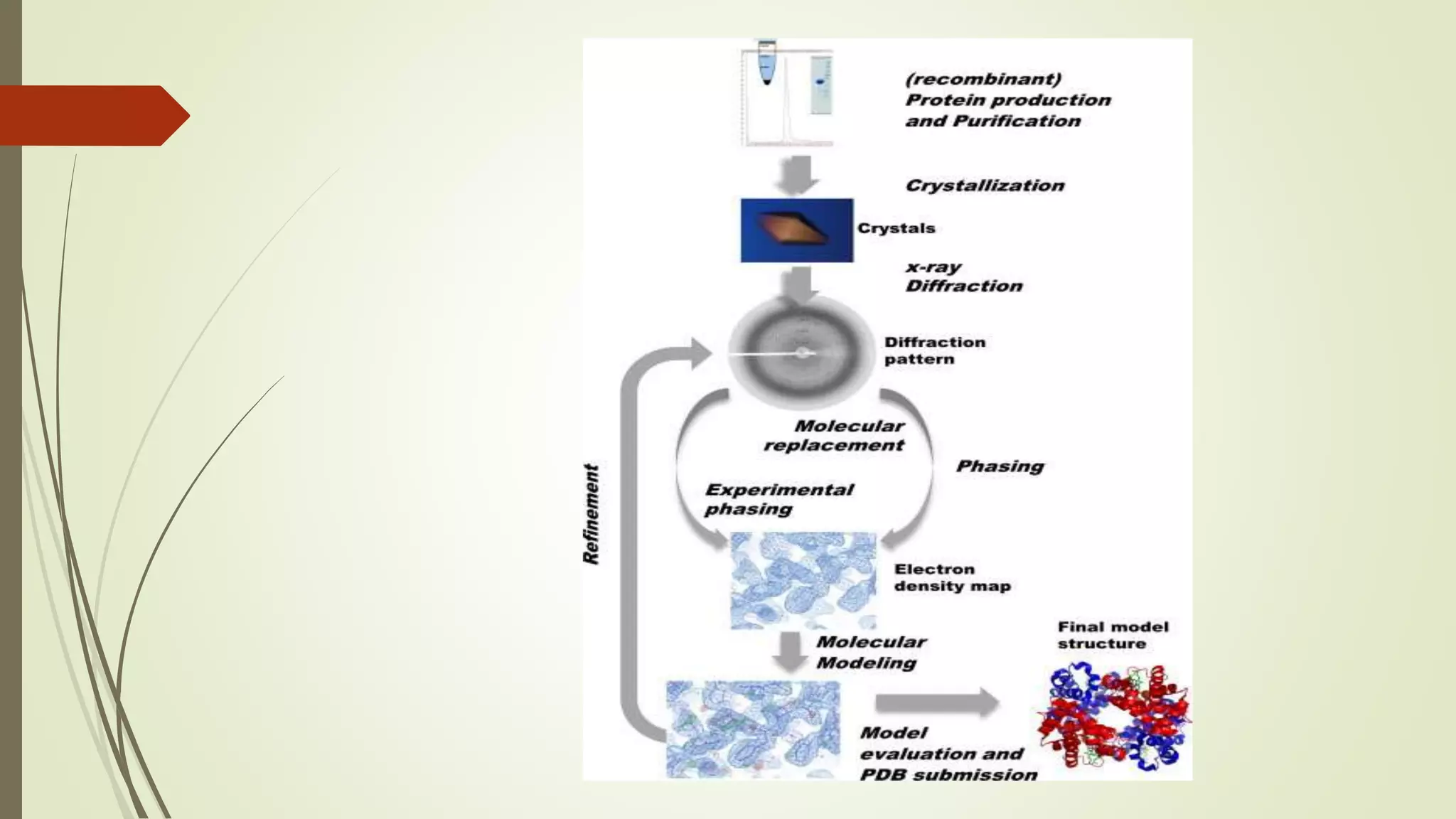
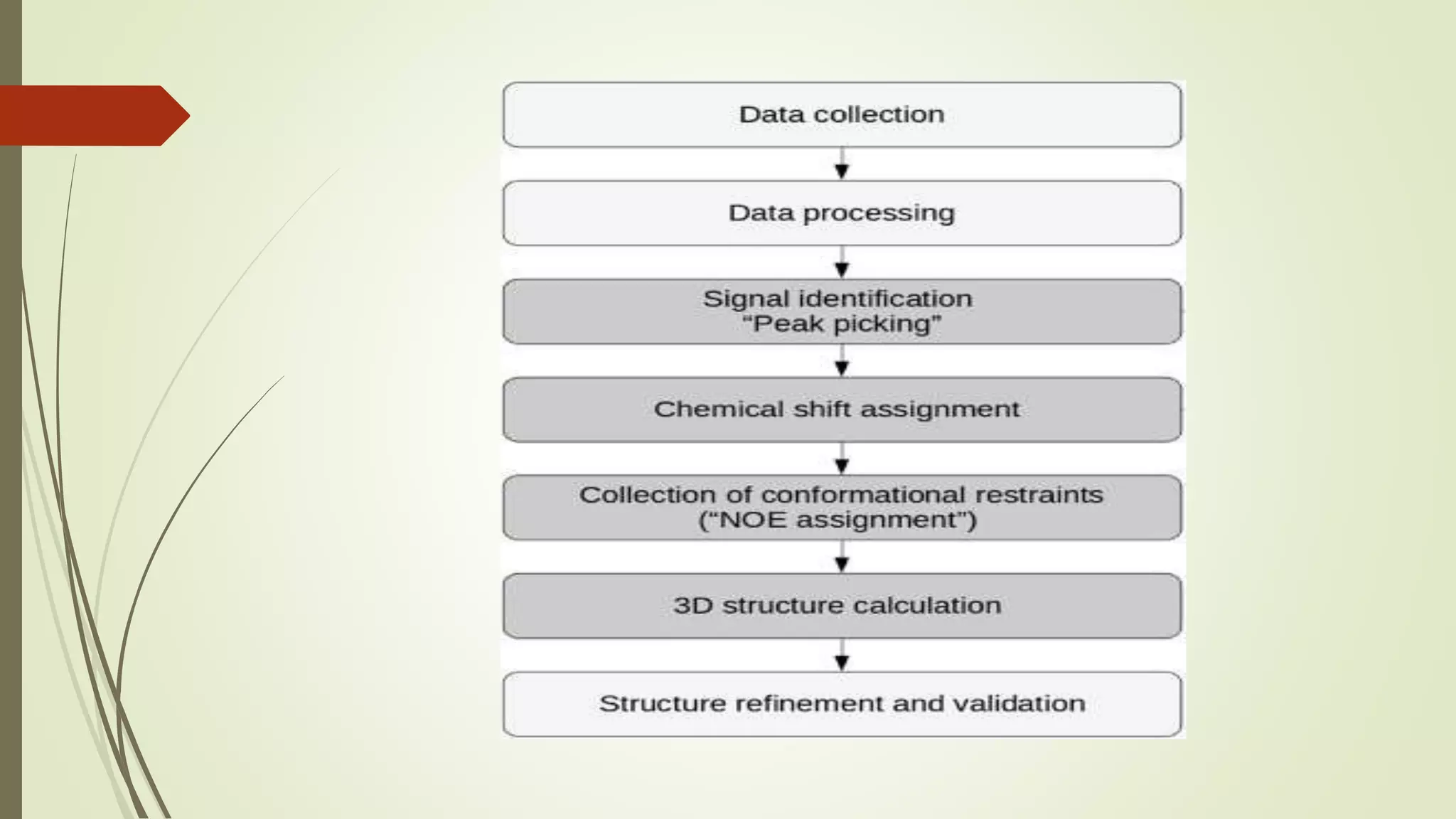
Quaternary structure refers to the structure of protein complexes containing multiple protein subunits. It is important because oligomeric proteins are involved in key biological processes like metabolism and signal transduction. Determining quaternary structure helps understand how proteins work and allows for hypotheses about controlling or modifying them. Common techniques used include X-ray crystallography, electron microscopy, and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. X-ray crystallography uses X-ray diffraction from protein crystals to determine atomic structure, while NMR spectroscopy analyzes nuclear properties to determine interatomic distances and overall structure in solution.