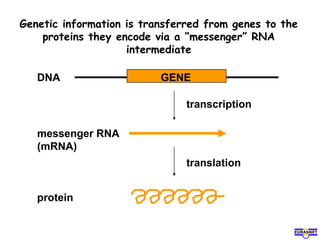
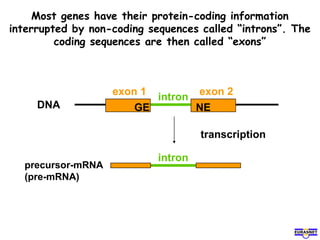
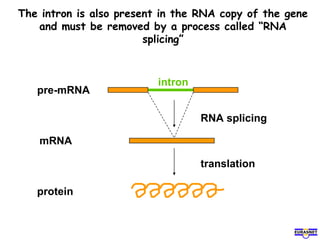
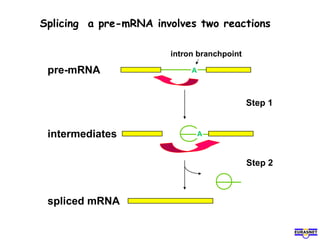
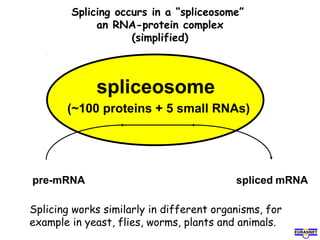
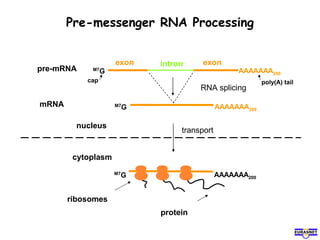
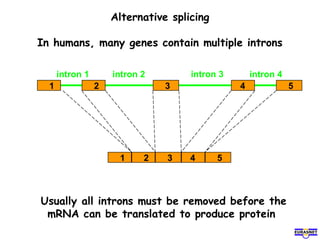
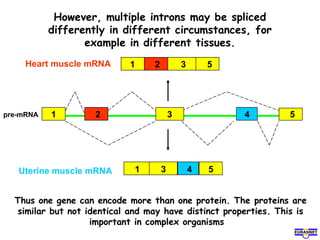
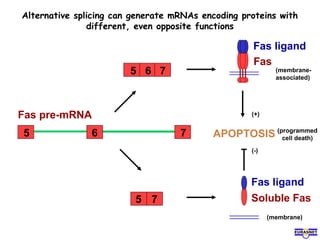
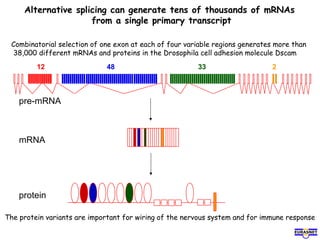
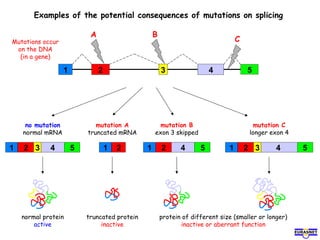
RNA splicing is the process by which introns, or non-coding sequences, are removed from pre-messenger RNA (pre-mRNA) to produce mature mRNA that can be translated into protein. Most genes contain introns that are removed by a spliceosome, a complex of RNA and proteins, leaving just the coding exons to form mRNA. Alternative splicing allows one gene to encode multiple proteins by selecting different combinations of exons. Errors in splicing can cause diseases if they result in truncated or abnormal proteins.