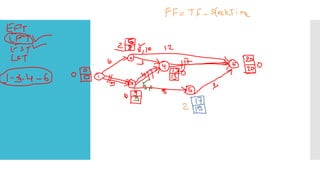
The document discusses the Critical Path Method (CPM), a project management technique used for scheduling activities based on mathematical calculations. Developed in 1959, CPM identifies the longest sequence of dependent activities to determine the minimum project duration. The document also outlines the steps for calculating early and late start/finish times, as well as concepts such as float time and various terminologies used in CPM.