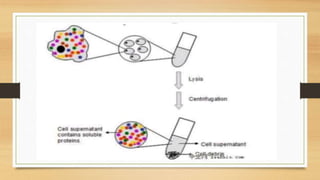
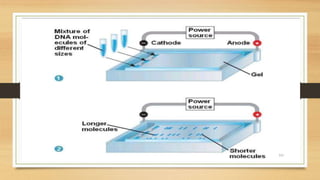
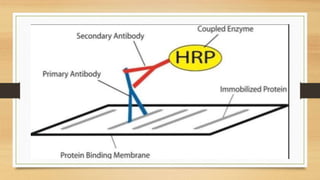
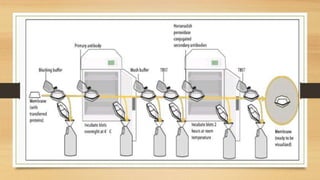
Western blotting is a technique used to detect specific proteins in a sample. It involves separating proteins by gel electrophoresis, transferring them to a membrane, and using antibodies to identify a target protein. The key steps are sample preparation, gel electrophoresis to separate proteins by size, transferring proteins to a membrane, blocking the membrane to reduce background noise, probing the membrane with antibodies to detect the target protein, washing unbound antibodies, and detecting the target protein to analyze its presence and quantity. Western blotting is widely used in research and medical diagnostics to study protein expression and identify proteins of interest.