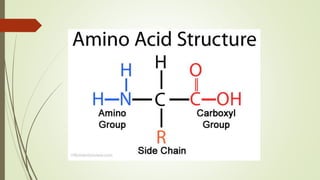
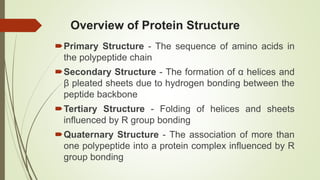
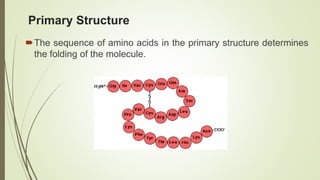
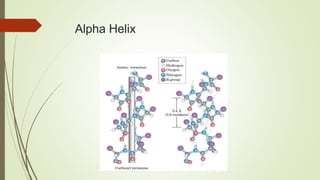
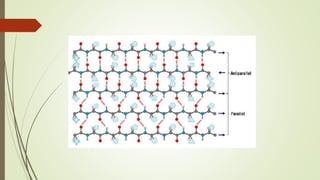
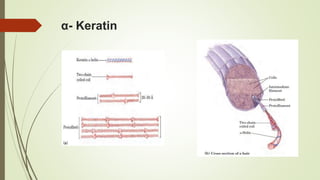
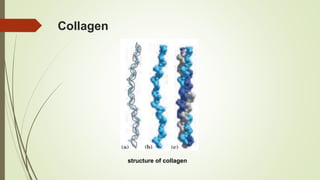
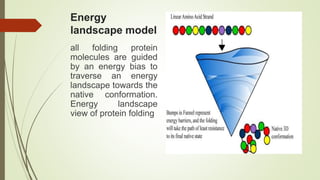
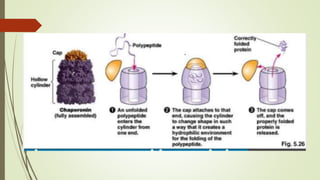
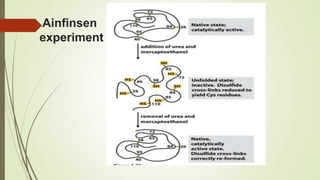
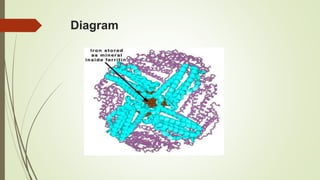
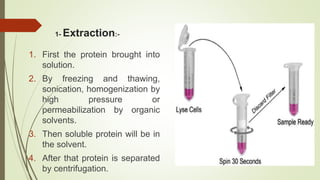
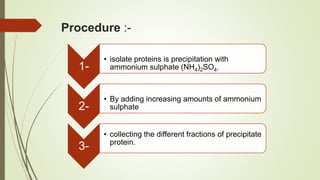
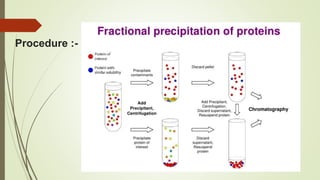
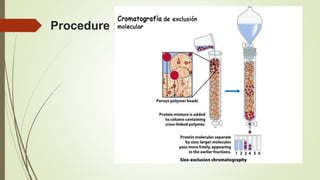
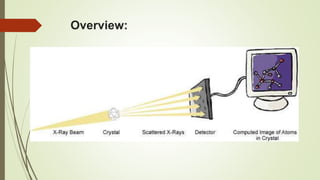
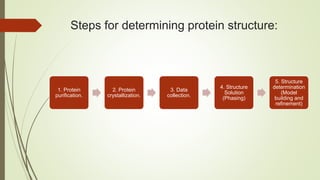
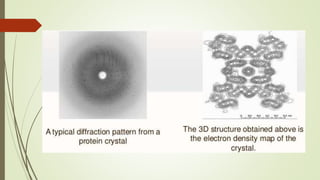
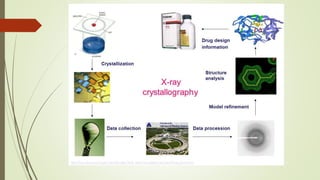
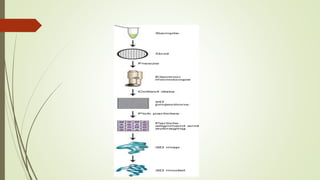
Proteins are polymers made of amino acids that carry out essential functions in organisms. They have primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary levels of structure determined by amino acid sequence and interactions. Stability depends on factors like temperature, pH, and solvents. Proteins misfold due to mutations or environmental stresses but normally fold into functional native states guided by energy landscapes. Functions include storage, transport, defense, cell signaling, and more. Purification techniques separate proteins from cell lysates using techniques like extraction, precipitation, chromatography. Determination methods identify proteins using X-ray crystallography or NMR spectroscopy.