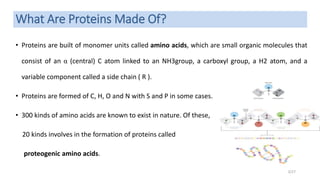
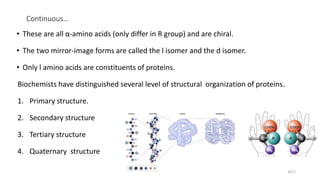
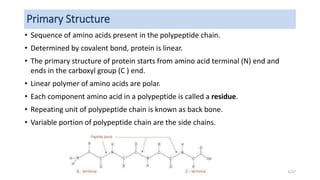
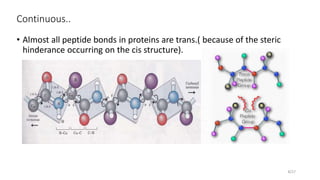
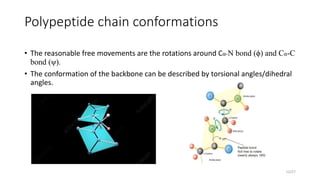
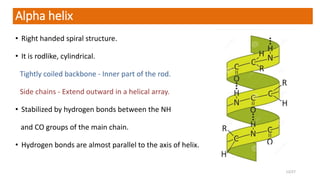
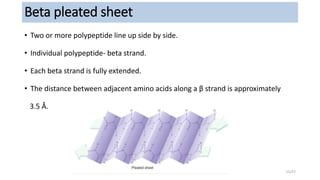
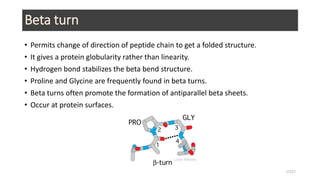
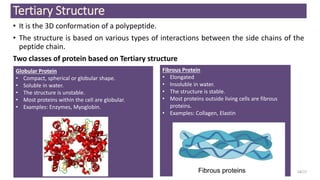
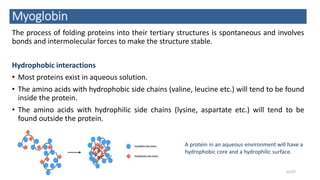
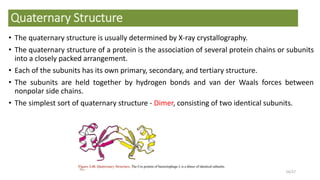
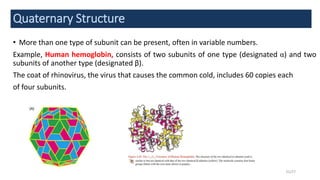
This document discusses the structure and function of proteins, emphasizing their significance as fundamental components of living matter built from amino acids. It outlines the various levels of protein structure—primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary—while detailing the processes involved in protein folding and the impact of amino acid sequences on protein functionality. It also references key historical figures and studies in the field of protein biochemistry.