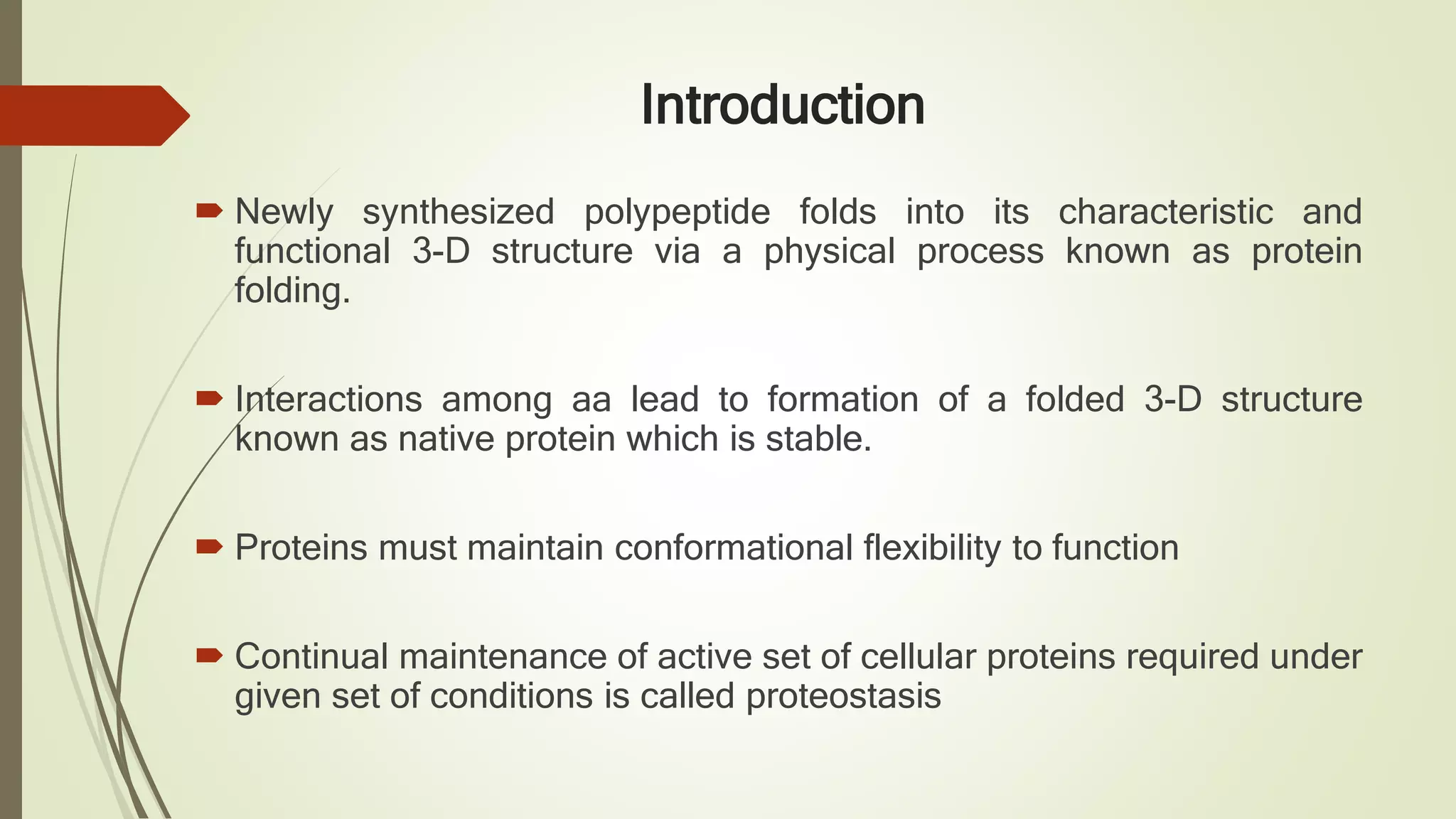
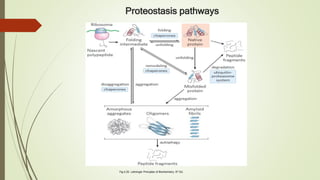
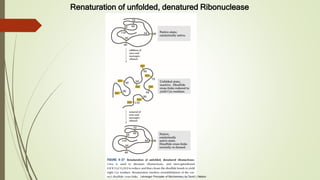
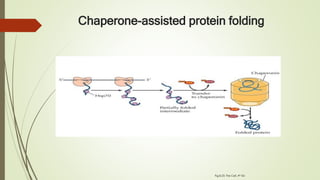
Protein folding is the physical process by which a polypeptide folds into its characteristic three-dimensional structure. Folding begins with interactions between amino acids that form regions of secondary structure, which then fold into a compact three-dimensional structure. For some proteins, folding requires assistance from molecular chaperones such as Hsp70 and chaperonins, which help prevent misfolding and aggregation. Misfolded proteins can lead to loss of function or formation of protein aggregates associated with diseases like cystic fibrosis and Alzheimer's.