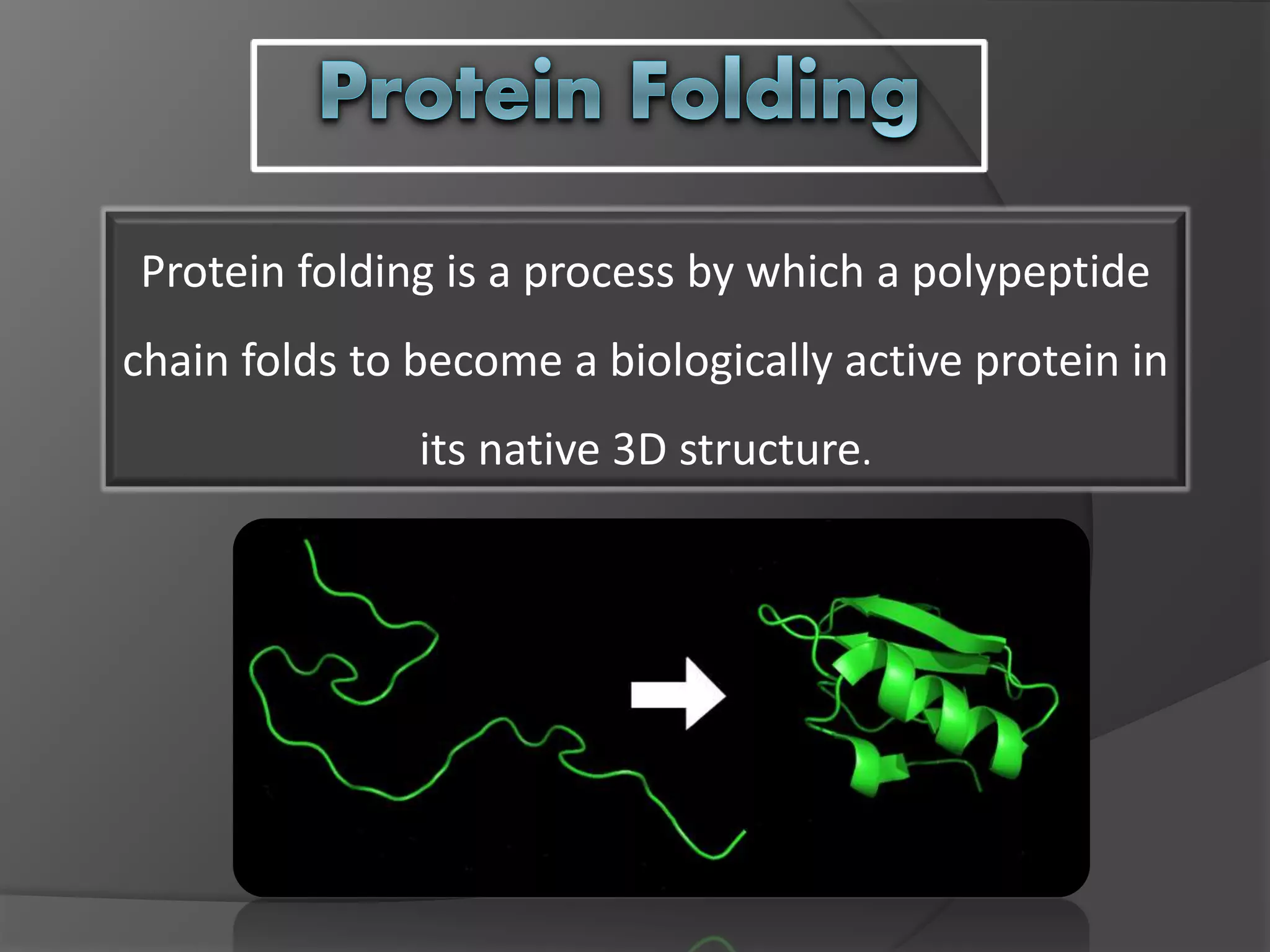
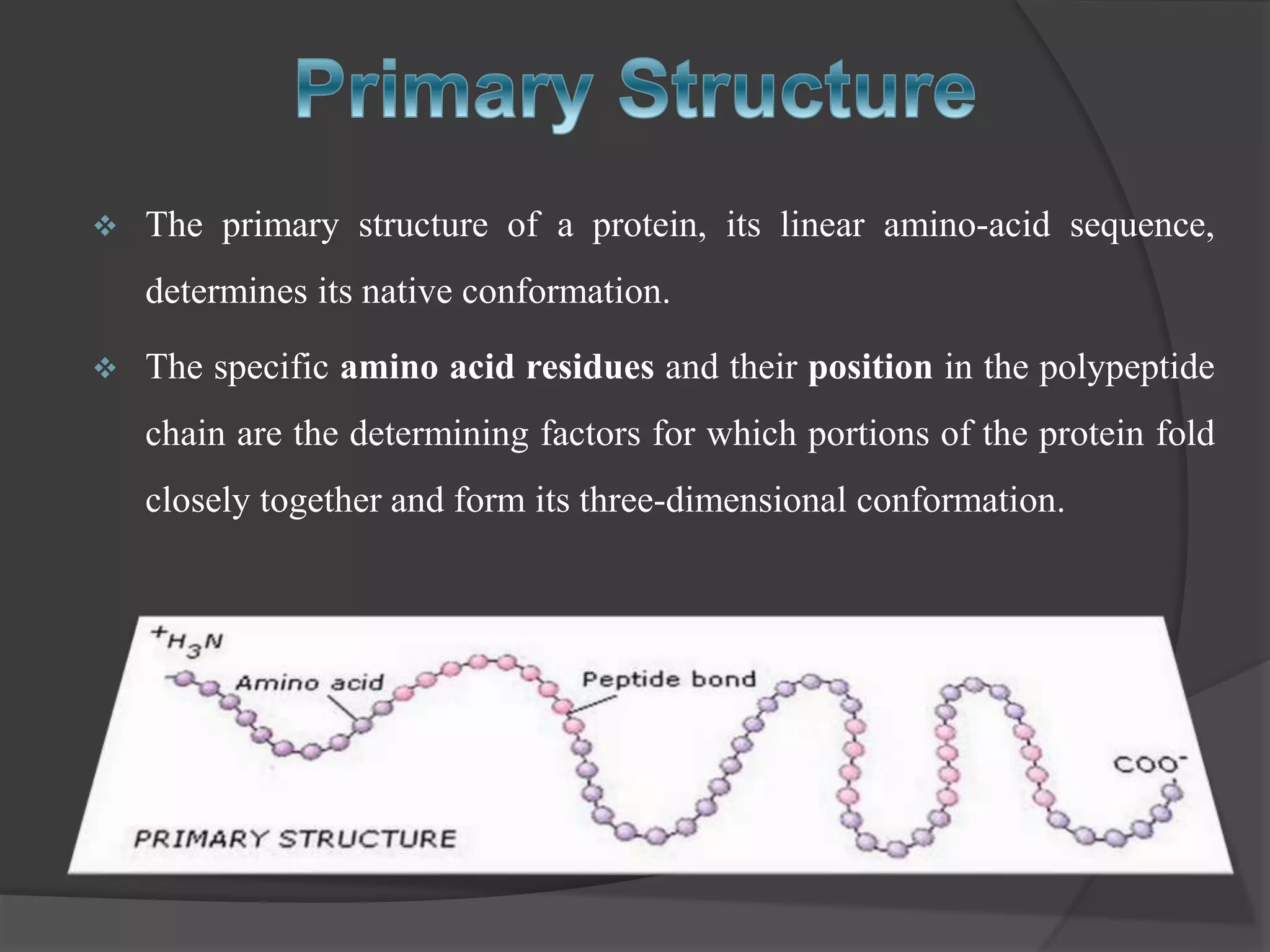
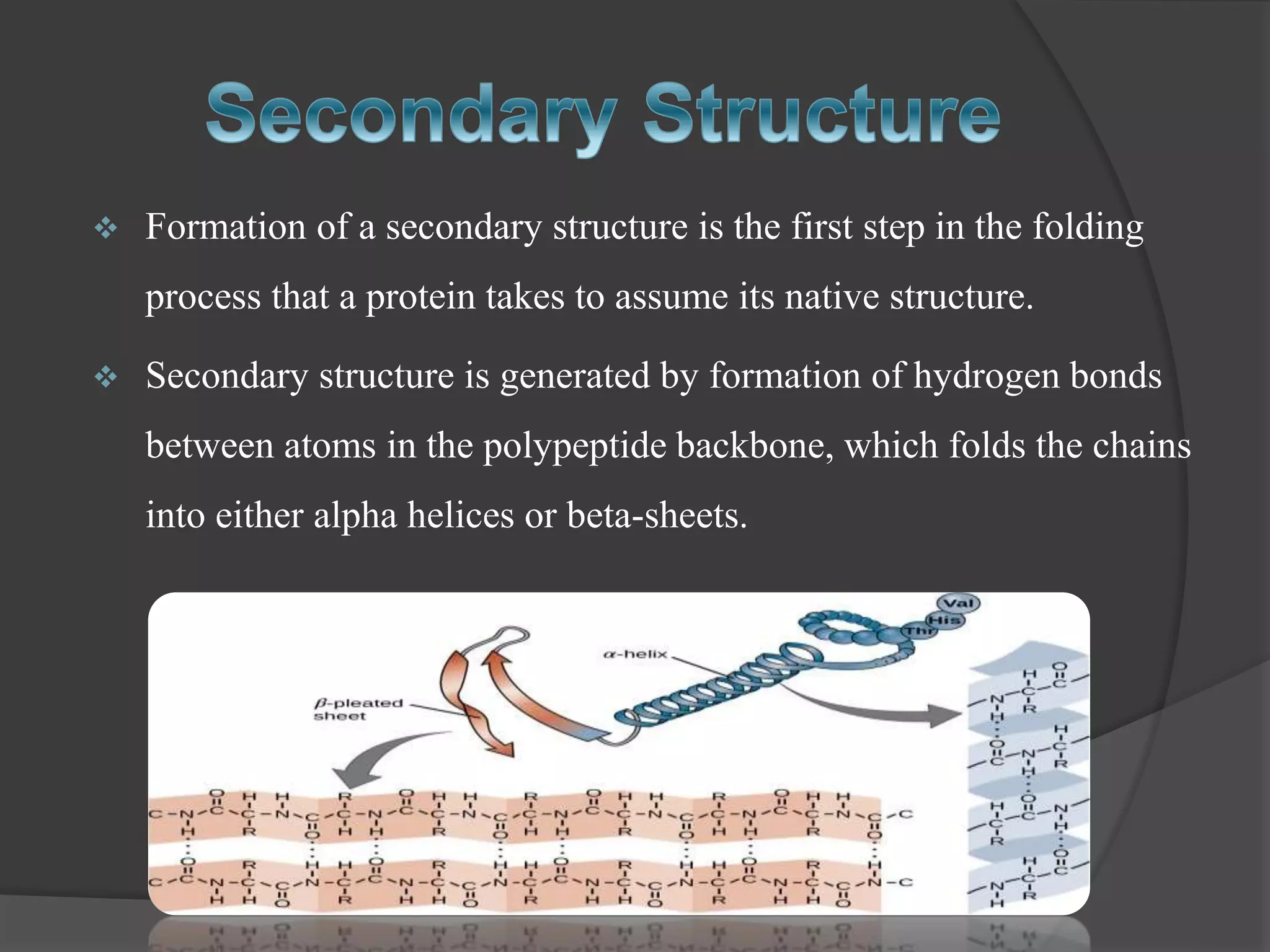
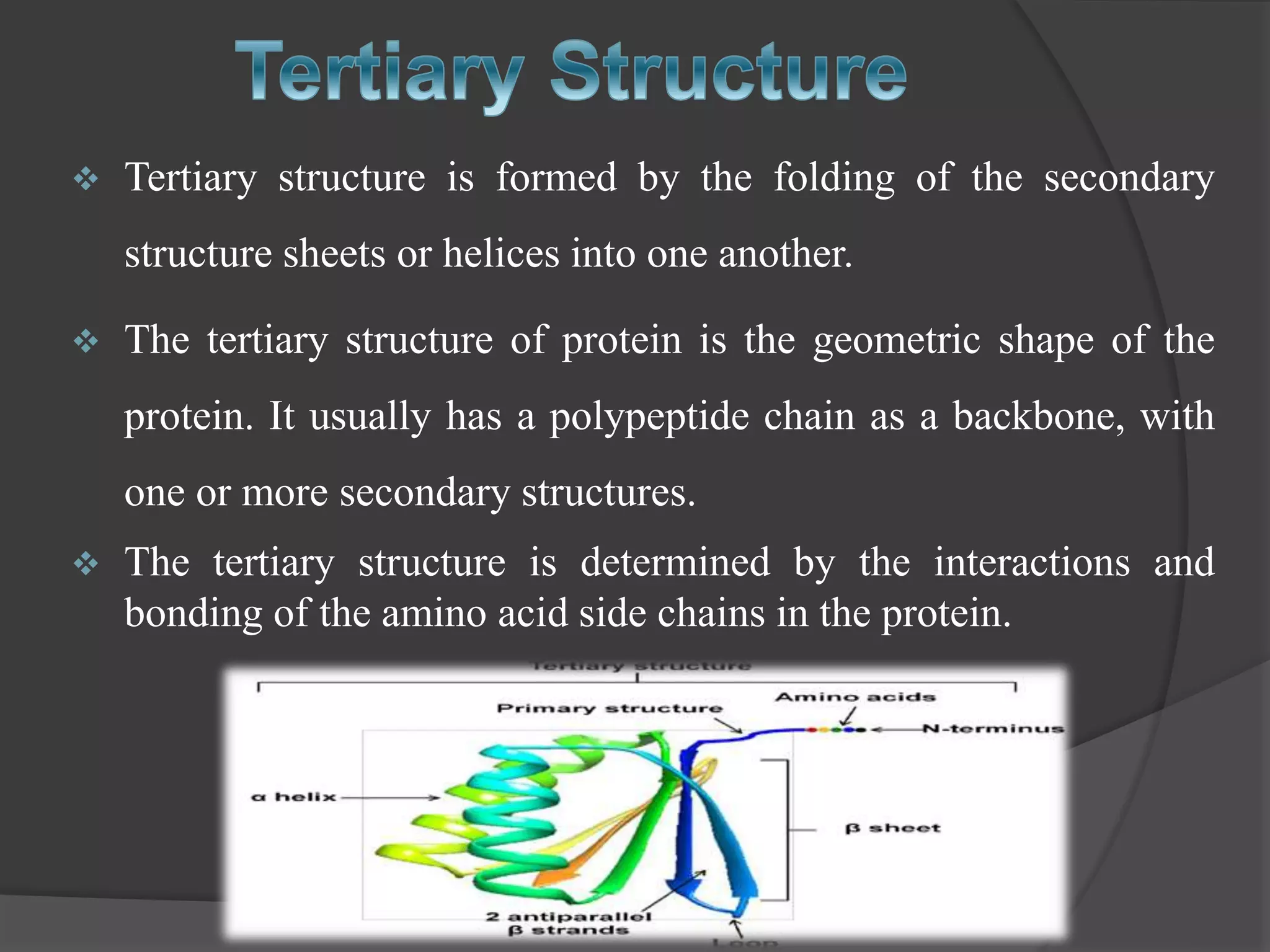
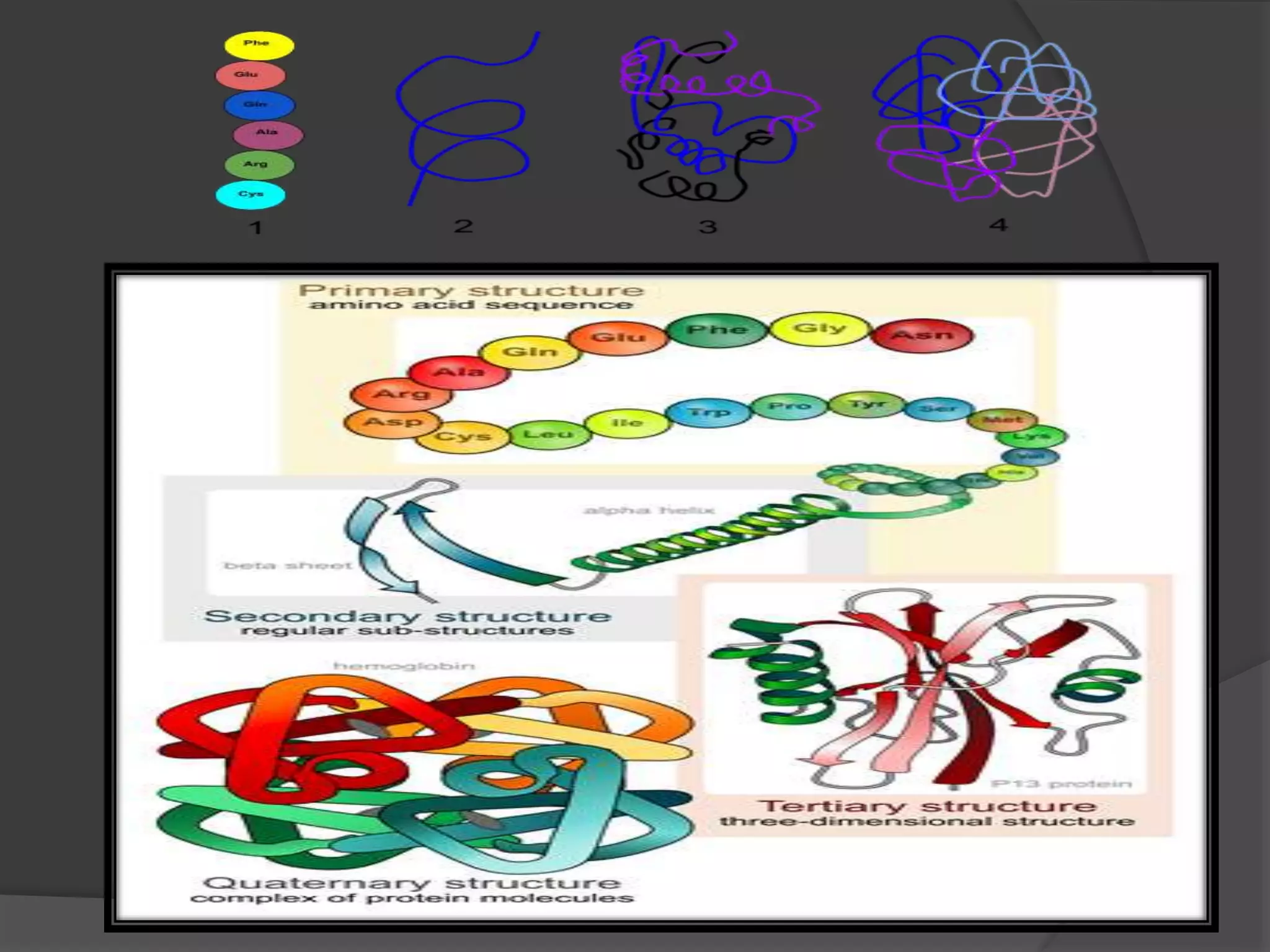
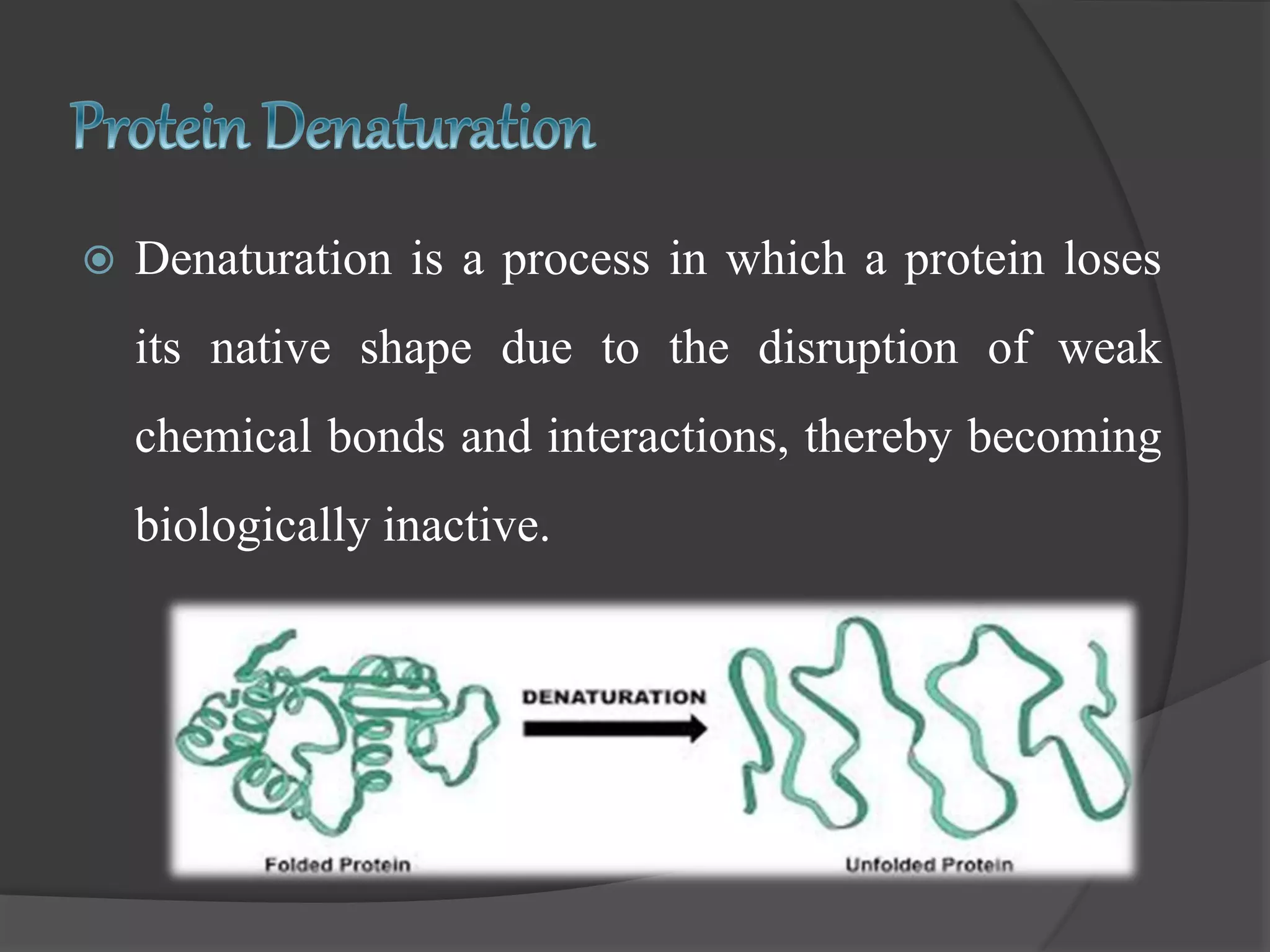
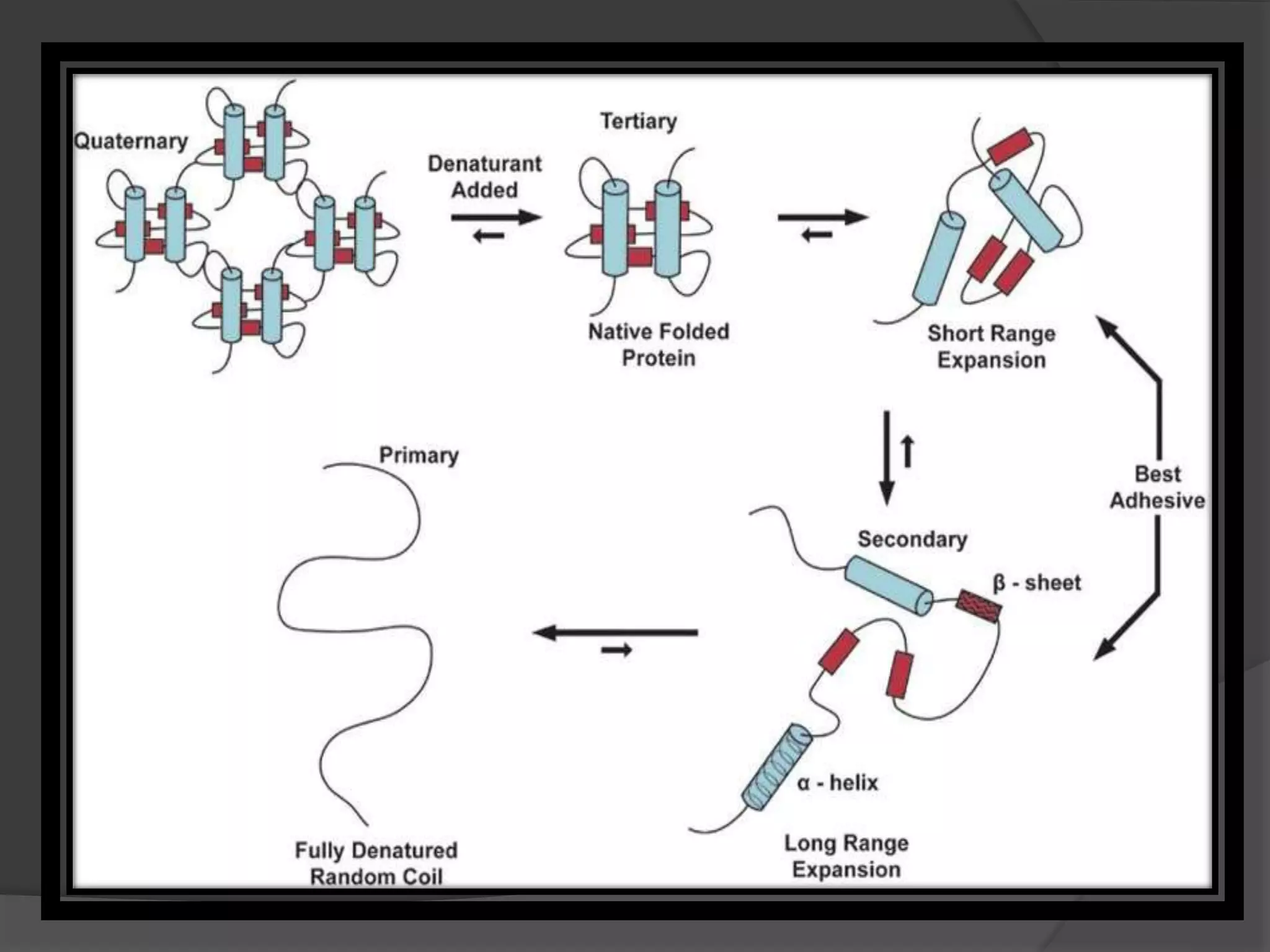
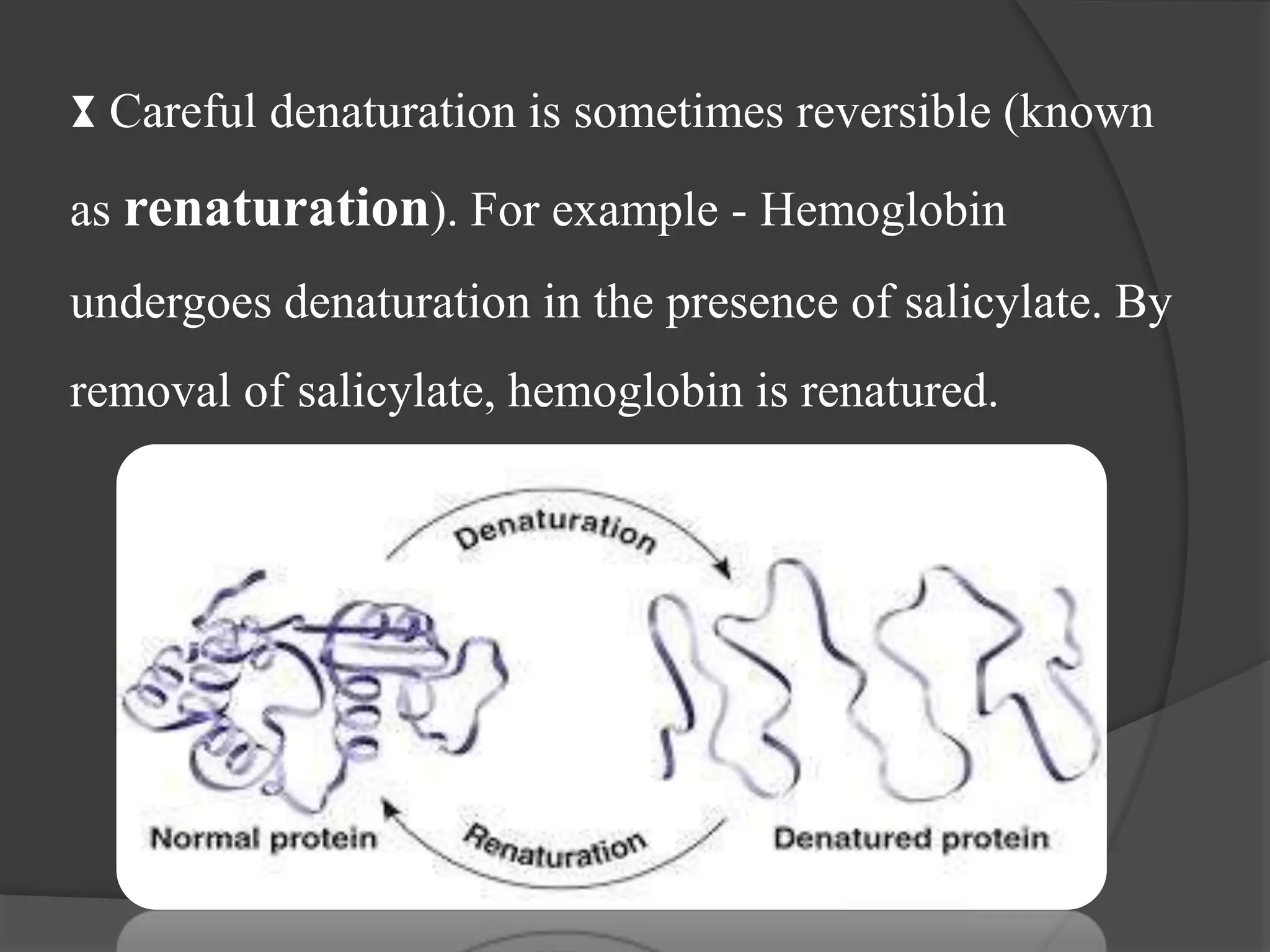
The document discusses protein folding and denaturation. It begins by explaining that protein folding is the process by which a polypeptide chain folds into its functional three-dimensional structure. It is driven by hydrophobic interactions, hydrogen bonding, and other forces. The document then describes the four levels of protein structure - primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary. It also lists factors that can affect folding and experimental techniques used to study folding. Next, it defines protein denaturation as the loss of native structure, discusses examples, and explains how denaturation occurs and its consequences. Finally, it lists chemical and physical agents that can cause denaturation.