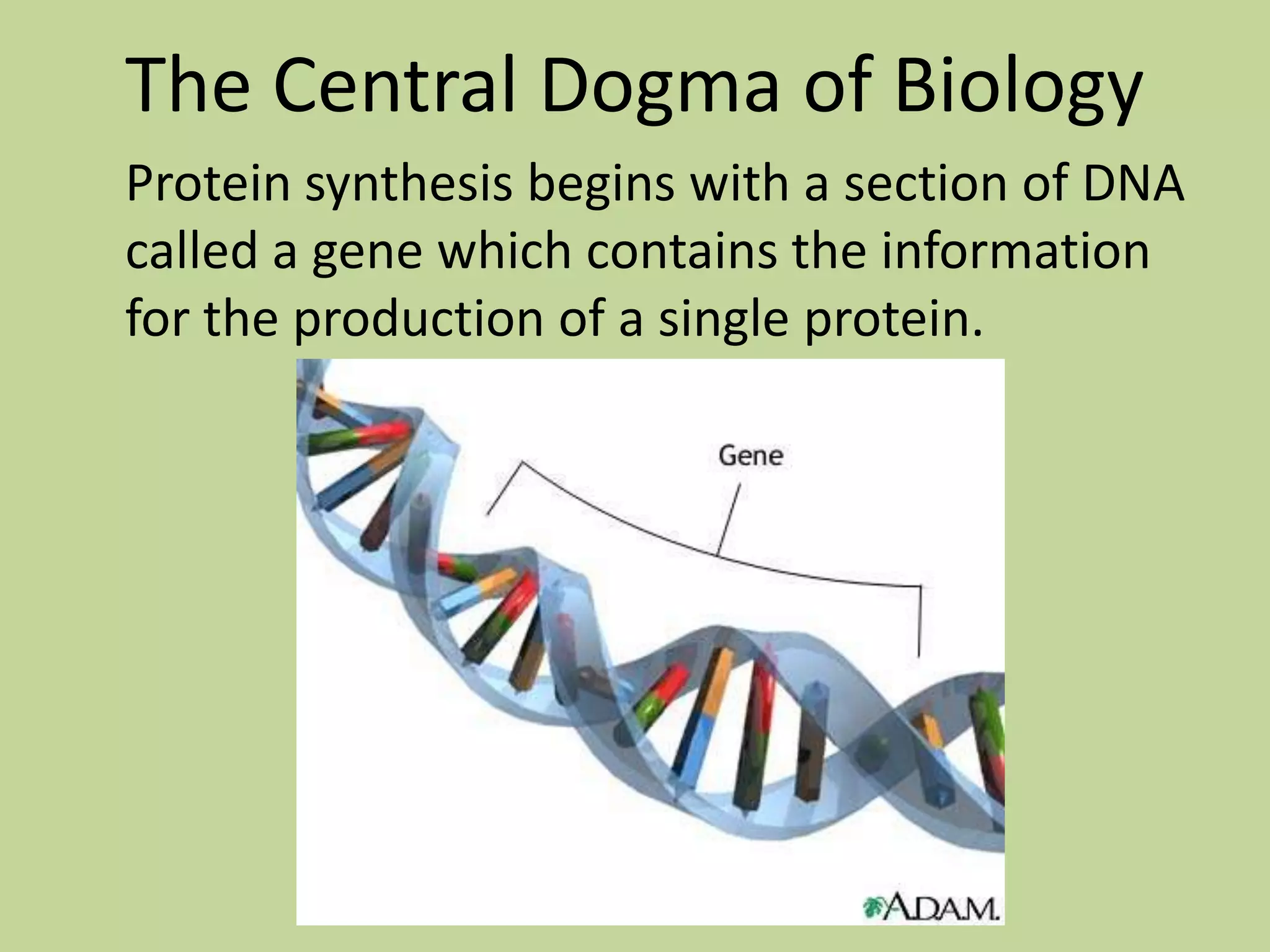
The Central Dogma of Biology describes the process of protein synthesis from DNA to RNA to protein. DNA is transcribed into messenger RNA (mRNA) in the cell nucleus. The mRNA then exits the nucleus and the process of translation occurs in the cytoplasm. During translation, ribosomes use the mRNA to assemble amino acids into a protein chain based on the mRNA codon sequence. Transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules match their anticodons to the mRNA codons and add the corresponding amino acids to the growing protein chain. Eventually a whole protein is produced based on the DNA code provided in the gene.