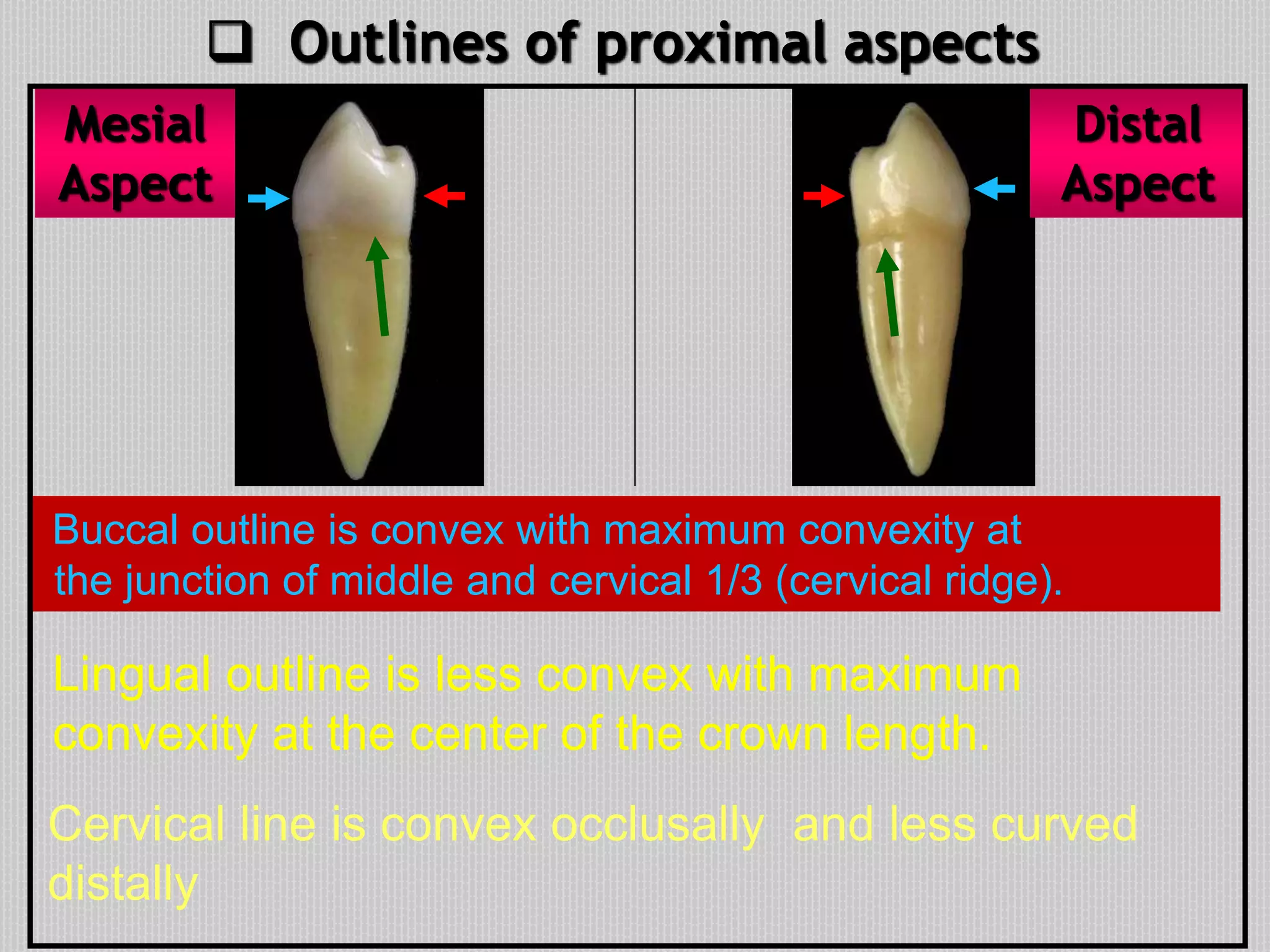
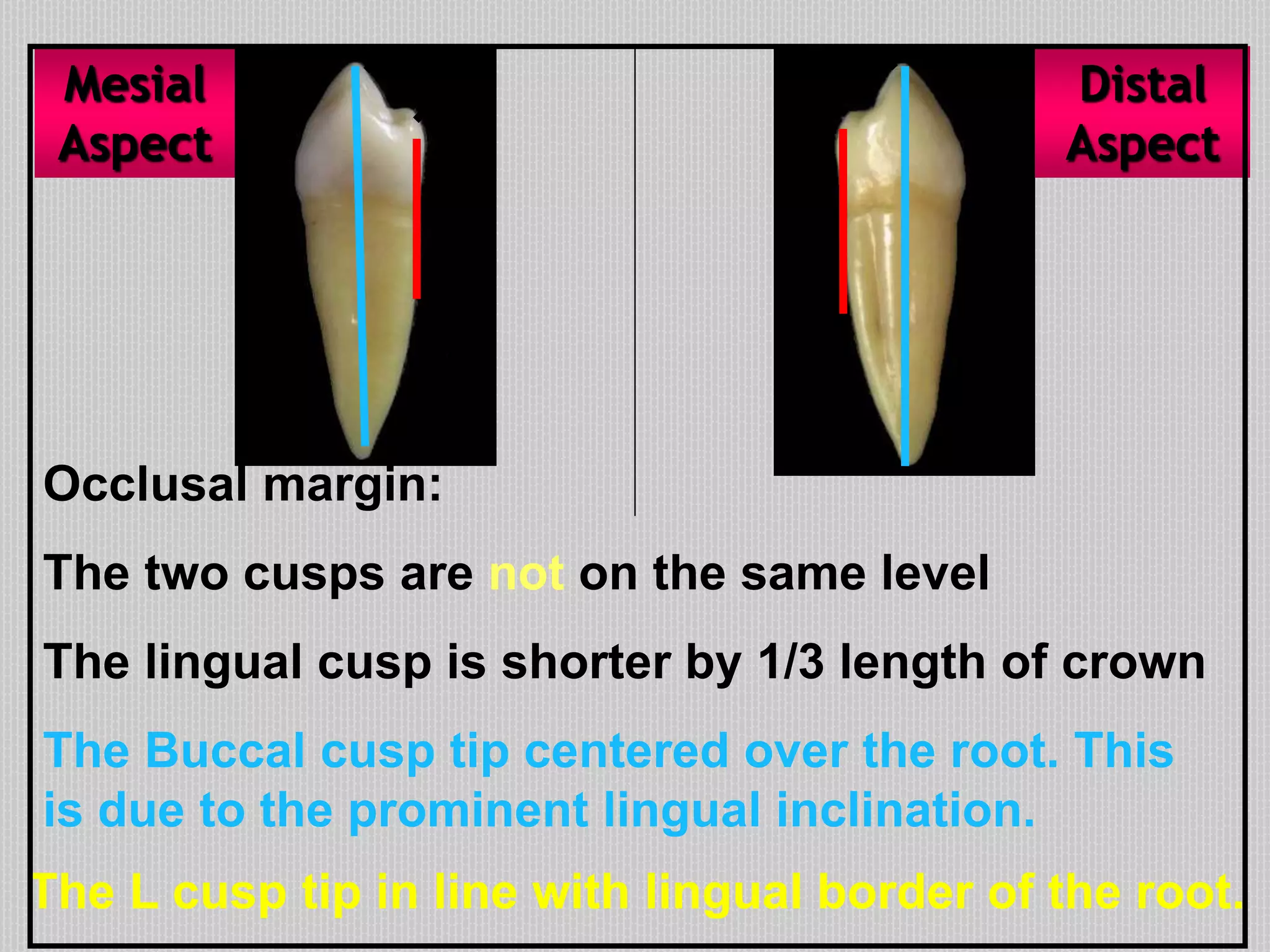
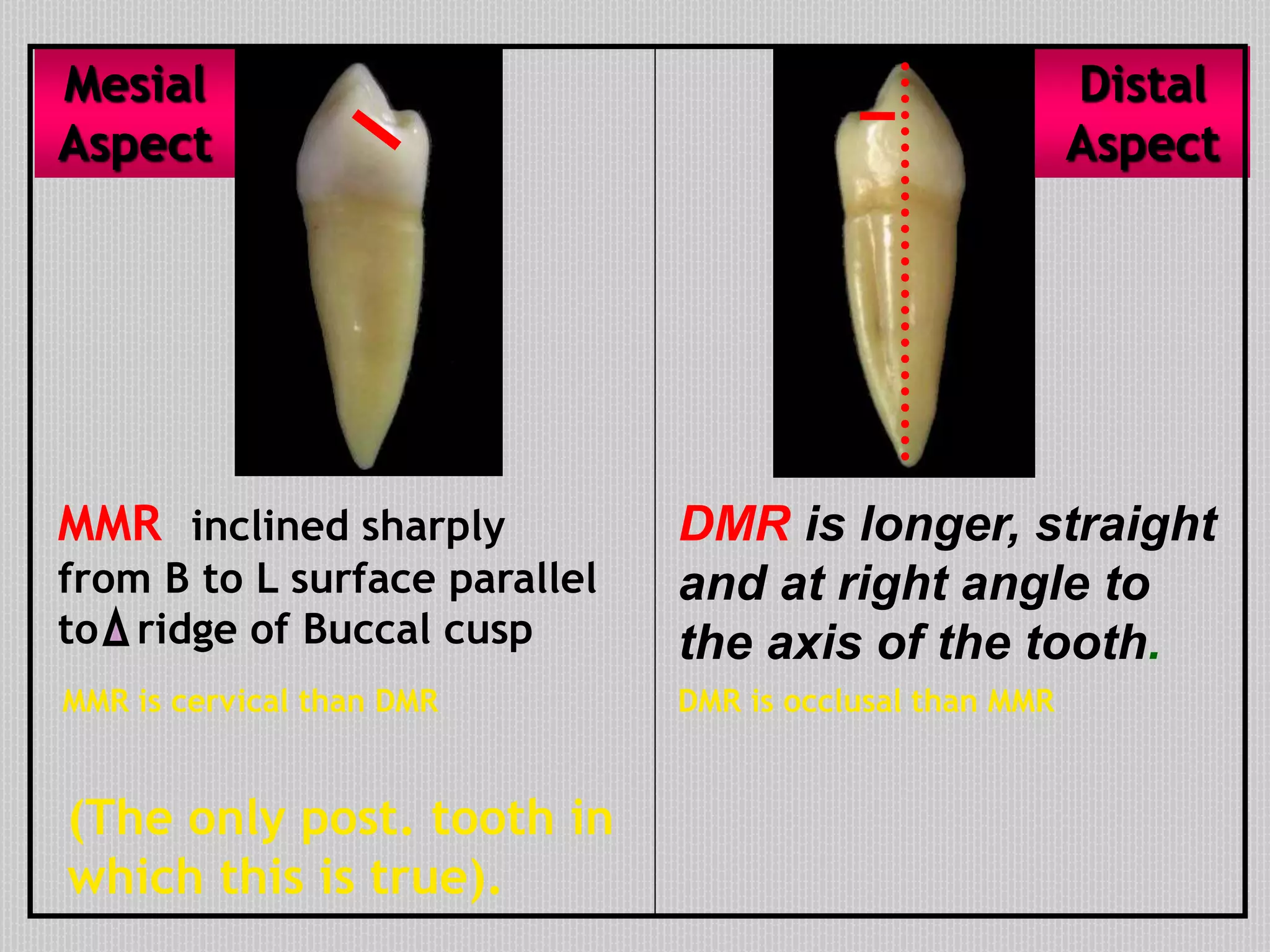
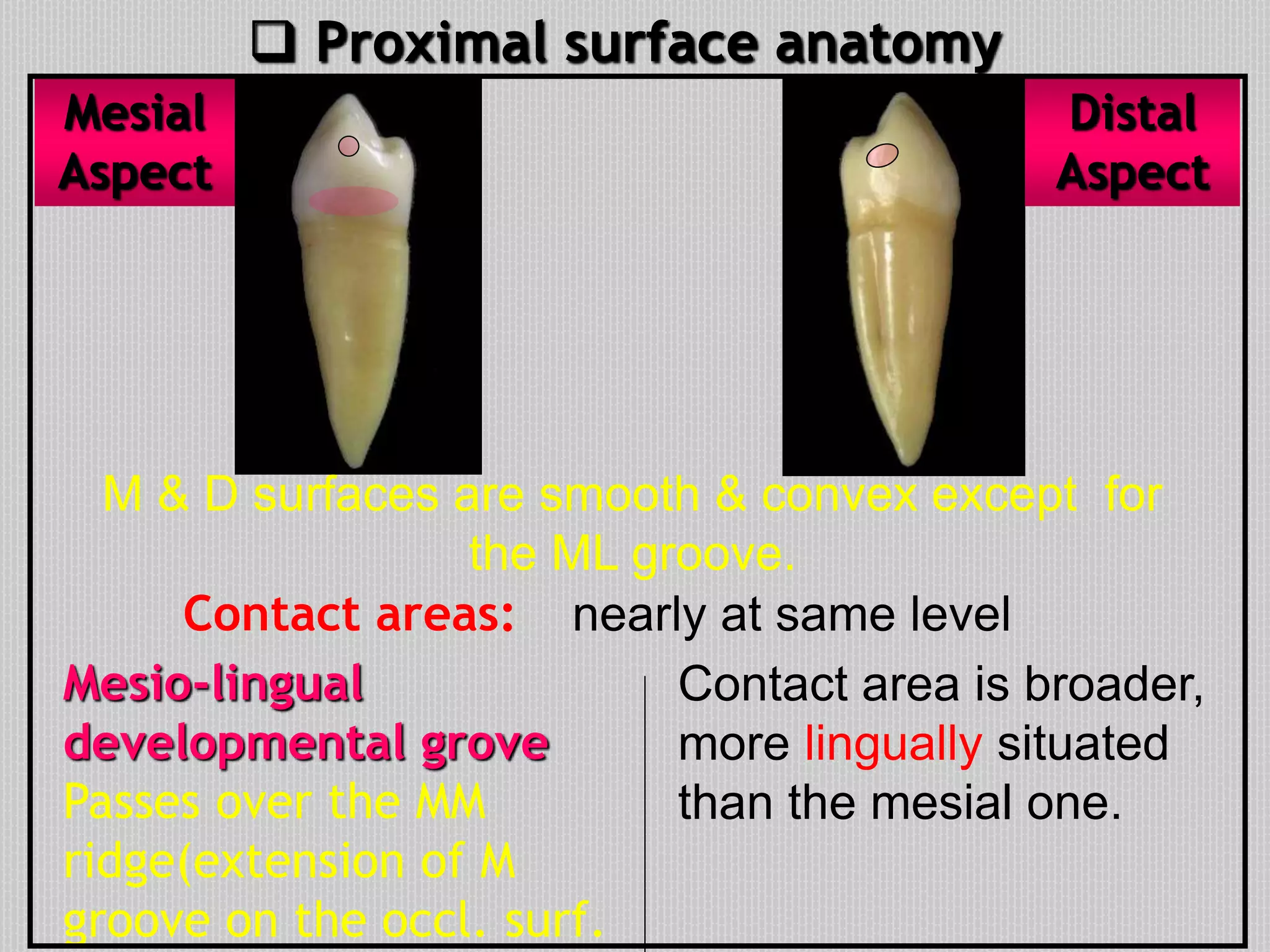
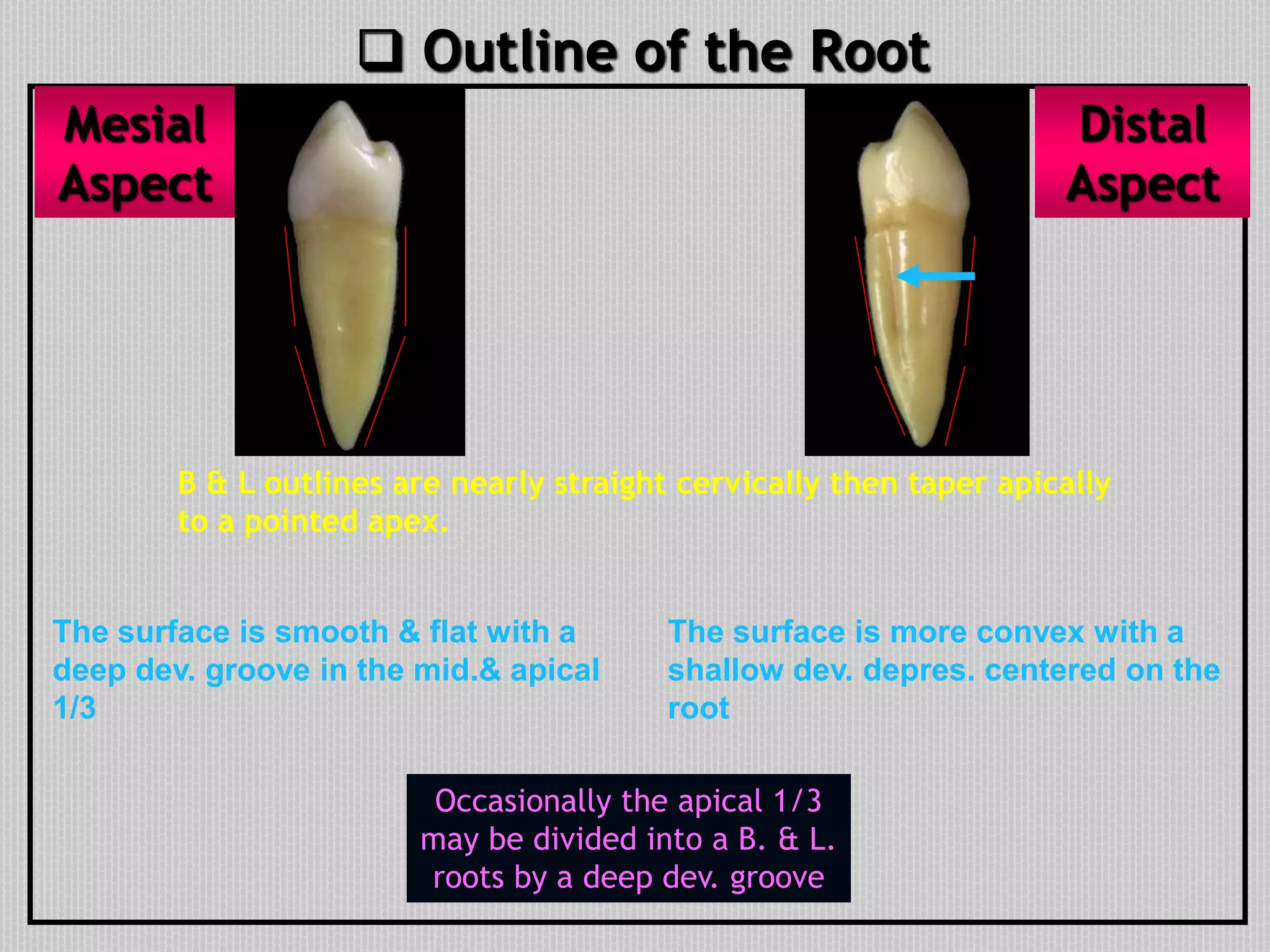
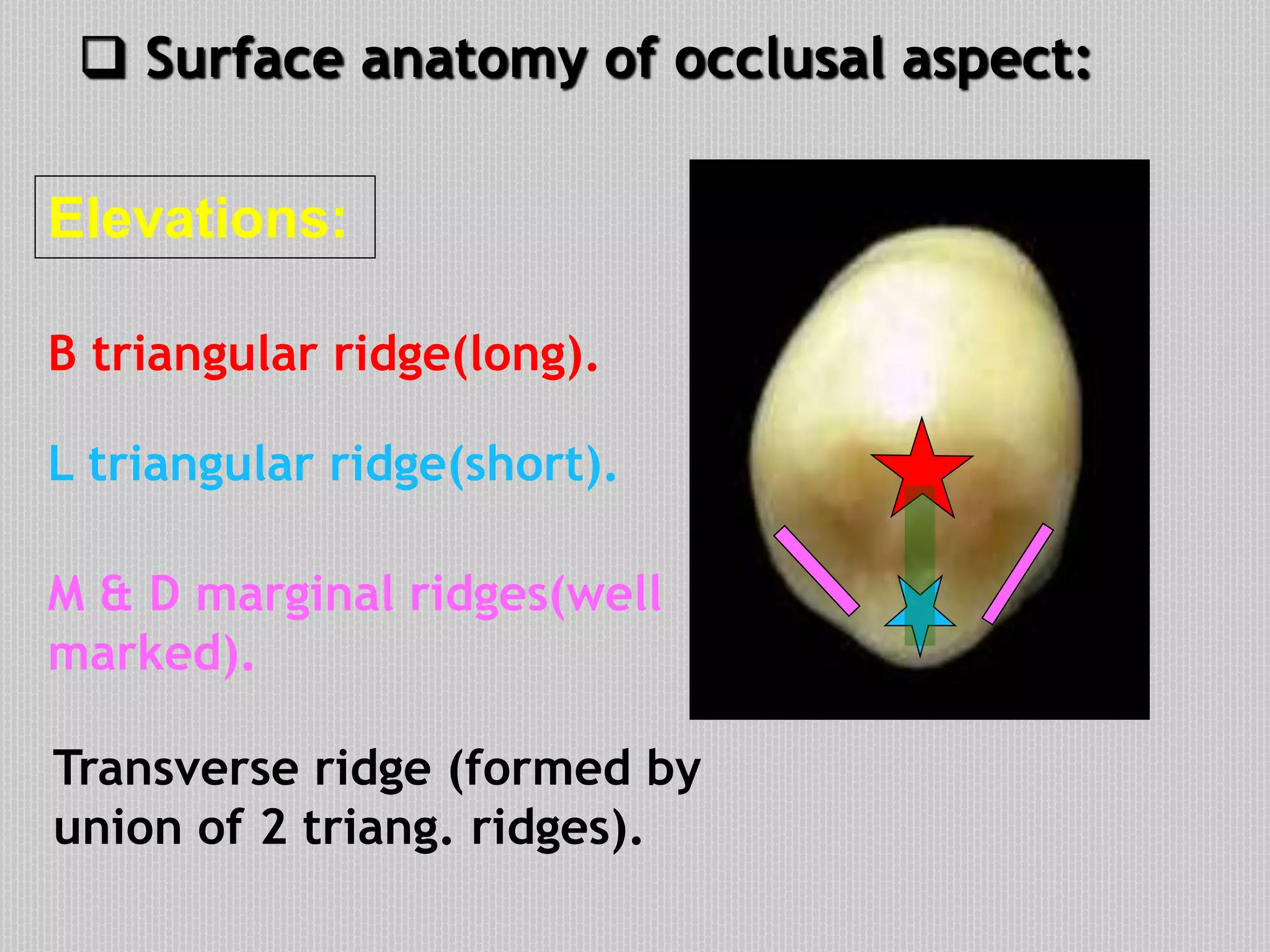
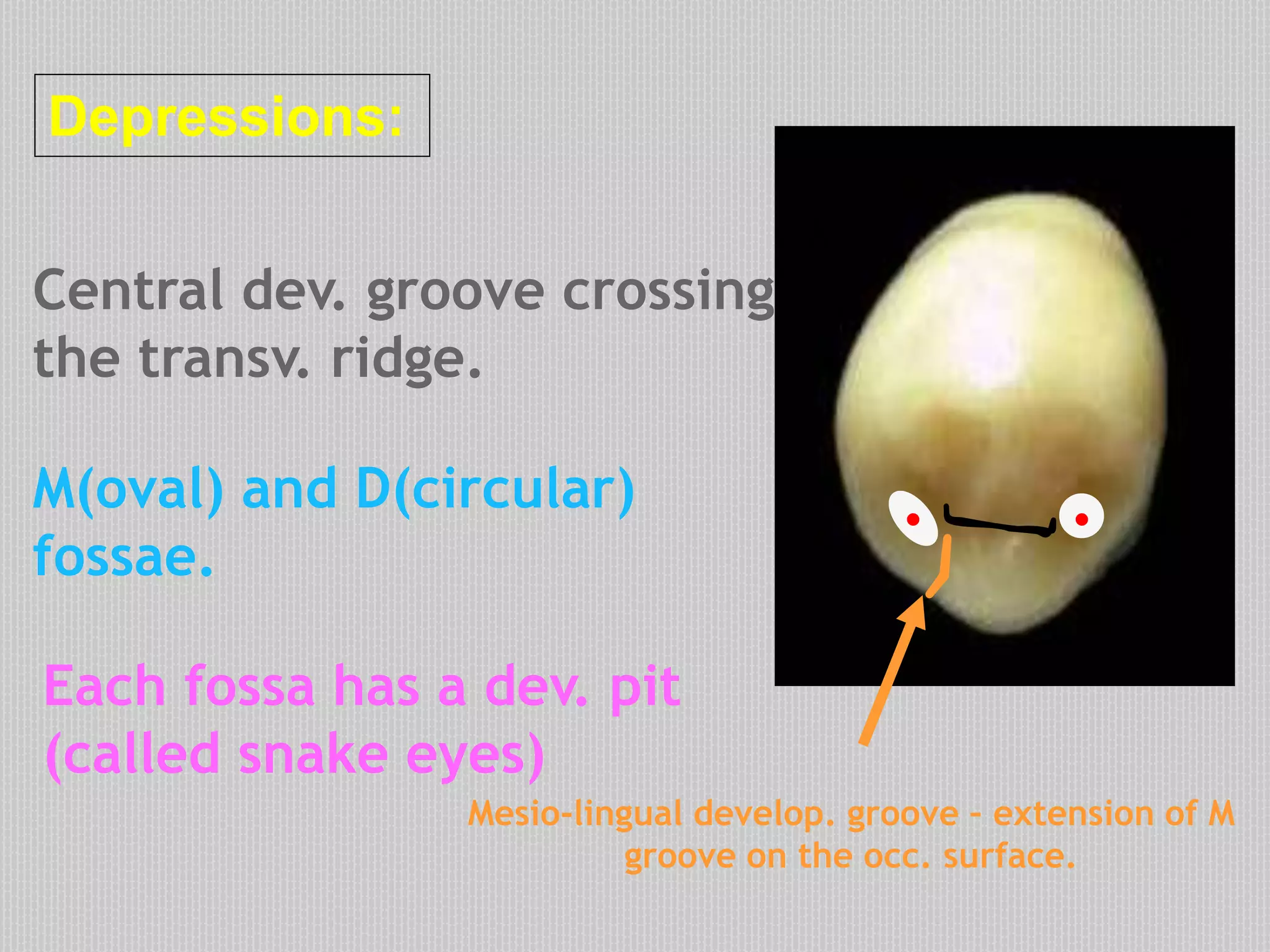
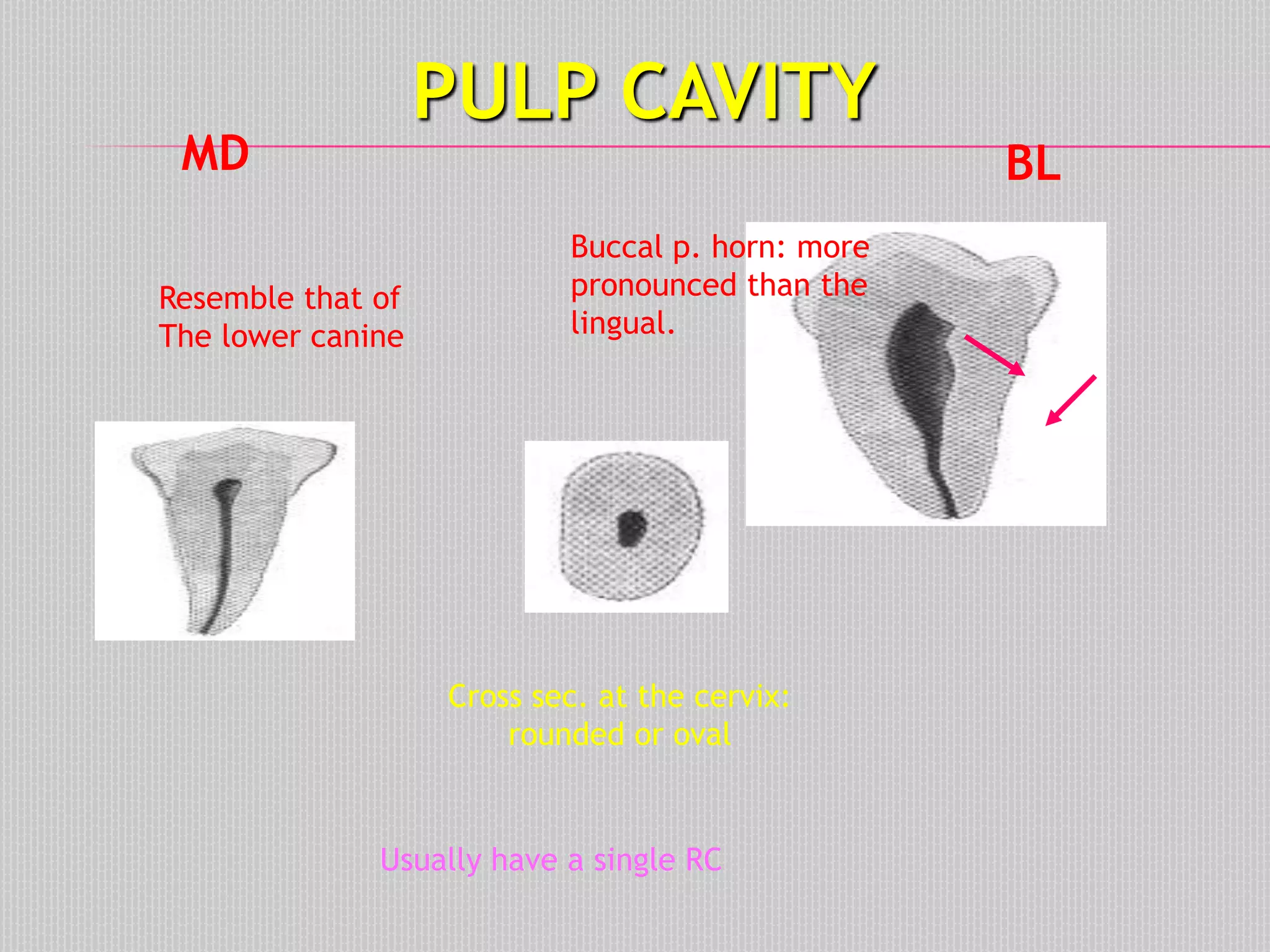
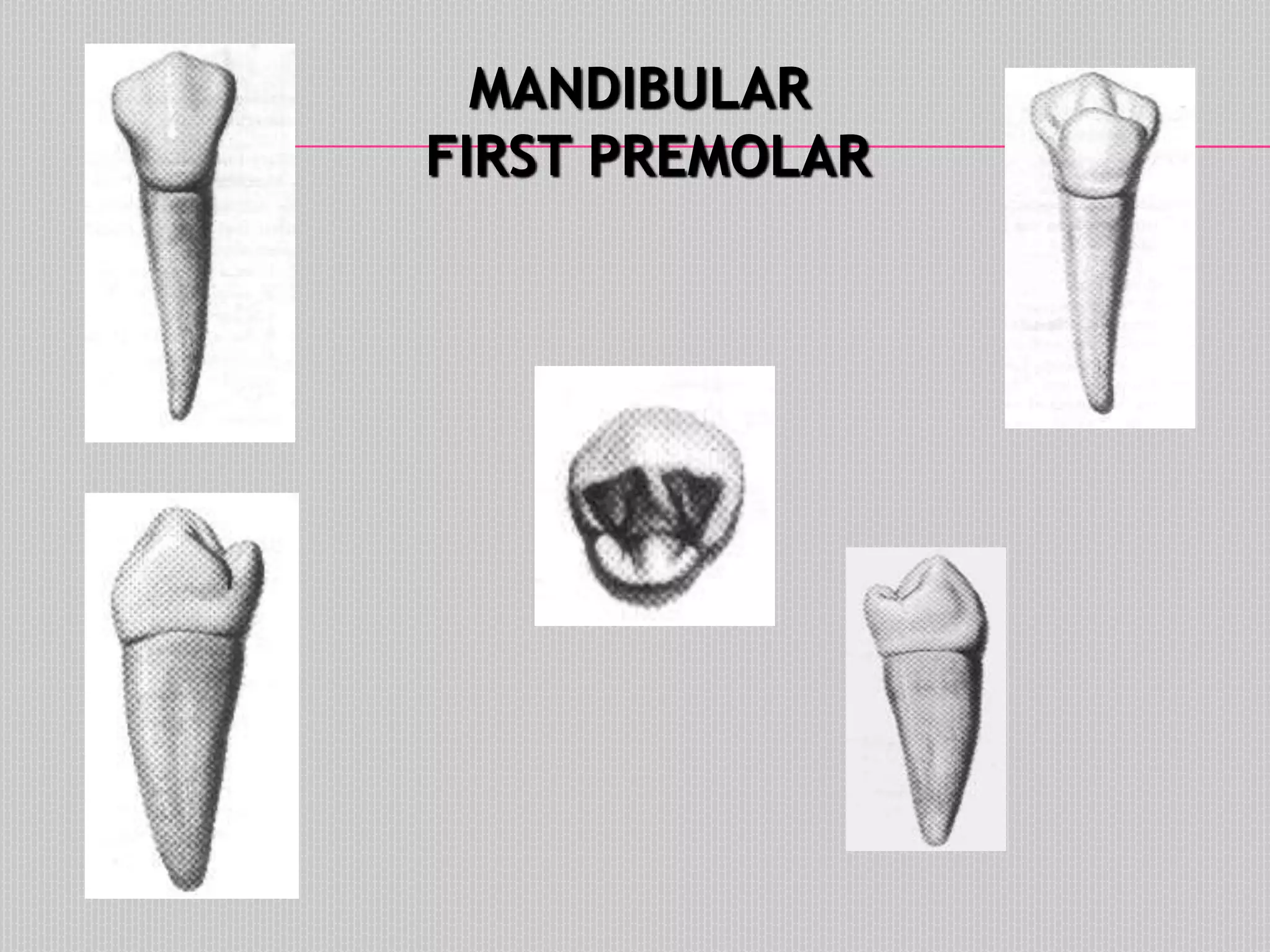
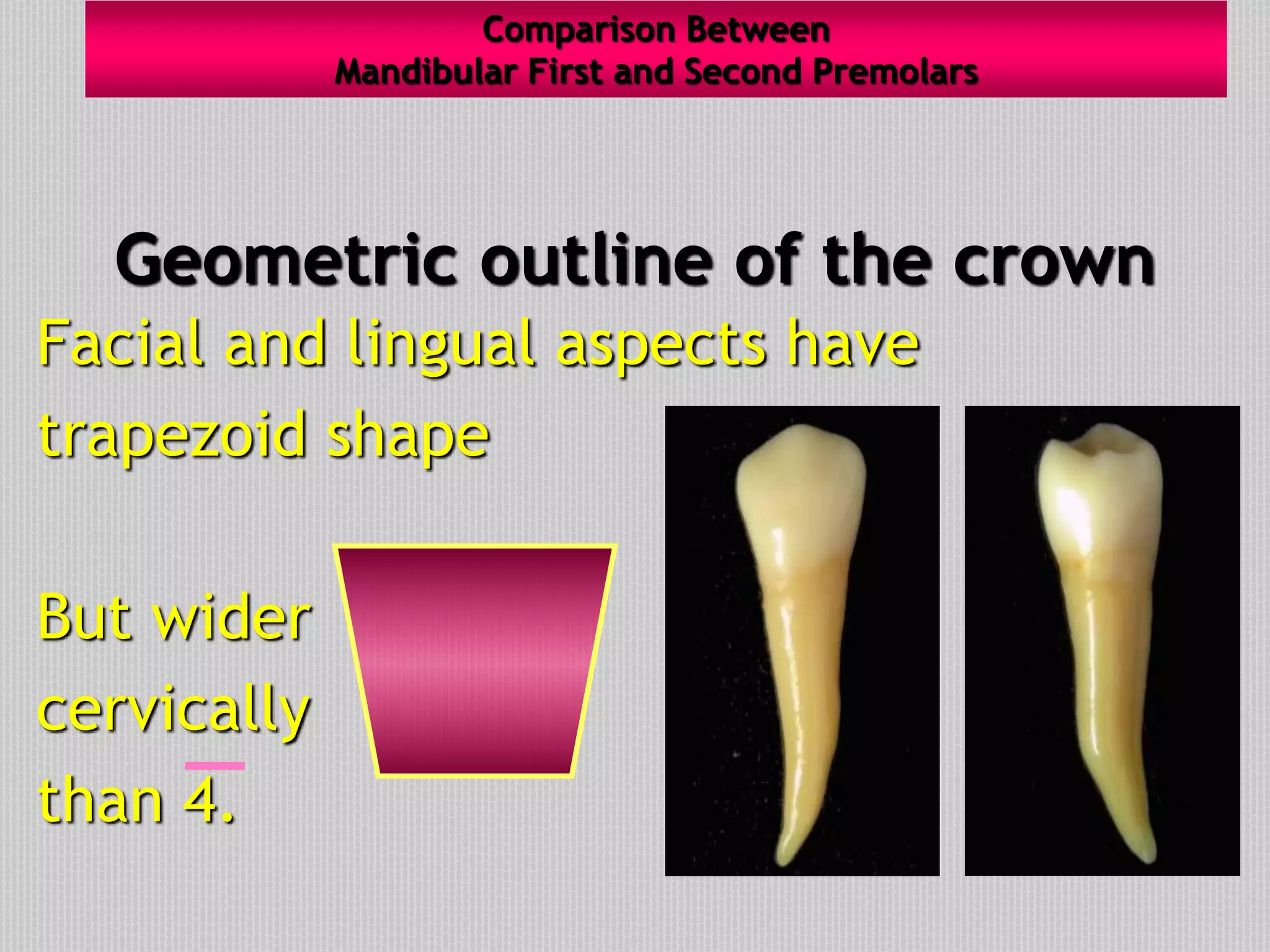
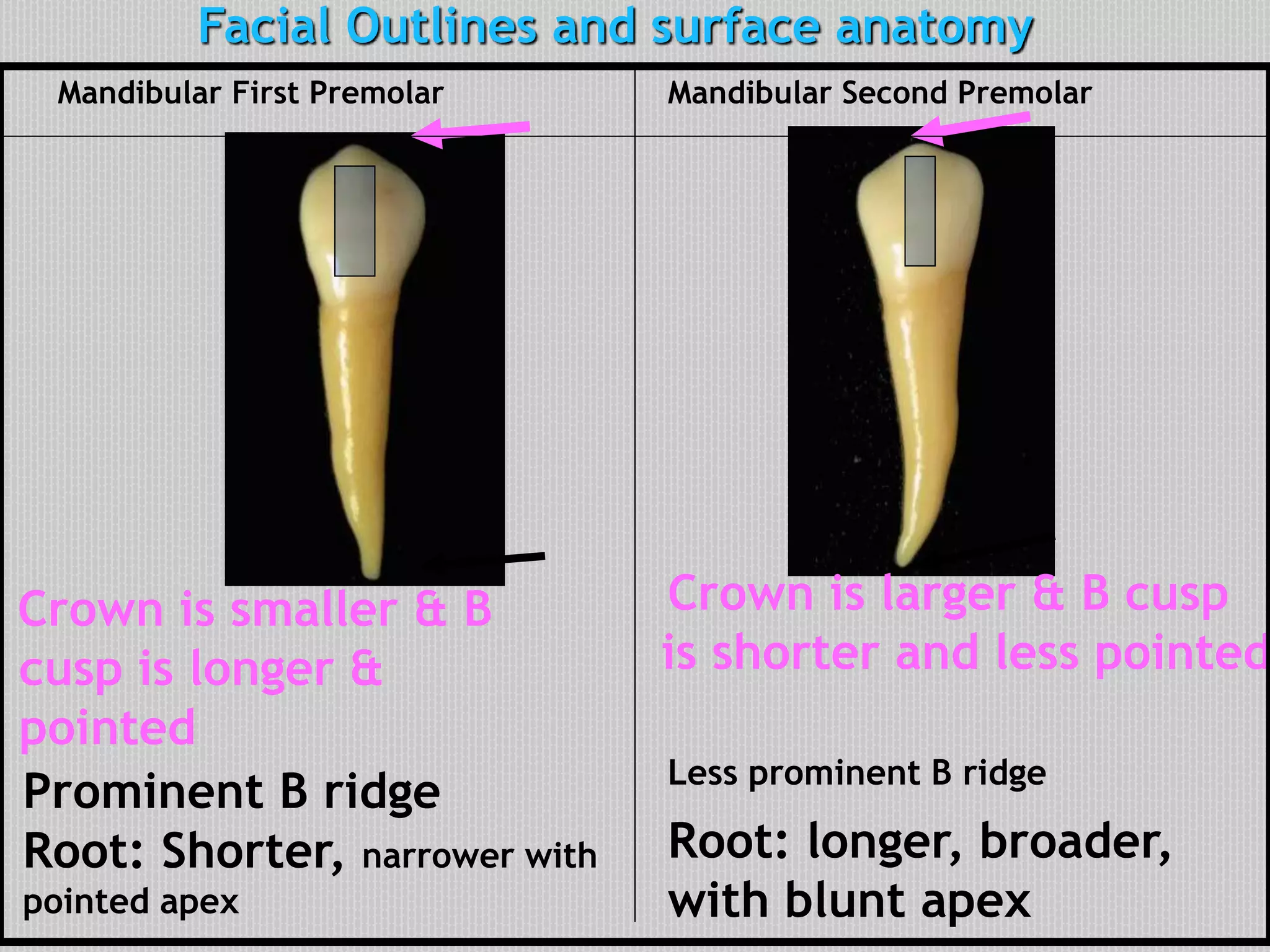
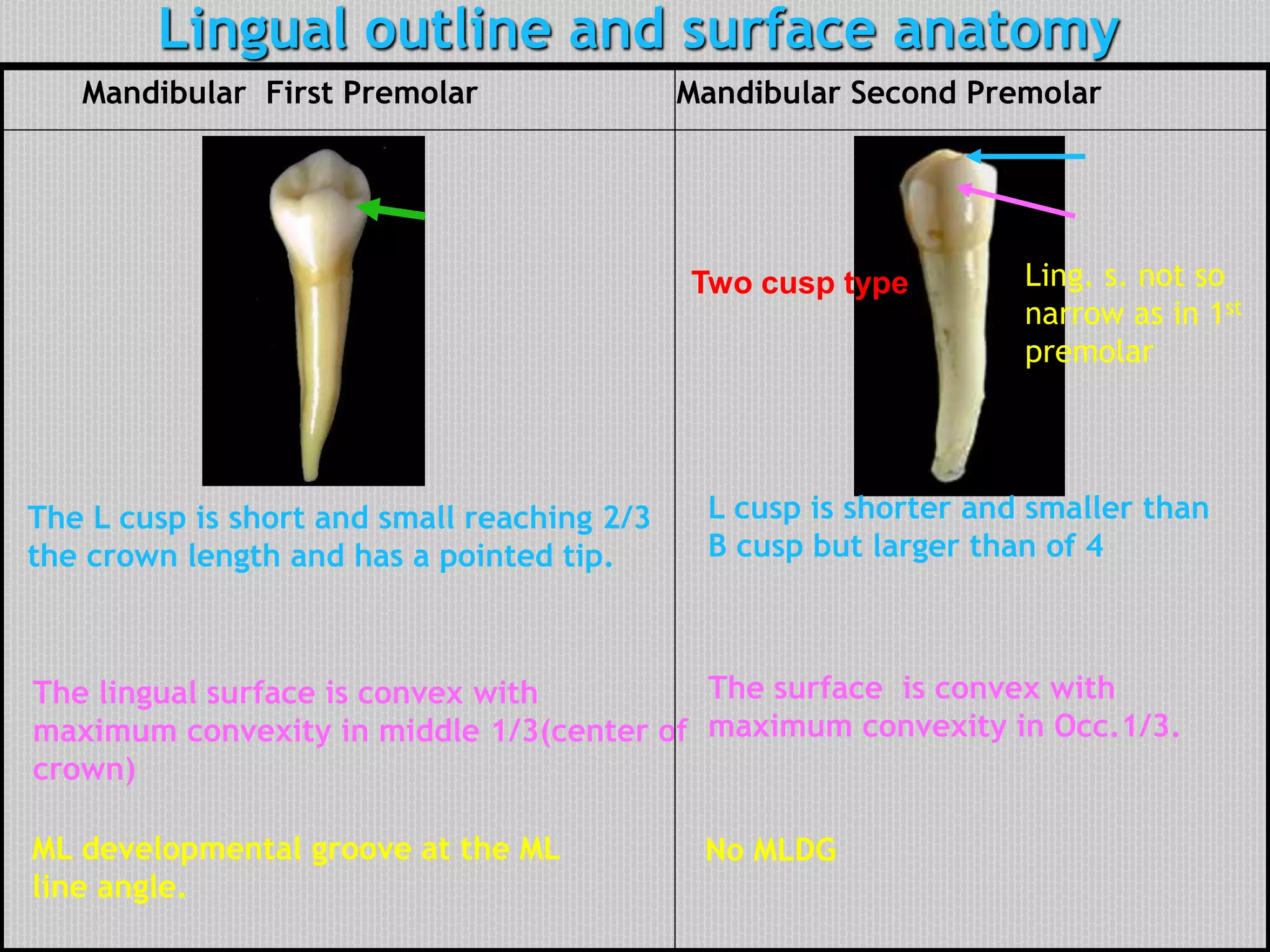
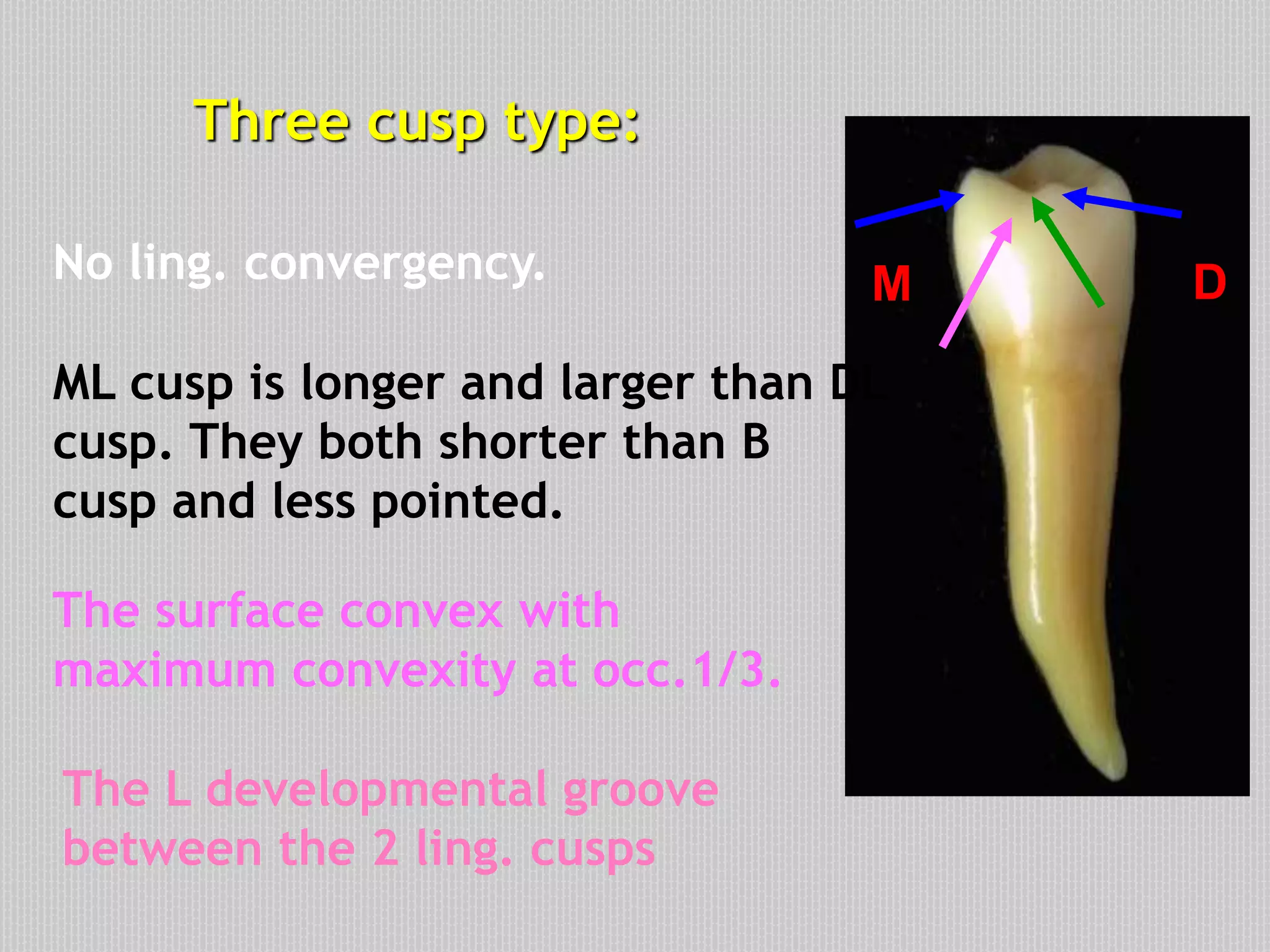
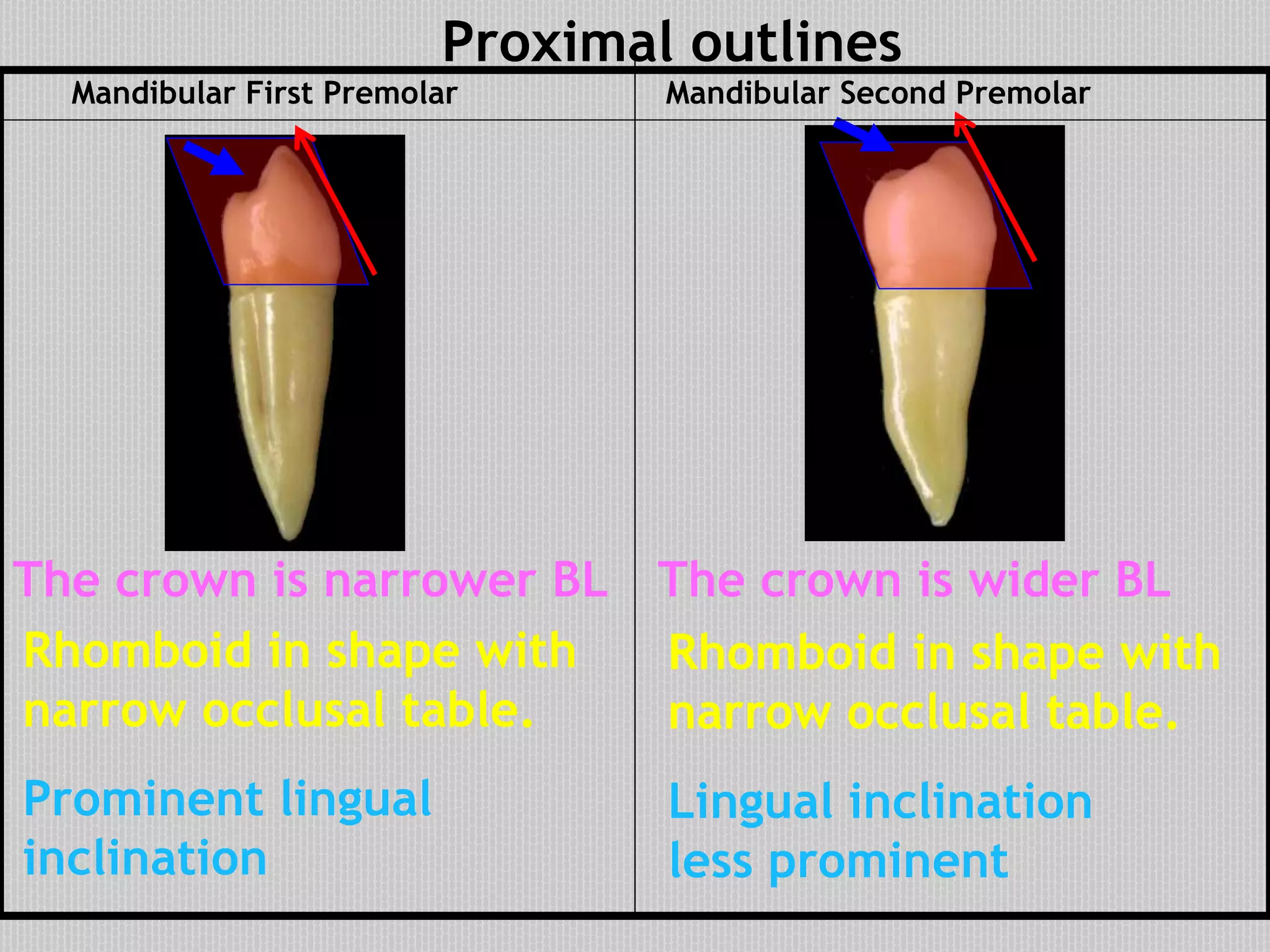
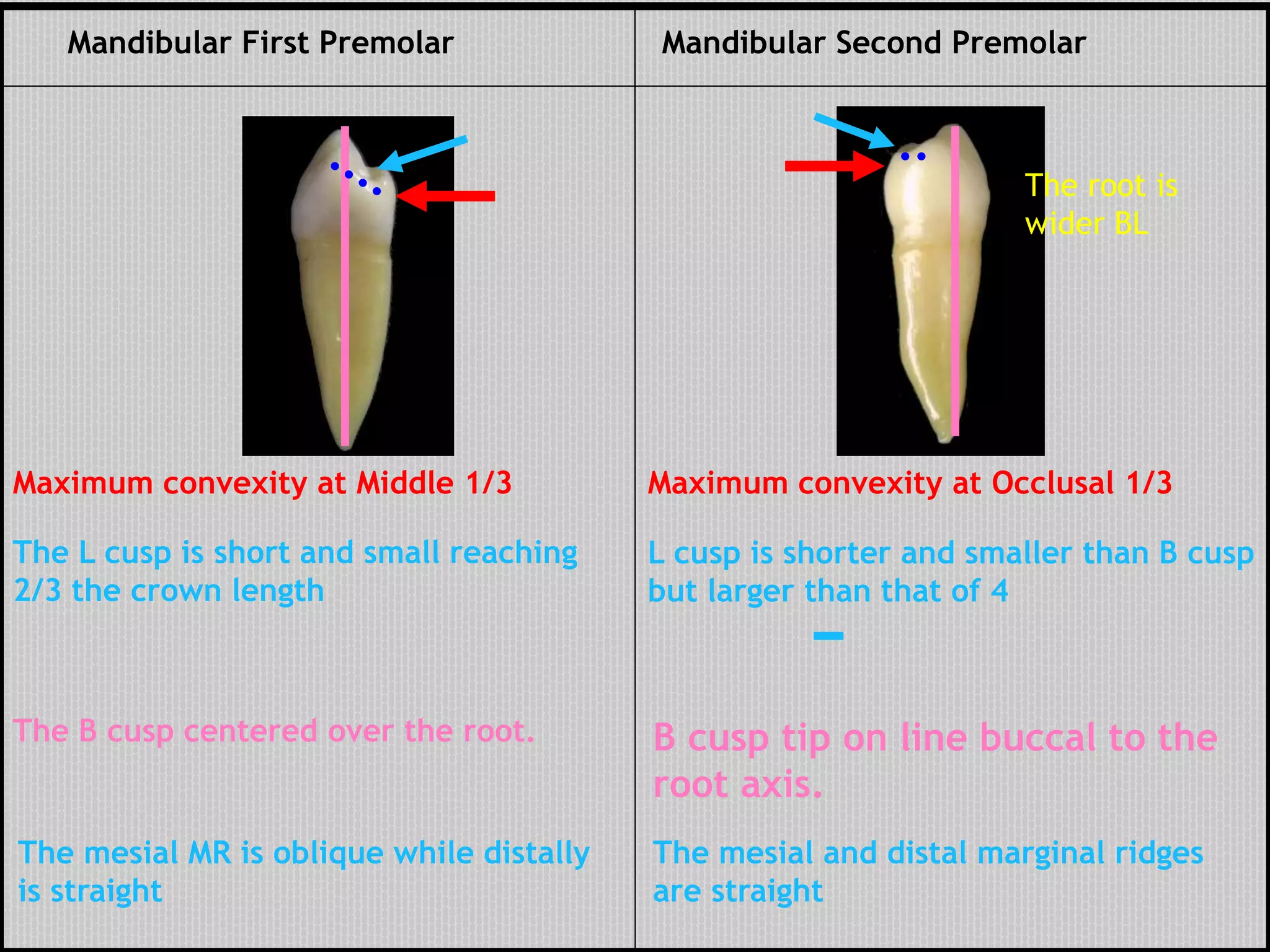
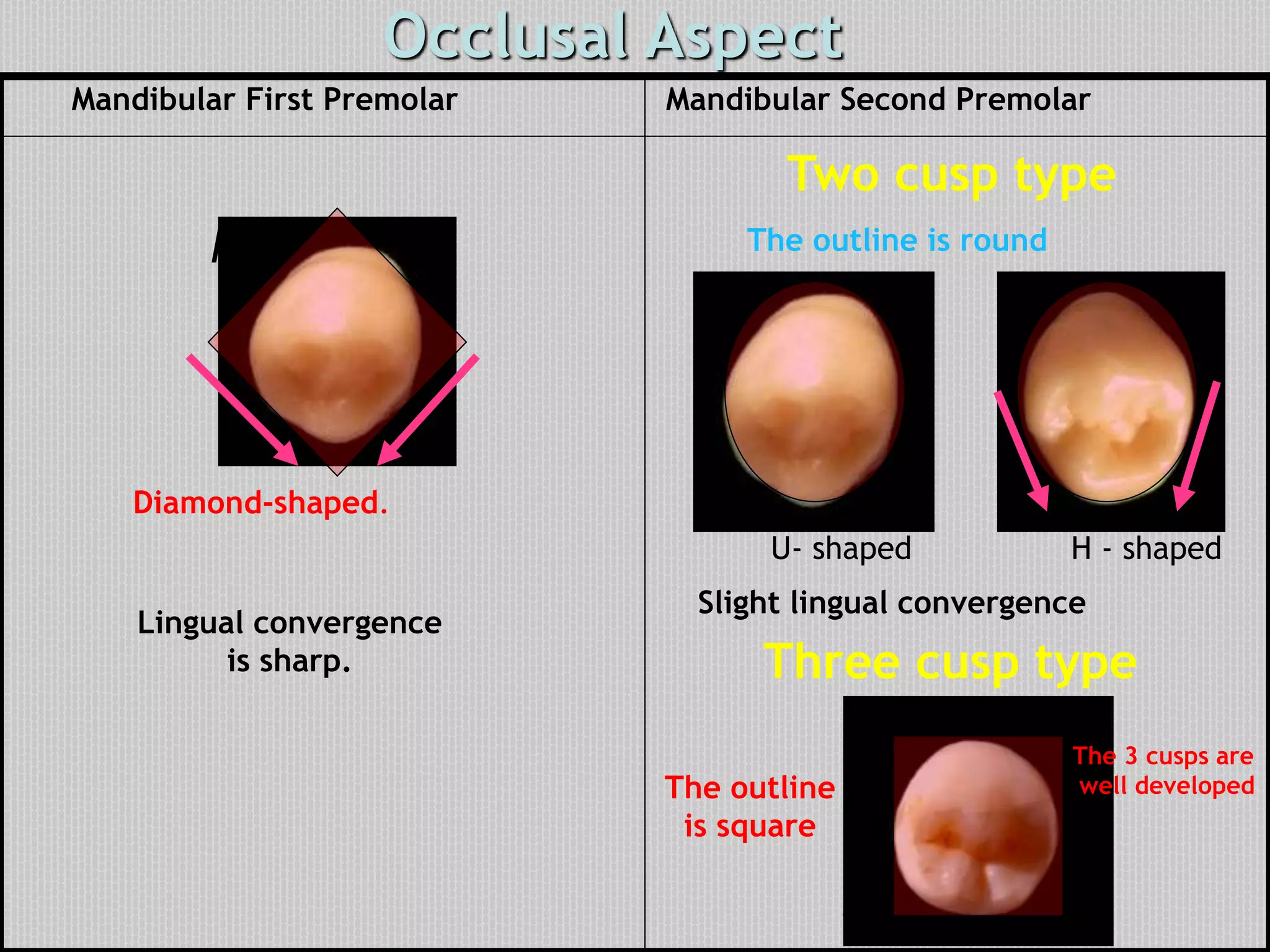
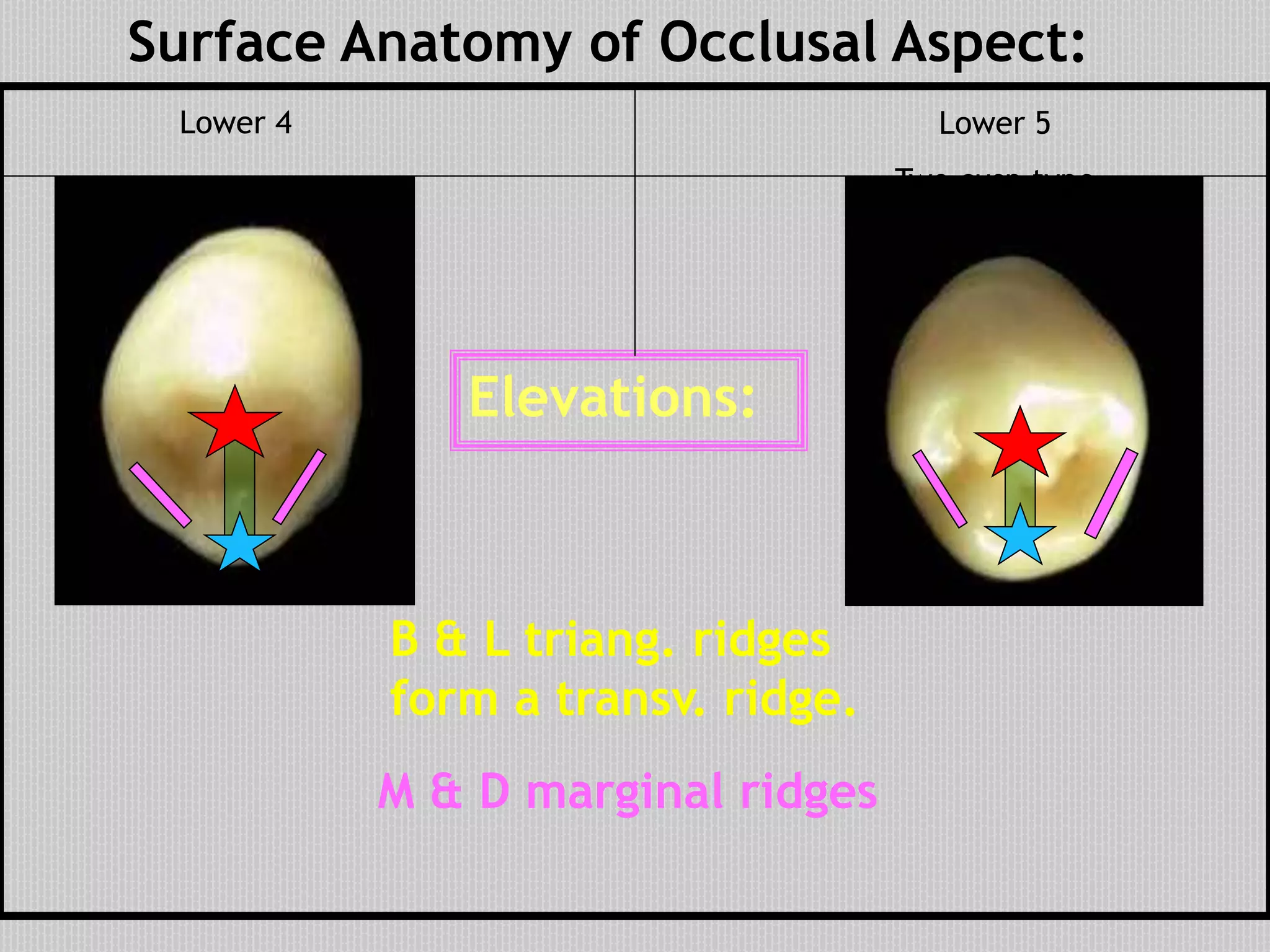
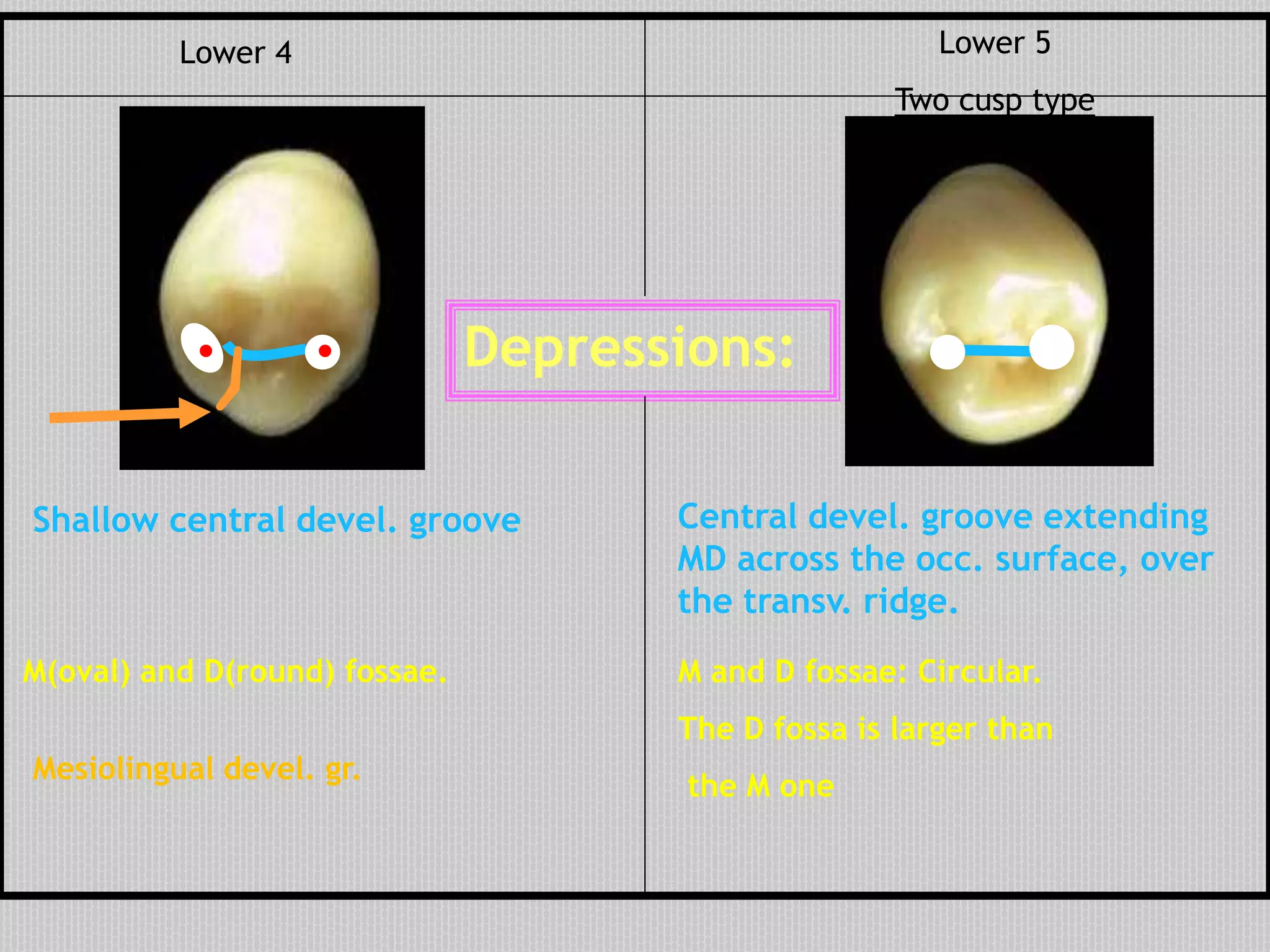
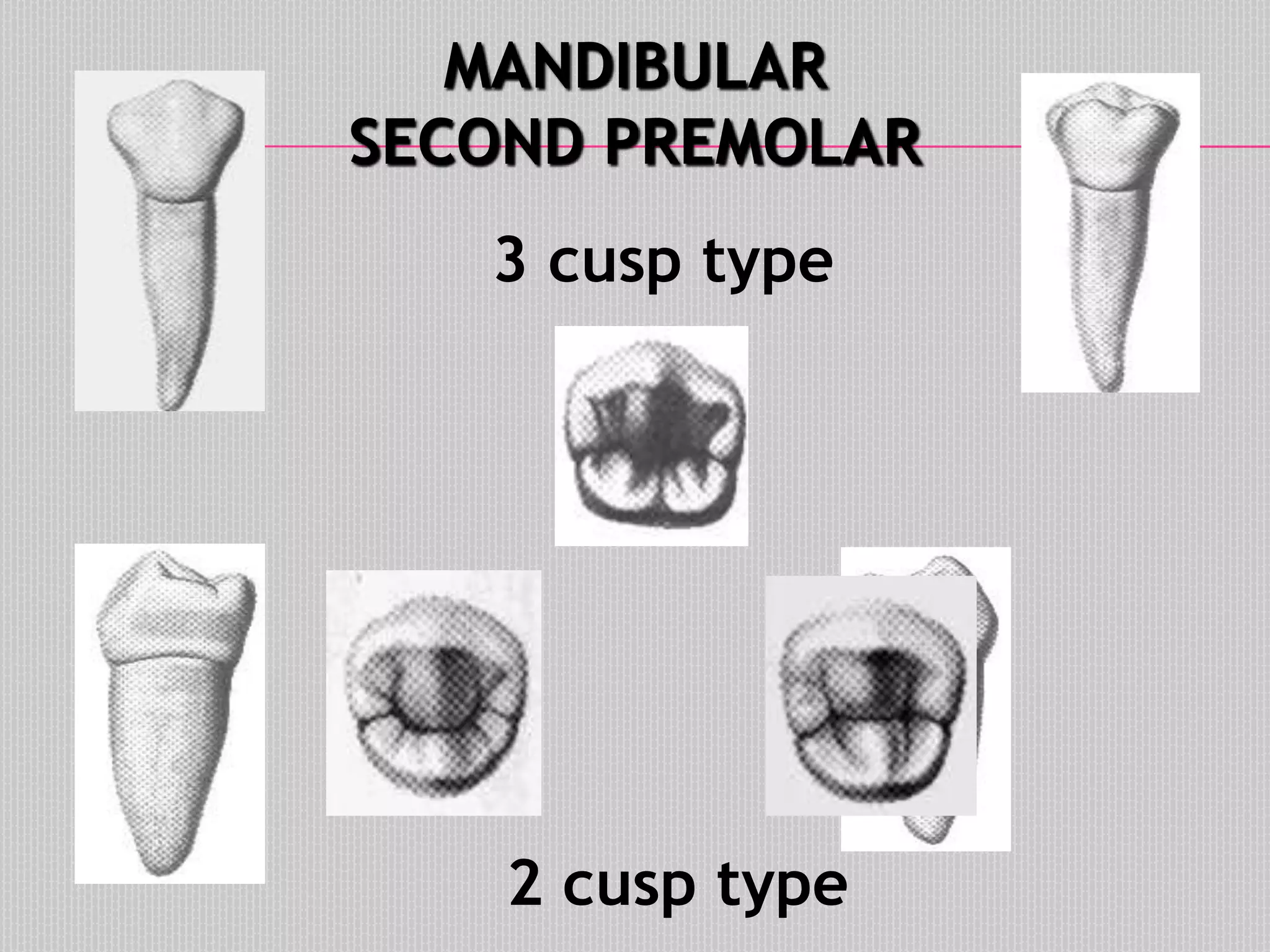
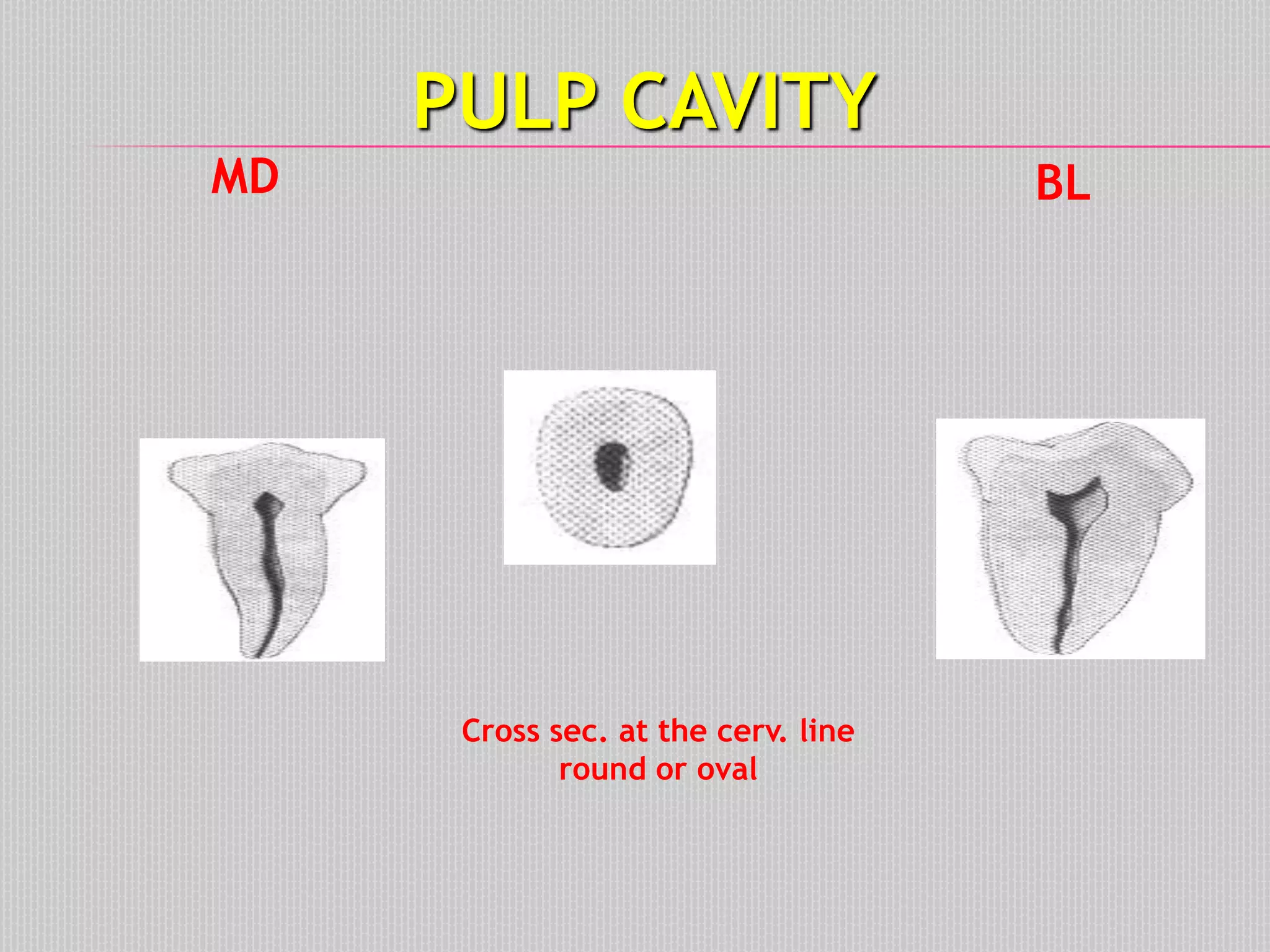
This document provides information about the permanent mandibular first premolar and differences between the mandibular first and second premolars. It discusses the general features of premolars, including their transitional location between canines and molars. For the mandibular first premolar, it describes the chronology, number of roots, crown and root outlines, contact areas, and surface anatomy from various aspects. It then compares the mandibular first and second premolars, noting differences in their geometric outlines, facial outlines and surface anatomy, lingual outlines, proximal outlines, occlusal aspects, and pulp cavities.