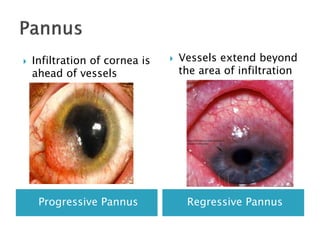
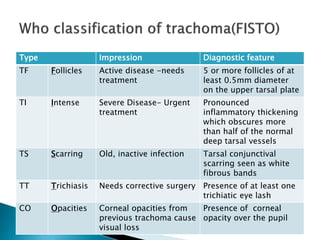
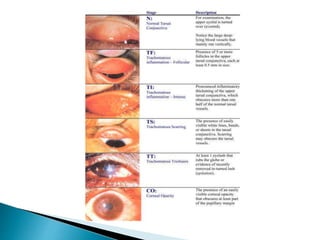
Trachoma is a chronic eye infection caused by Chlamydia trachomatis that often leads to blindness. It spreads easily in dry, dusty areas with poor sanitation and is the world's leading cause of infectious blindness. The infection causes eyelid changes and scarring that can result in trichiasis, where eyelashes turn inward and scratch the cornea. Treatment involves antibiotics and improving hygiene and sanitation to prevent spread. The WHO's SAFE strategy aims to eliminate trachoma blindness worldwide by 2020 through surgery, antibiotics, facial cleanliness, and environmental improvement.