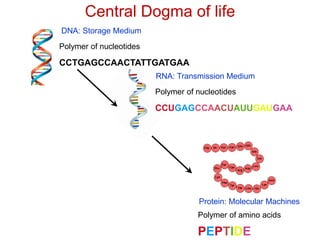
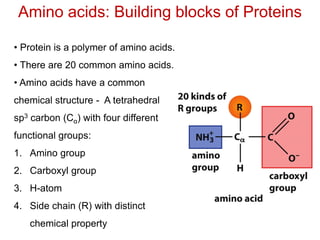
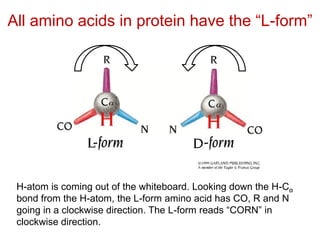
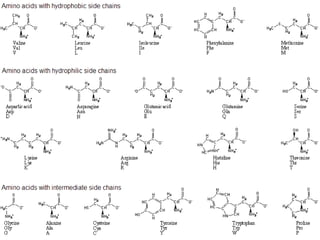
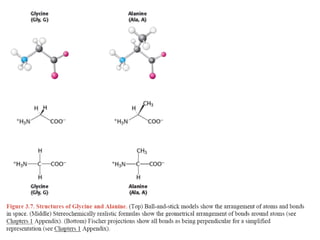
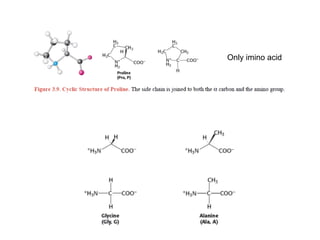
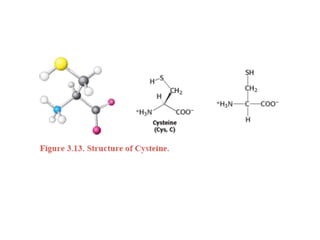
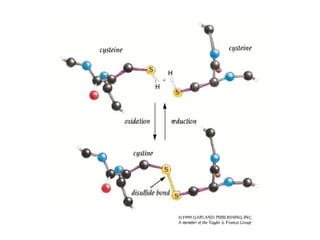
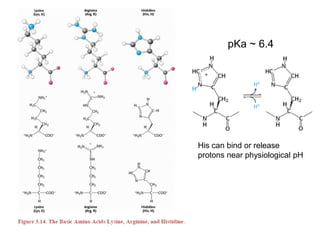
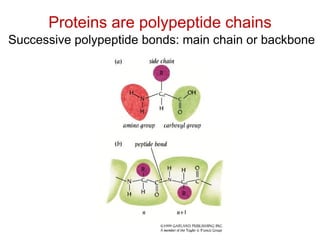
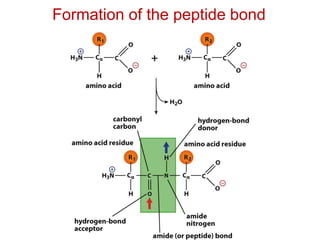
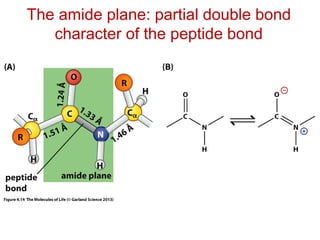
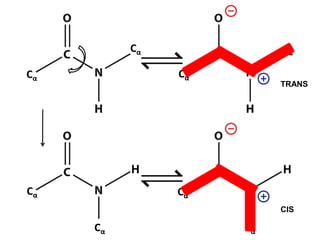
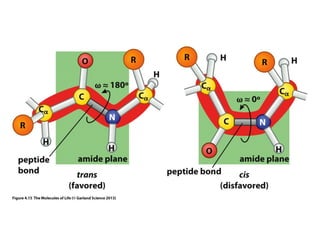
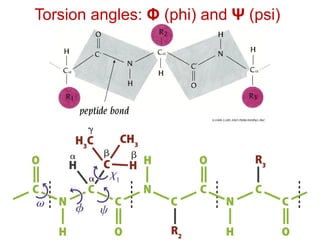
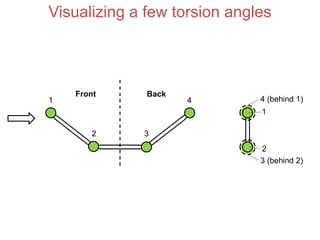
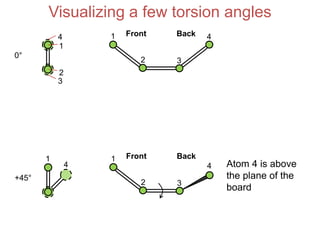
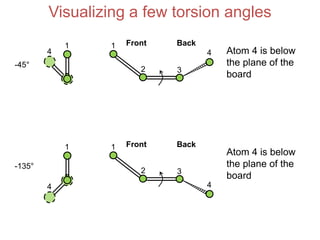
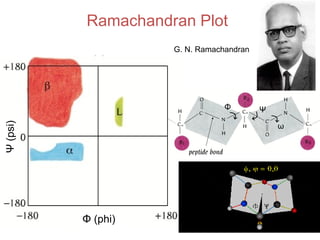
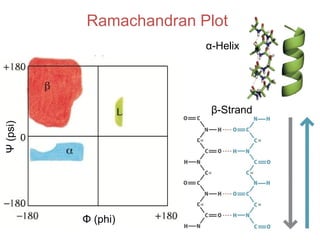
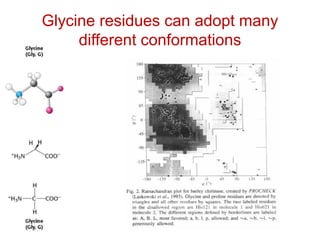
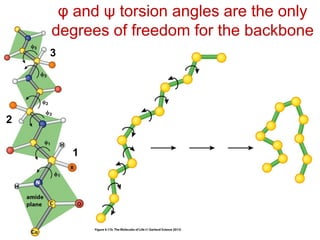
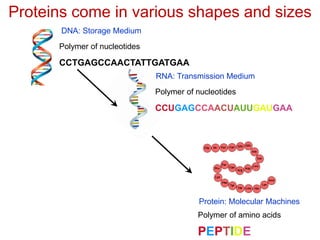
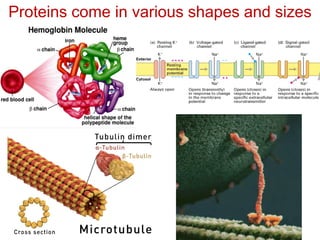
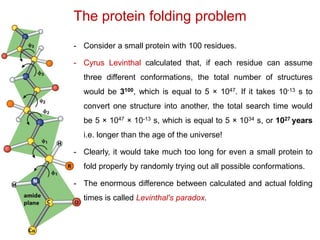
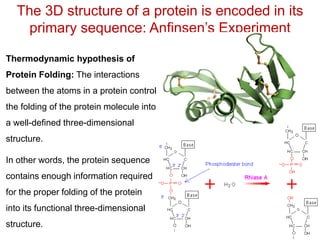
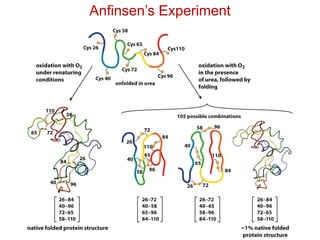
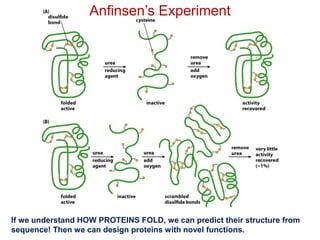
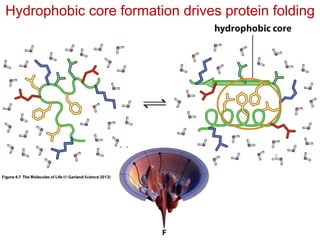
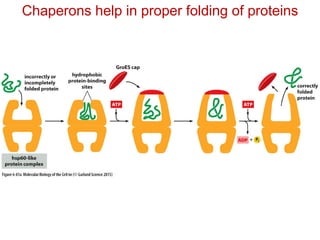
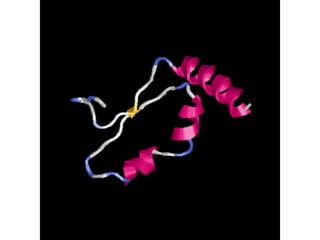
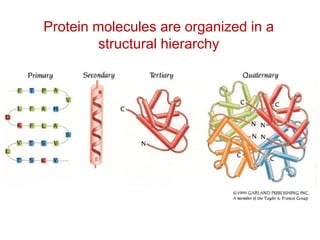
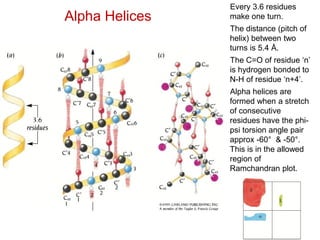
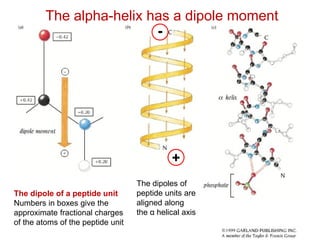
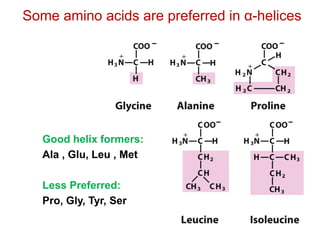
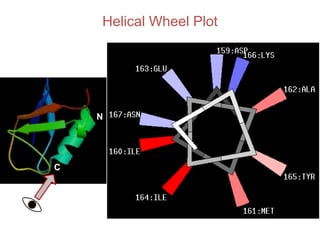
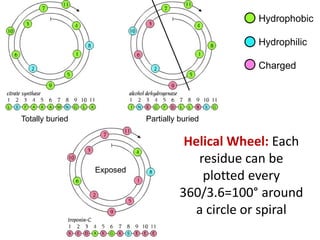
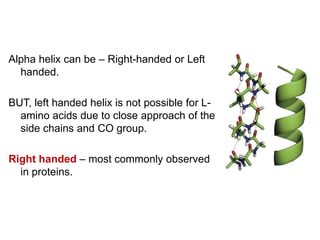
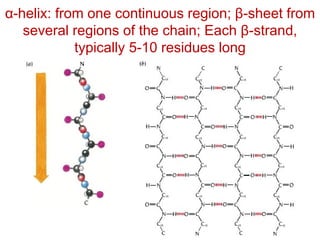
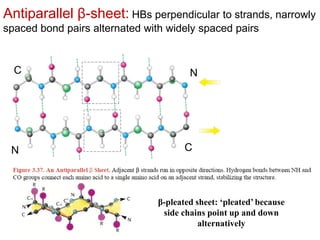
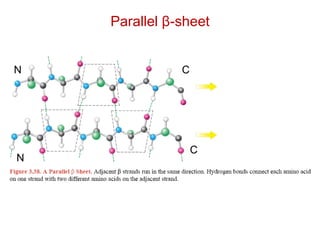
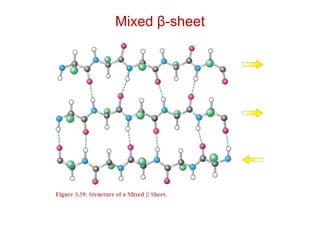
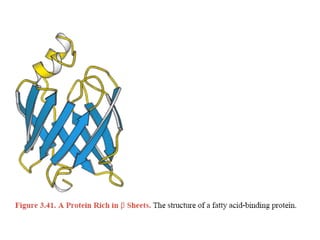
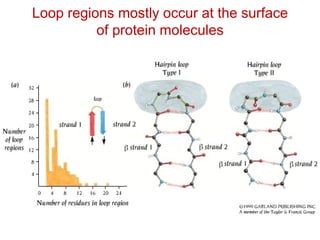
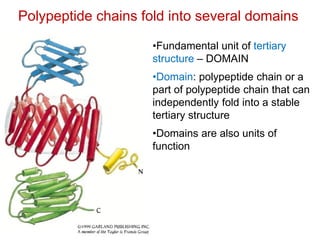
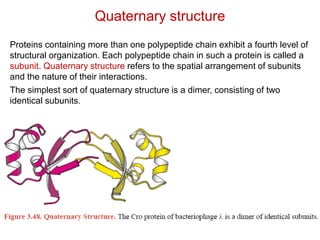
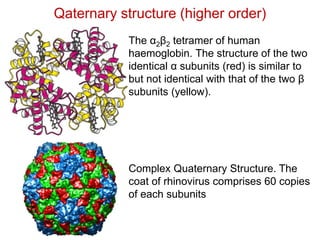
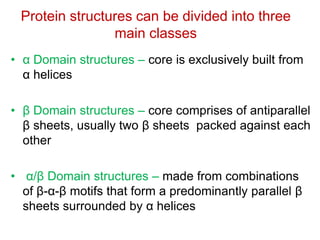
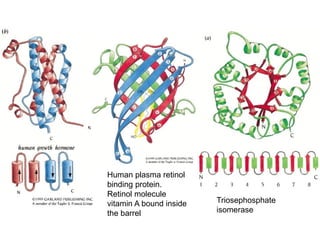
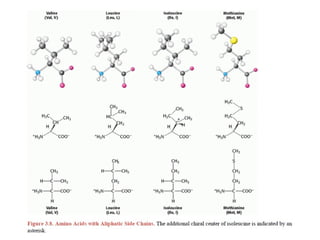
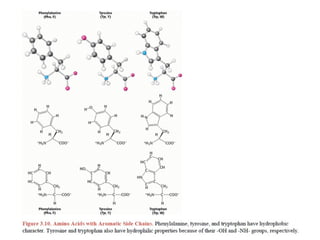
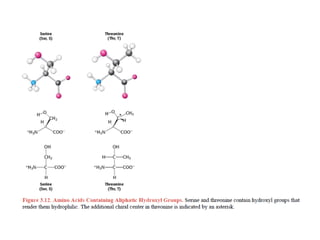
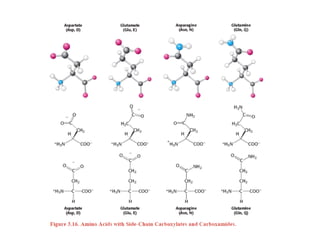
This document provides an overview of protein structure and function. It discusses the central dogma of life, the 20 common amino acids that make up proteins, and how they fold into defined structures like alpha helices and beta sheets. Key concepts covered include the hydrophobic effect that drives protein folding, domains as fundamental units of structure, and the three main classes of protein structures - alpha, beta, and alpha/beta domains. Real-world protein examples are also briefly mentioned.