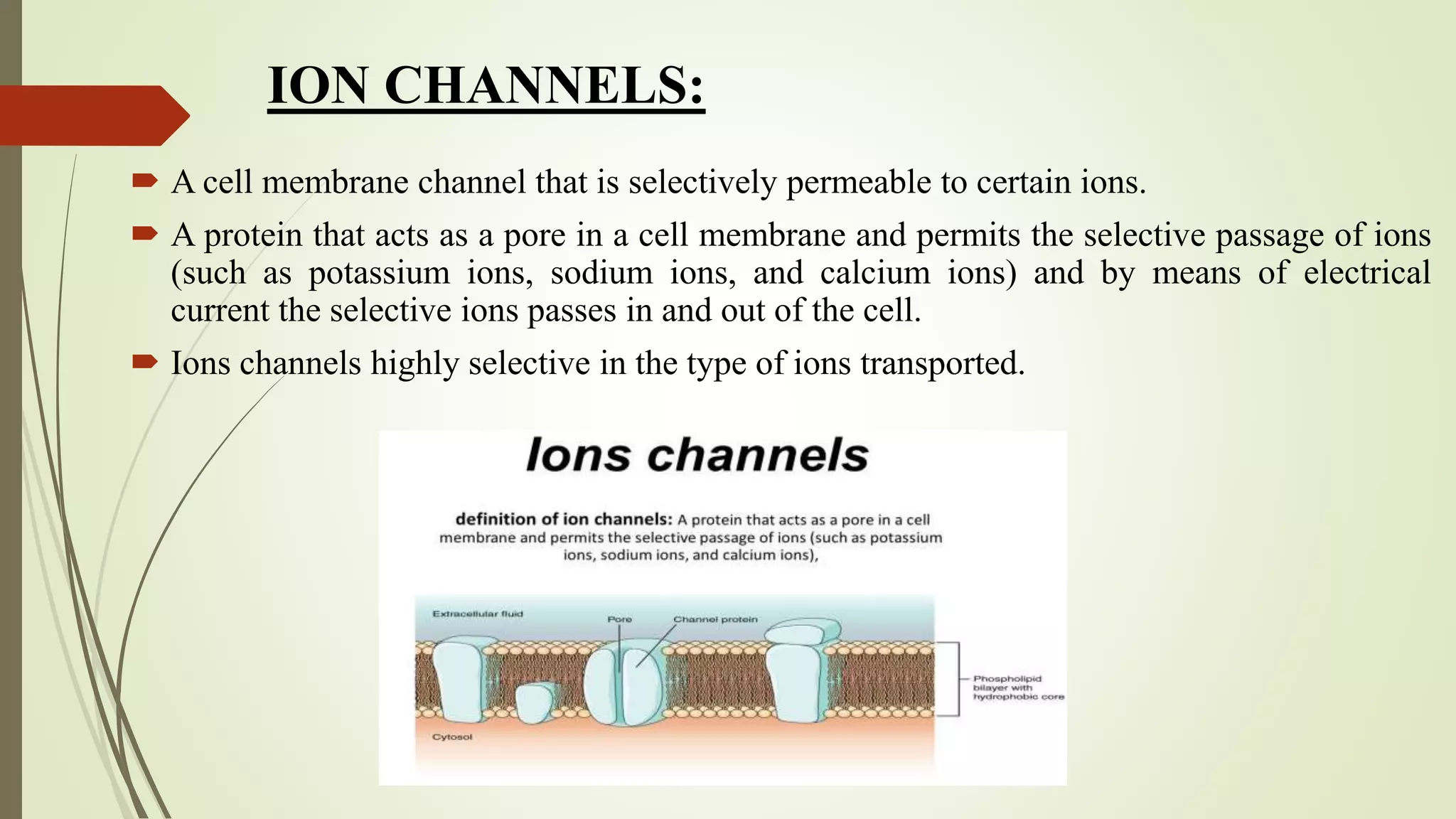
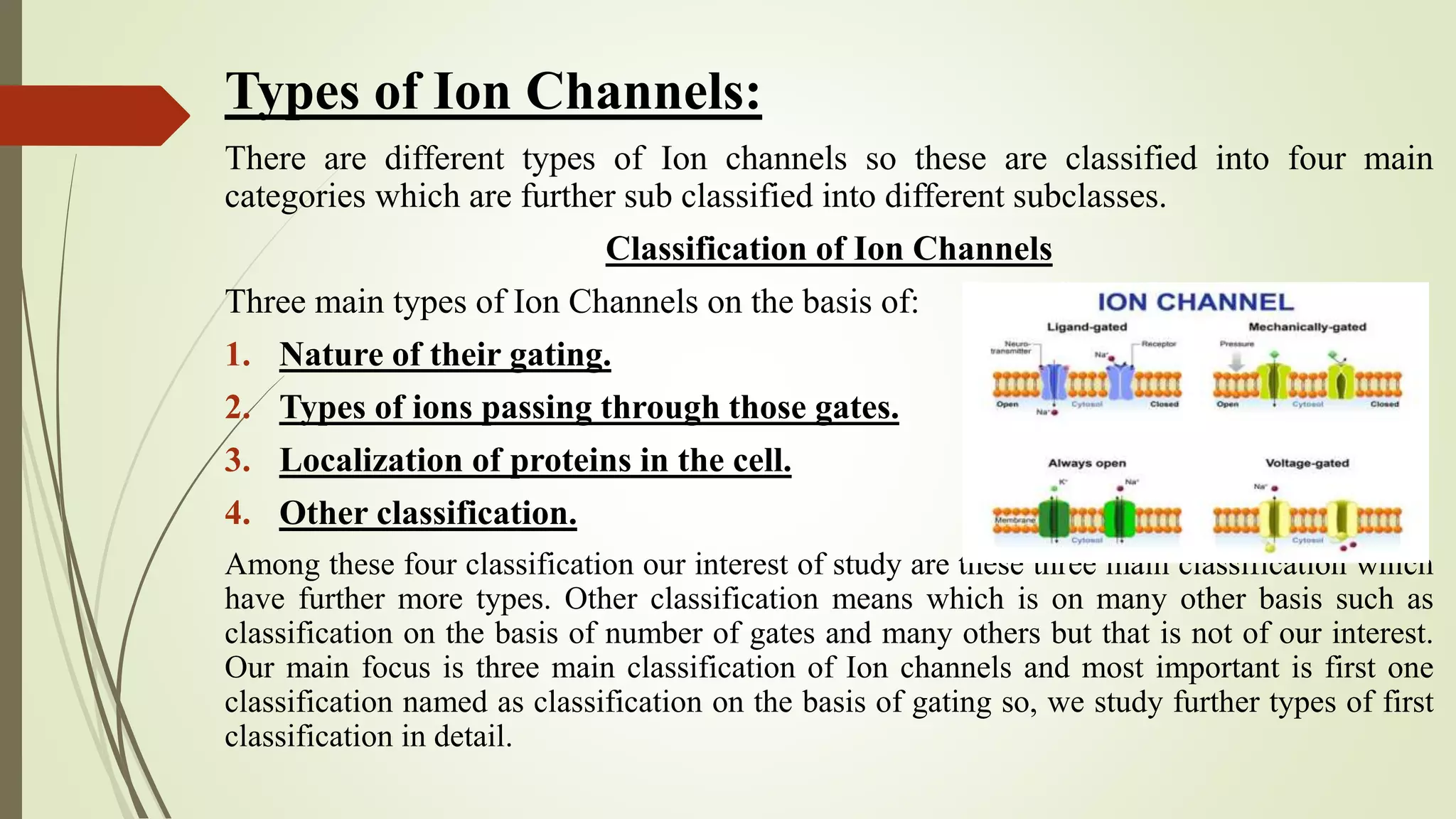
Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins that regulate the flow of ions across cell membranes. There are several types of ion channels classified by their gating mechanism and selectivity for specific ions like potassium, sodium, calcium, and chloride. Voltage-gated ion channels open or close in response to changes in membrane potential, while ligand-gated channels are activated by binding of neurotransmitters or other ligands. Ion channels play crucial roles in generating electrical signals in excitable cells and regulating various cellular processes. Diseases caused by mutations in ion channel genes are known as channelopathies.