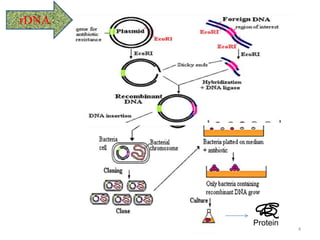
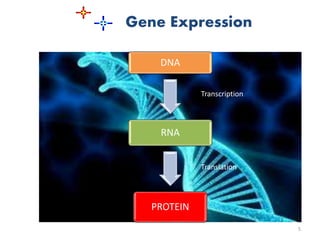
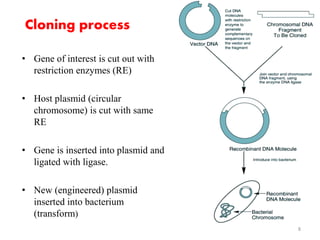
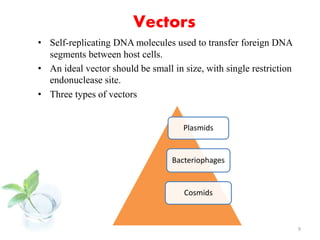
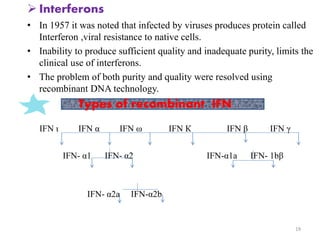
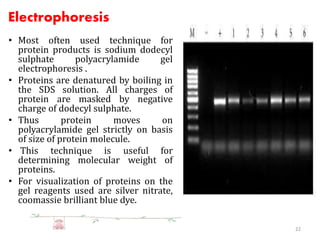
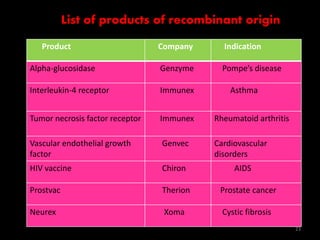
The document discusses recombinant proteins, including their production through recombinant DNA technology. It describes how genes can be isolated and inserted into expression vectors, which are then transferred into host cells to produce the recombinant protein. Various methods are covered, including molecular cloning and polymerase chain reaction. Examples of recombinant proteins discussed include insulin, interferons, hormones, and monoclonal antibodies that are used for medical applications.