Embed presentation
Downloaded 132 times

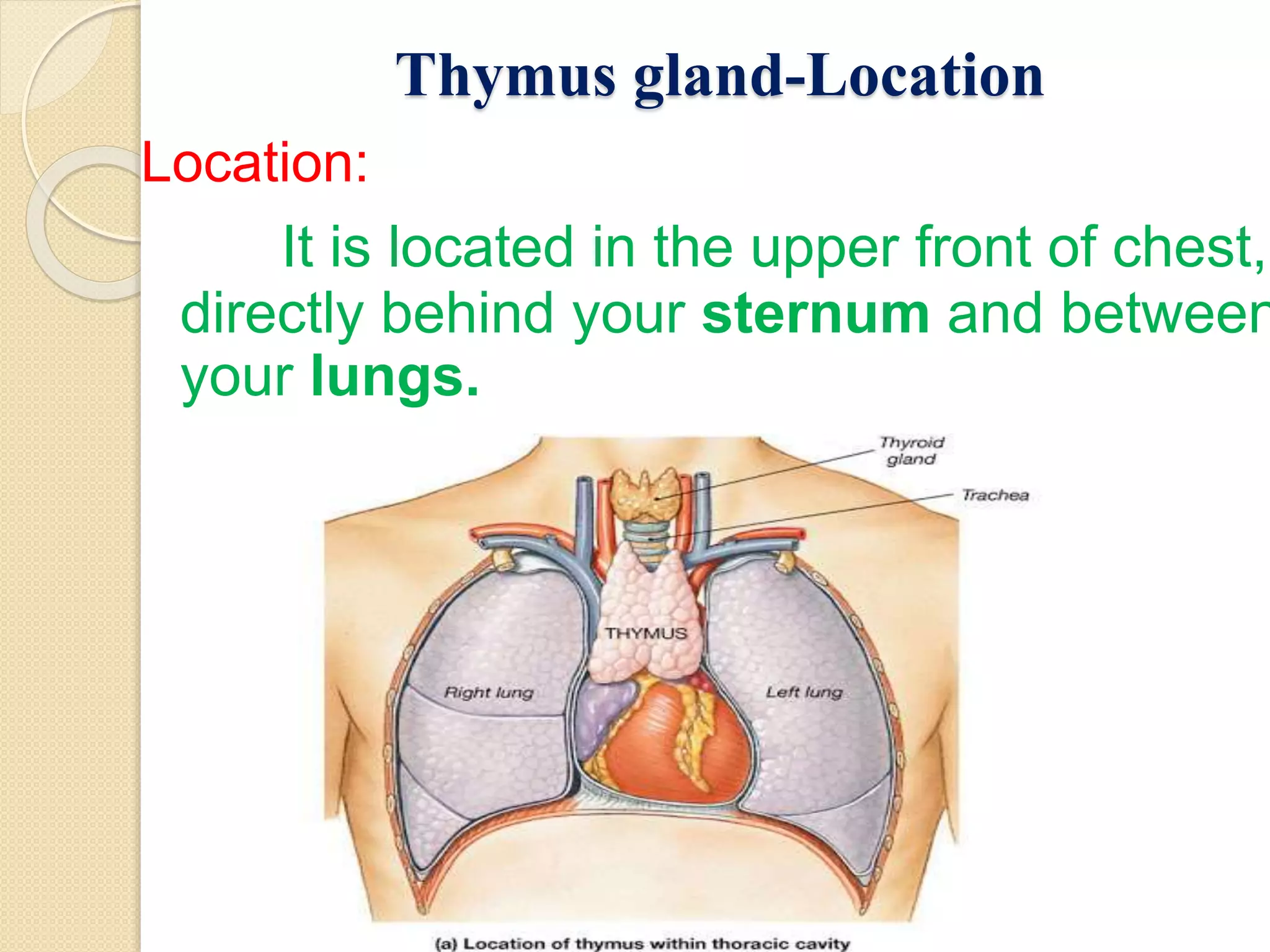
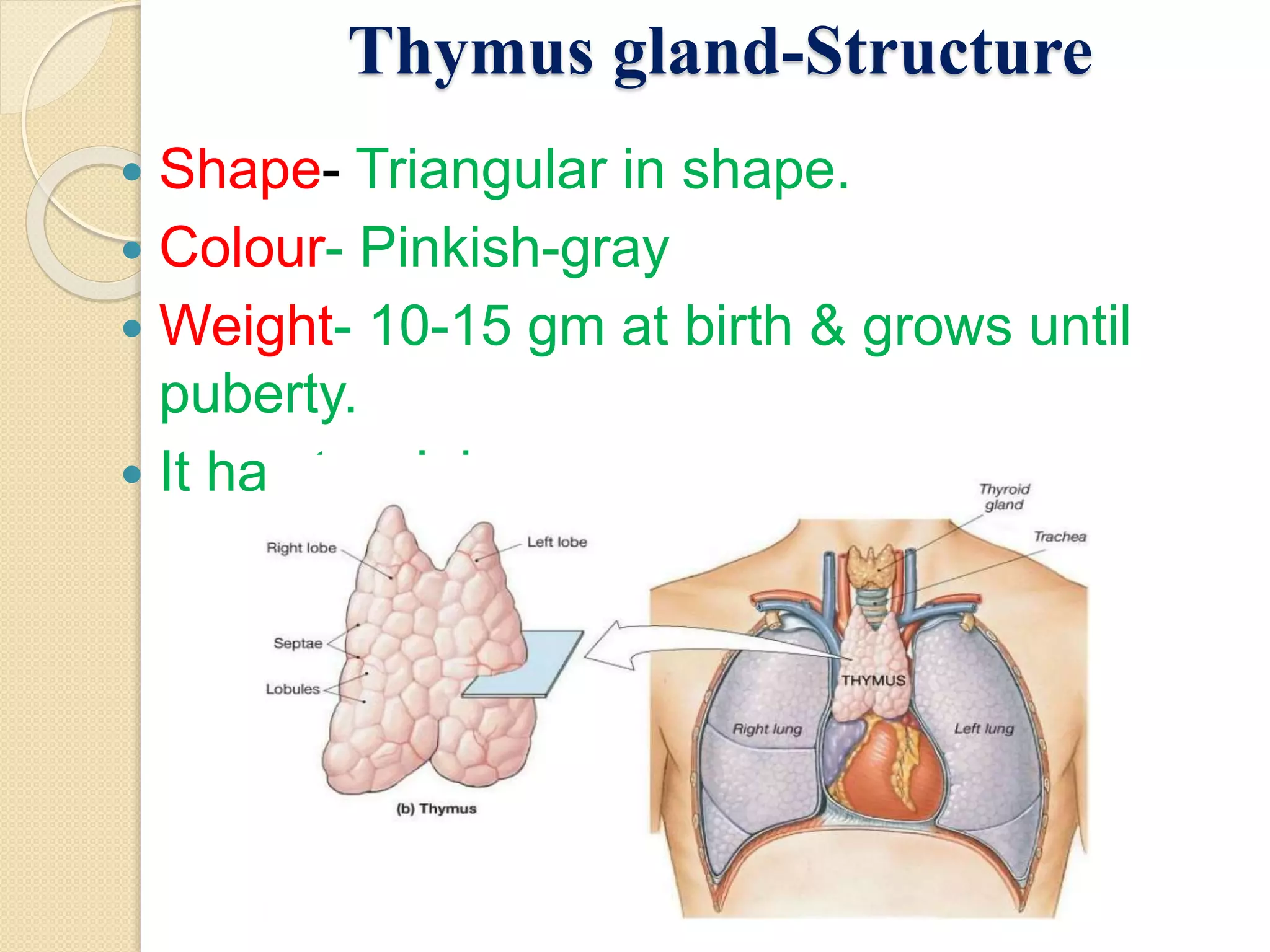
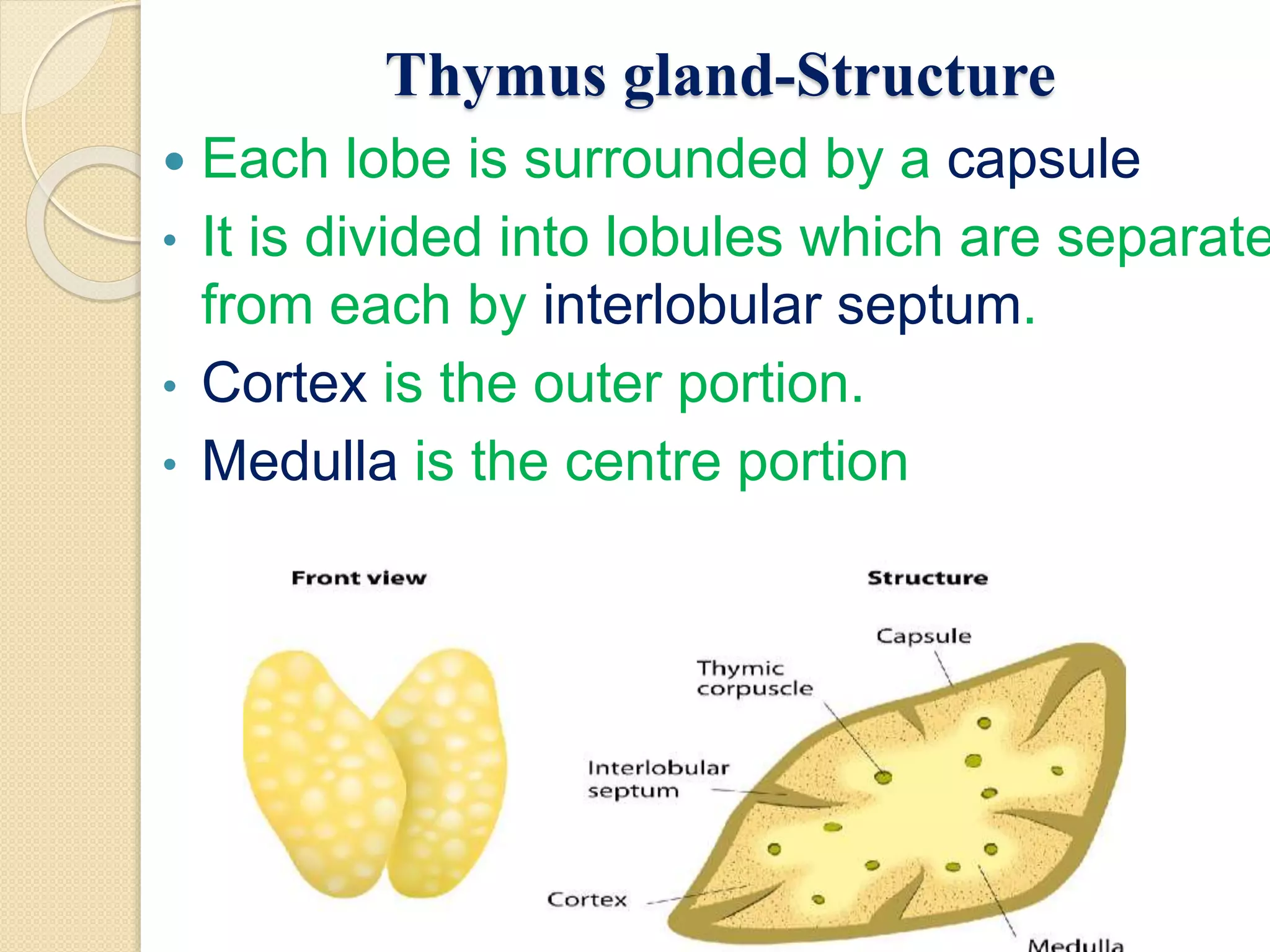
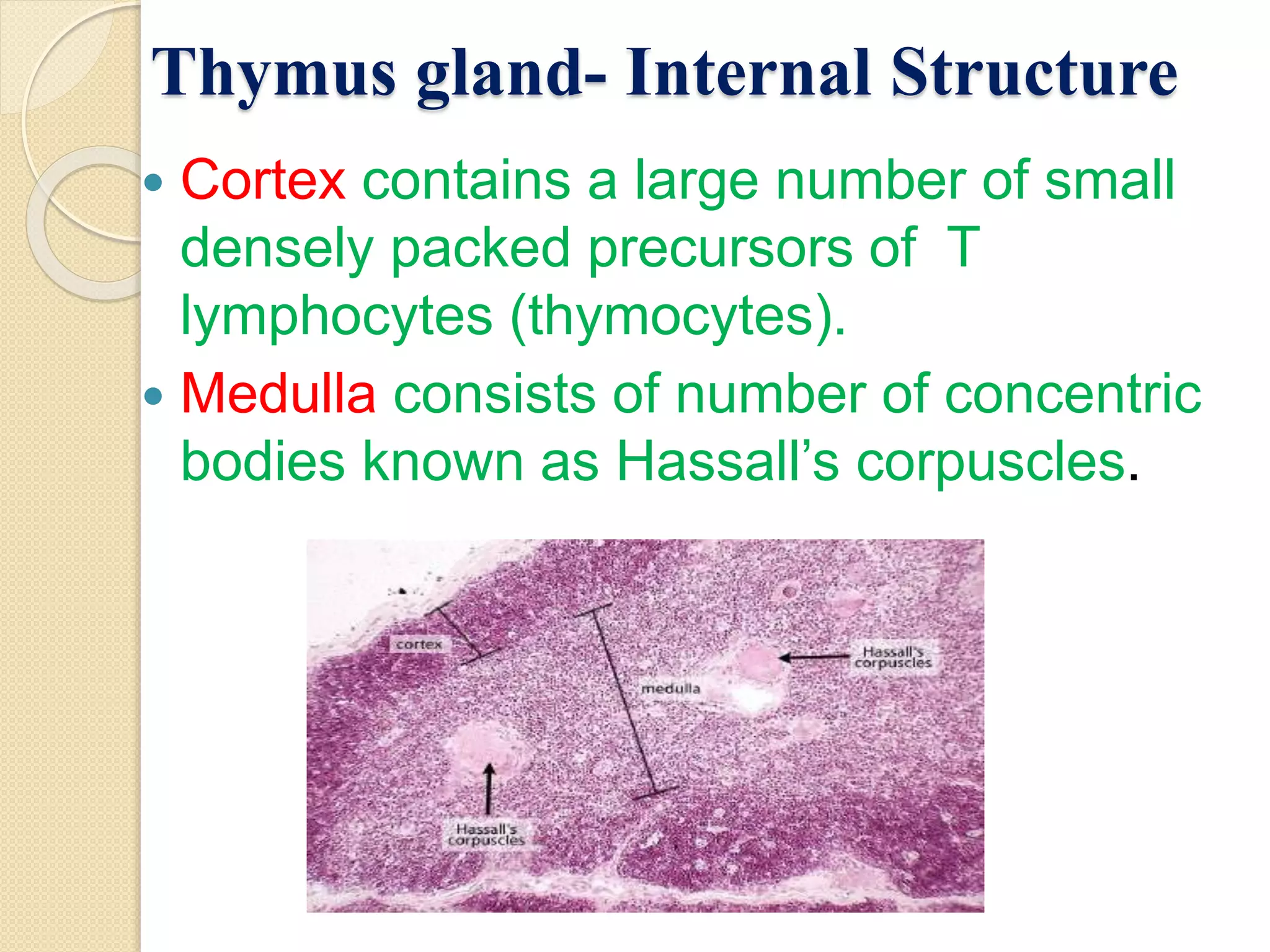

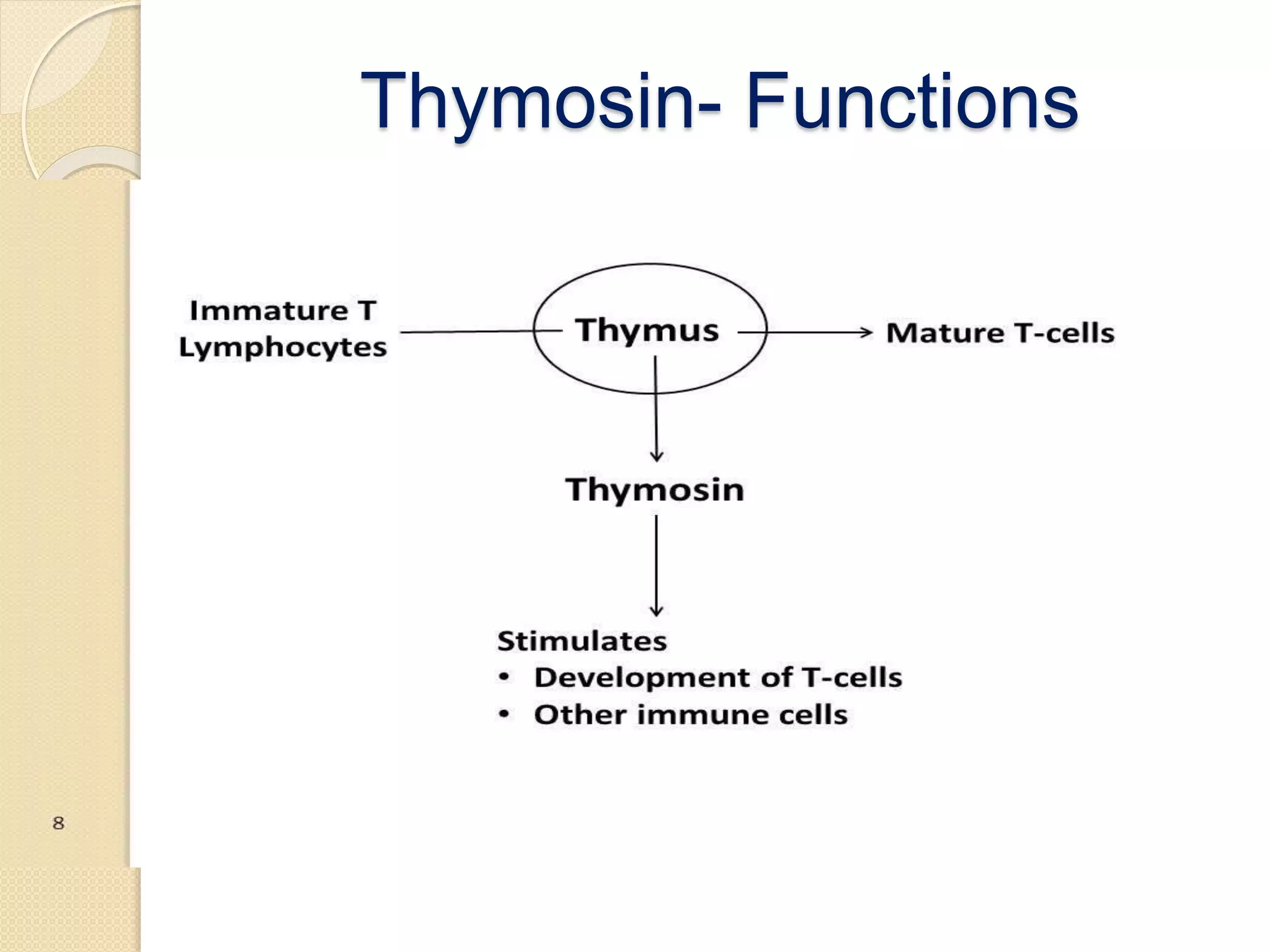
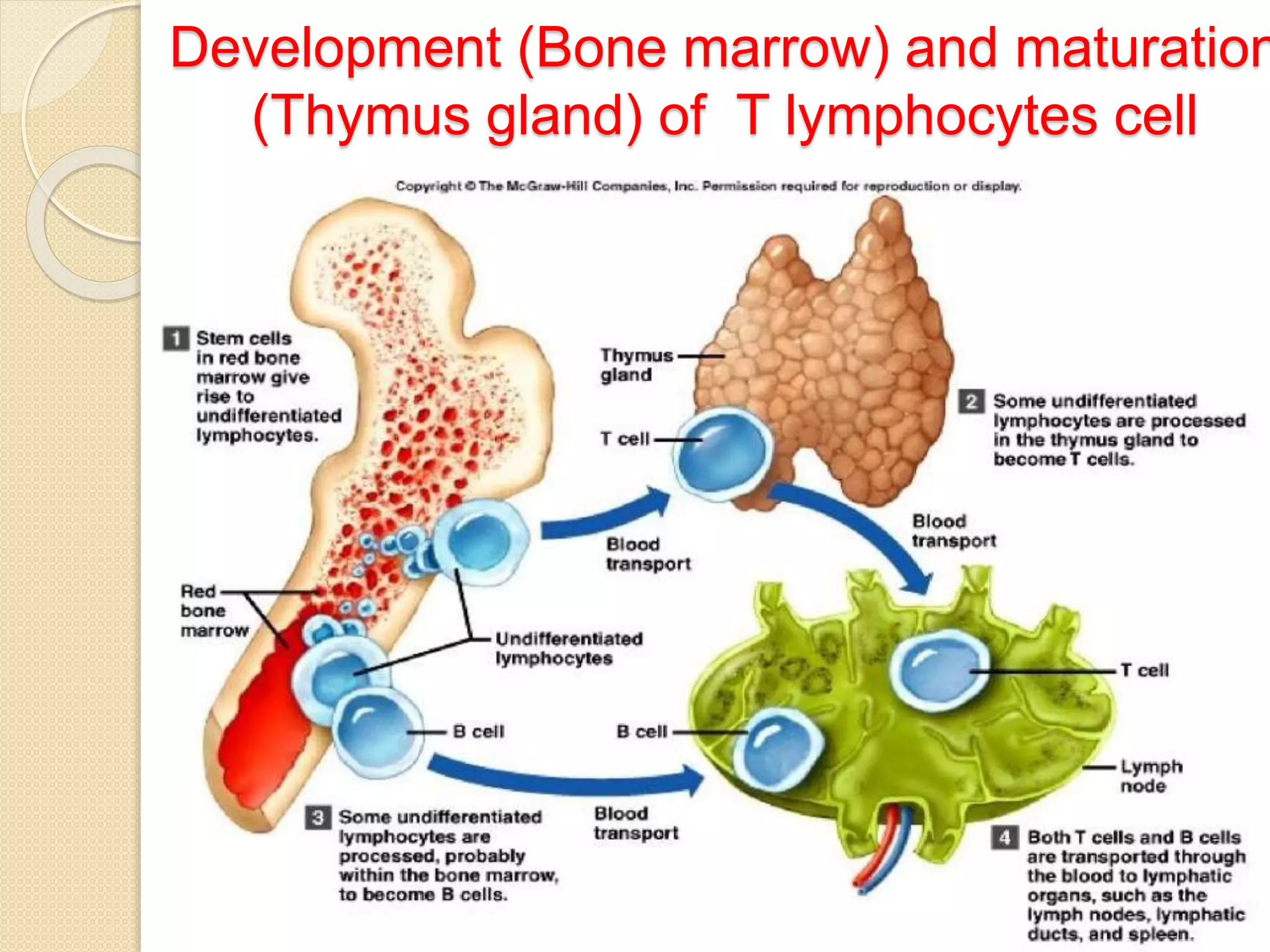




The document summarizes key information about the thymus gland: 1. The thymus gland is located in the upper front of the chest behind the sternum and between the lungs. 2. It has a triangular shape and pinkish-gray color, weighing 10-15 grams at birth and growing until puberty. 3. Internally, it is divided into lobules surrounded by septa, with an outer cortex containing thymocytes and an inner medulla containing Hassall's corpuscles.











