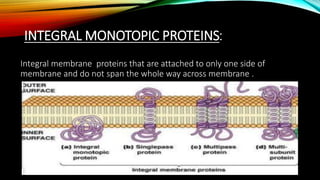
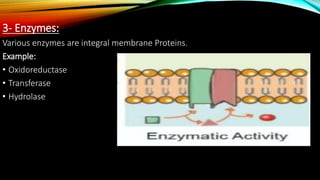
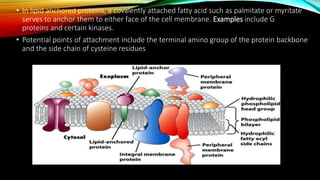
Membrane binding proteins interact with and are part of biological membranes. There are three main classifications: integral proteins that are permanently anchored, peripheral proteins that are temporarily attached, and lipid-anchored proteins. Integral proteins can span the entire membrane or be attached to only one side. They perform important functions like membrane transport, serving as receptors or enzymes, and cell adhesion. Peripheral proteins are temporarily attached via interactions with integral proteins or the membrane lipids. Lipid-anchored proteins have fatty acids that serve to anchor them to the membrane. All three types play critical roles in cell signaling, transport, and other membrane-related functions.