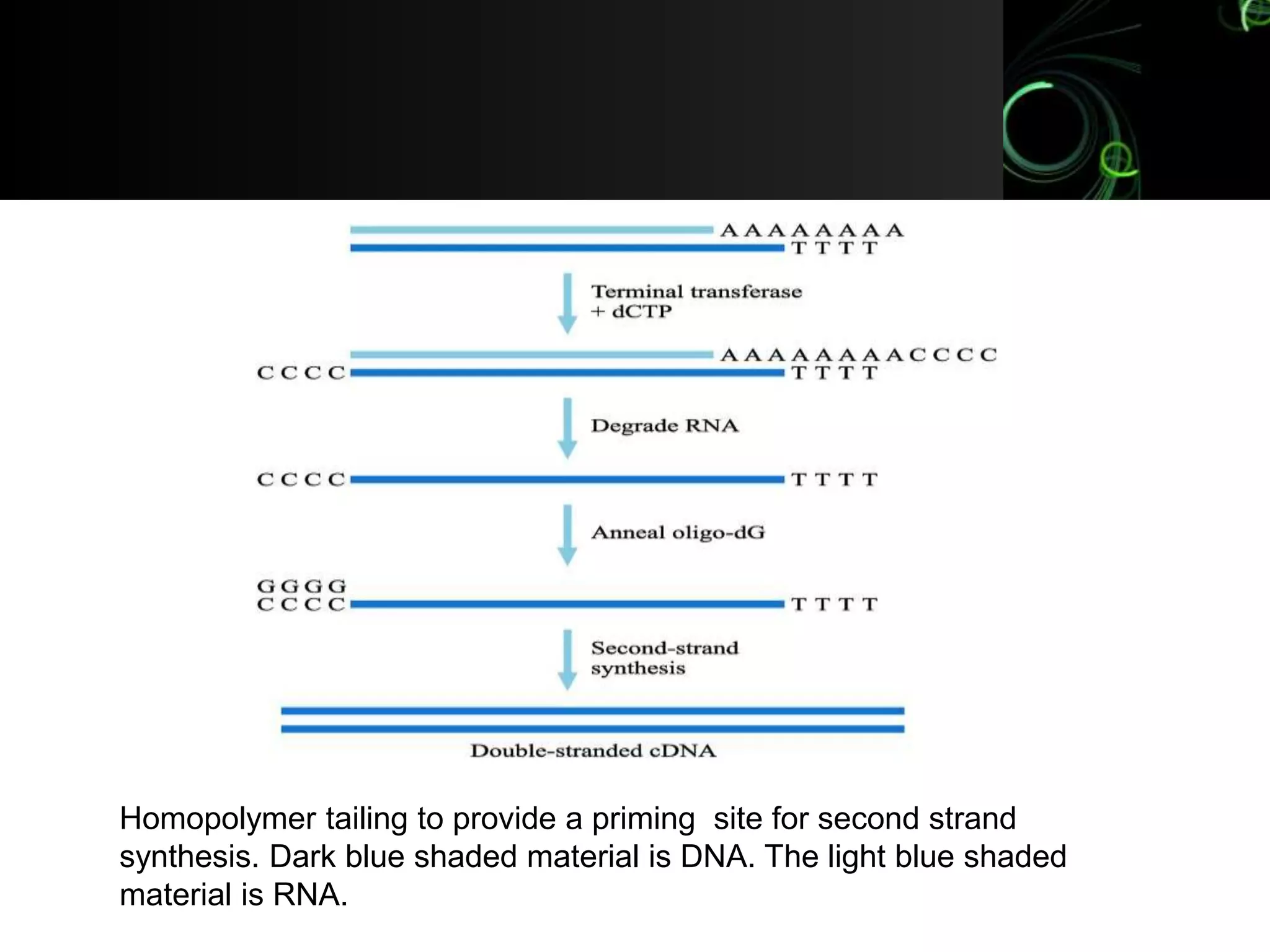
This document is a seminar submission on the topic of homopolymer tailing. It introduces homopolymer tailing as a method for joining DNA molecules by annealing complementary homopolymer sequences. Specifically, it involves adding homopolymer sequences like oligo(dA) to the 3' ends of one DNA molecule and complementary sequences like oligo(dT) to another molecule. This is done using the enzyme terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase. The molecules can then be incubated to allow the complementary homopolymer sequences to anneal together via hydrogen bonding. Common applications include using poly dC tails on vectors and poly dG tails on DNA fragments to be cloned, in order to ligate the two molecules together