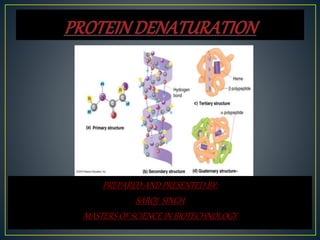
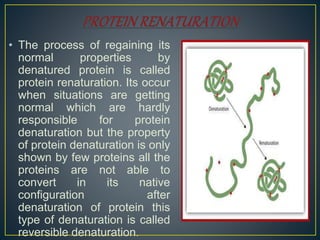
This document discusses protein denaturation. It defines protein denaturation as the alteration of a protein's native tertiary and quaternary structure due to external stresses like heat, chemicals, or pressure. This disrupts bonds within the protein and can disrupt cell activity or cause cell death. Protein denaturation can be reversible or irreversible depending on if the protein can regain its native structure. Common causes of denaturation include temperature changes, pH changes, oxidation, and enzymatic degradation. Effects include loss of biological activity and changes to size, shape, and physical appearance.