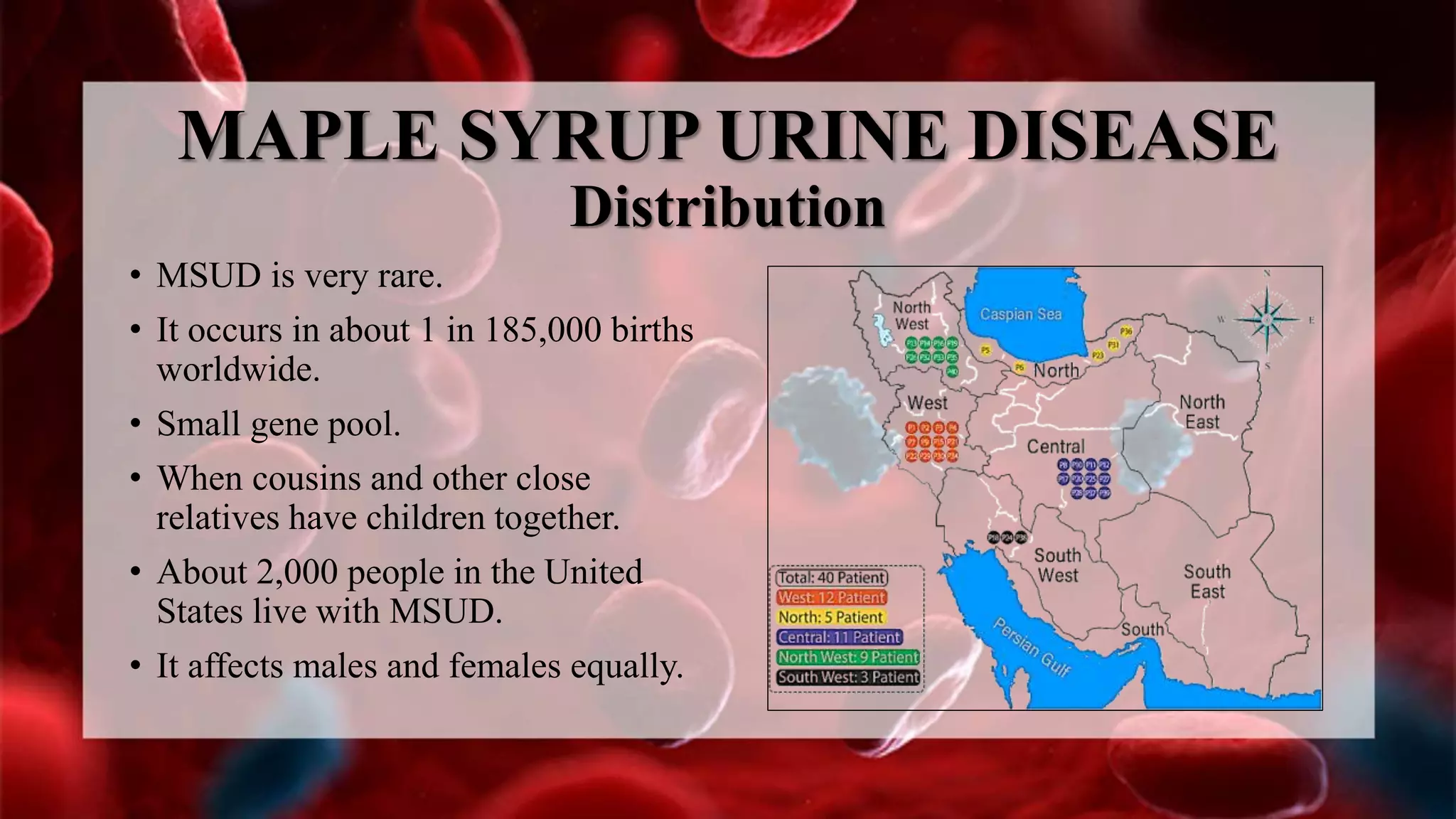
Maple syrup urine disease (MSUD) is a rare genetic metabolic disorder caused by a deficiency of the enzyme branched chain alpha ketoacid dehydrogenase, which prevents the body from properly breaking down three amino acids found in protein. This causes a buildup of these amino acids and their byproducts in the body. Symptoms can range from a characteristic maple syrup smell in urine to poor feeding, vomiting, and weight loss. Treatment involves a restricted diet low in these amino acids and use of a special metabolic formula. Management aims to keep amino acid levels from becoming too high or too low to prevent health complications.