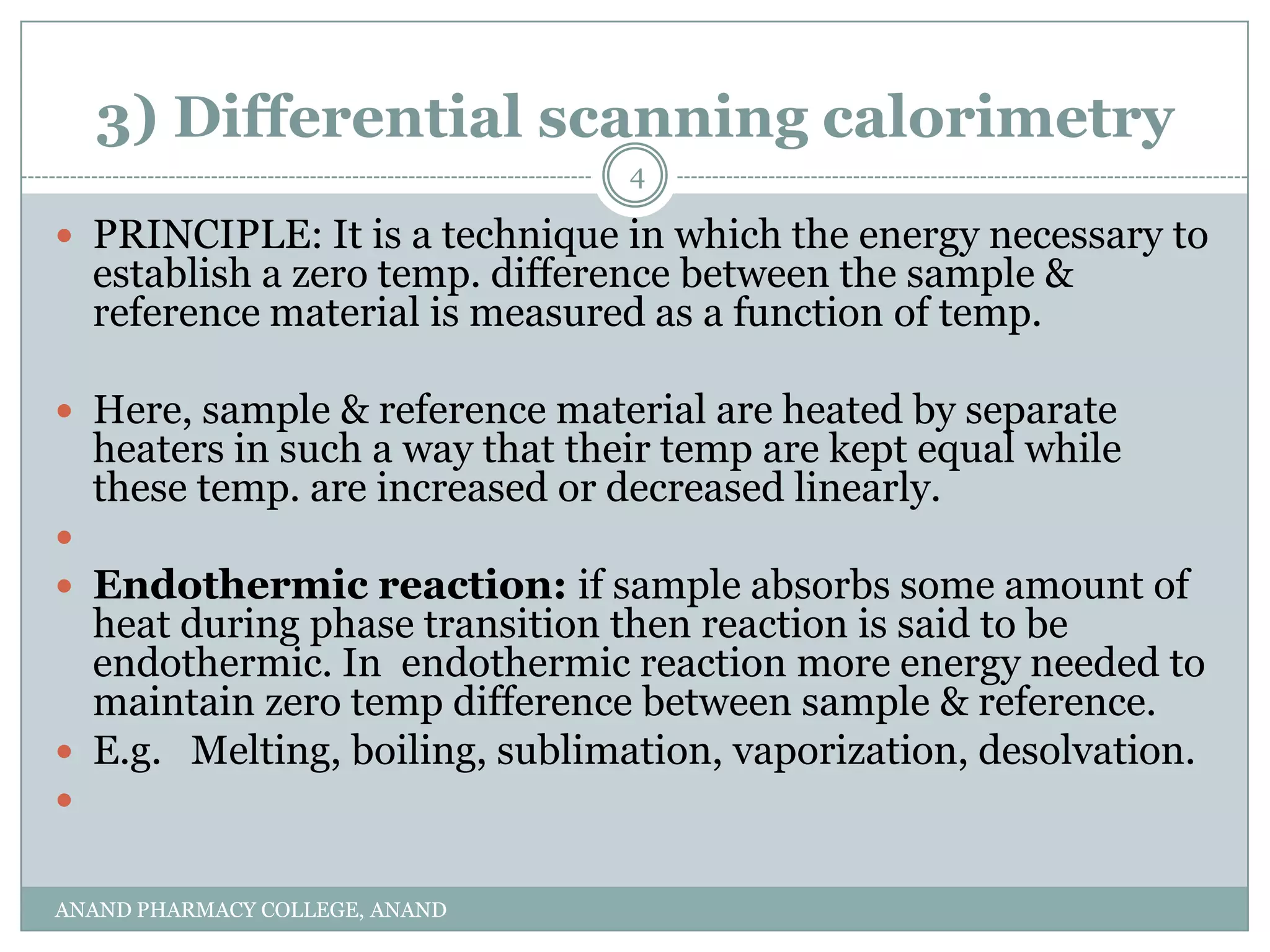
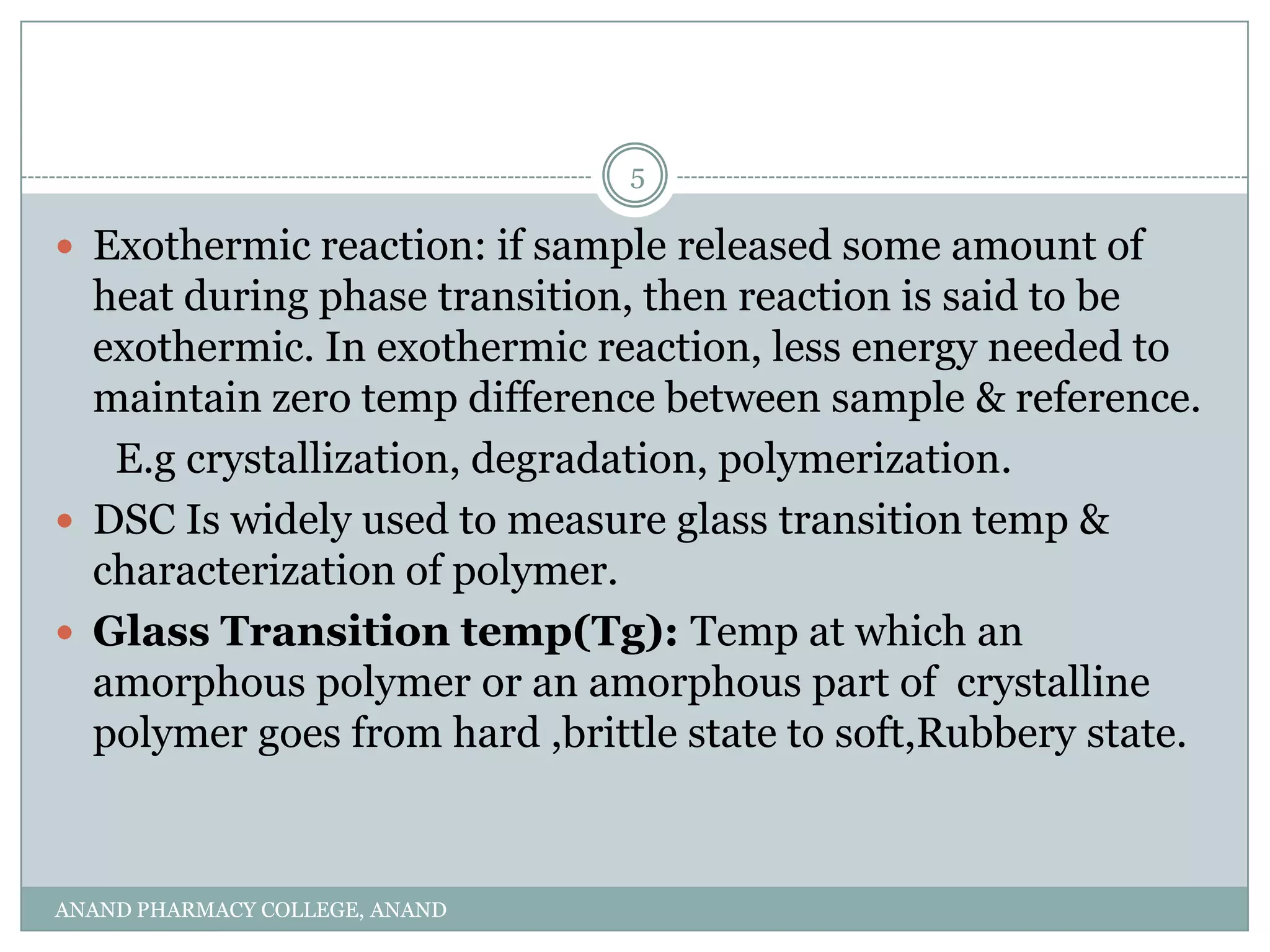
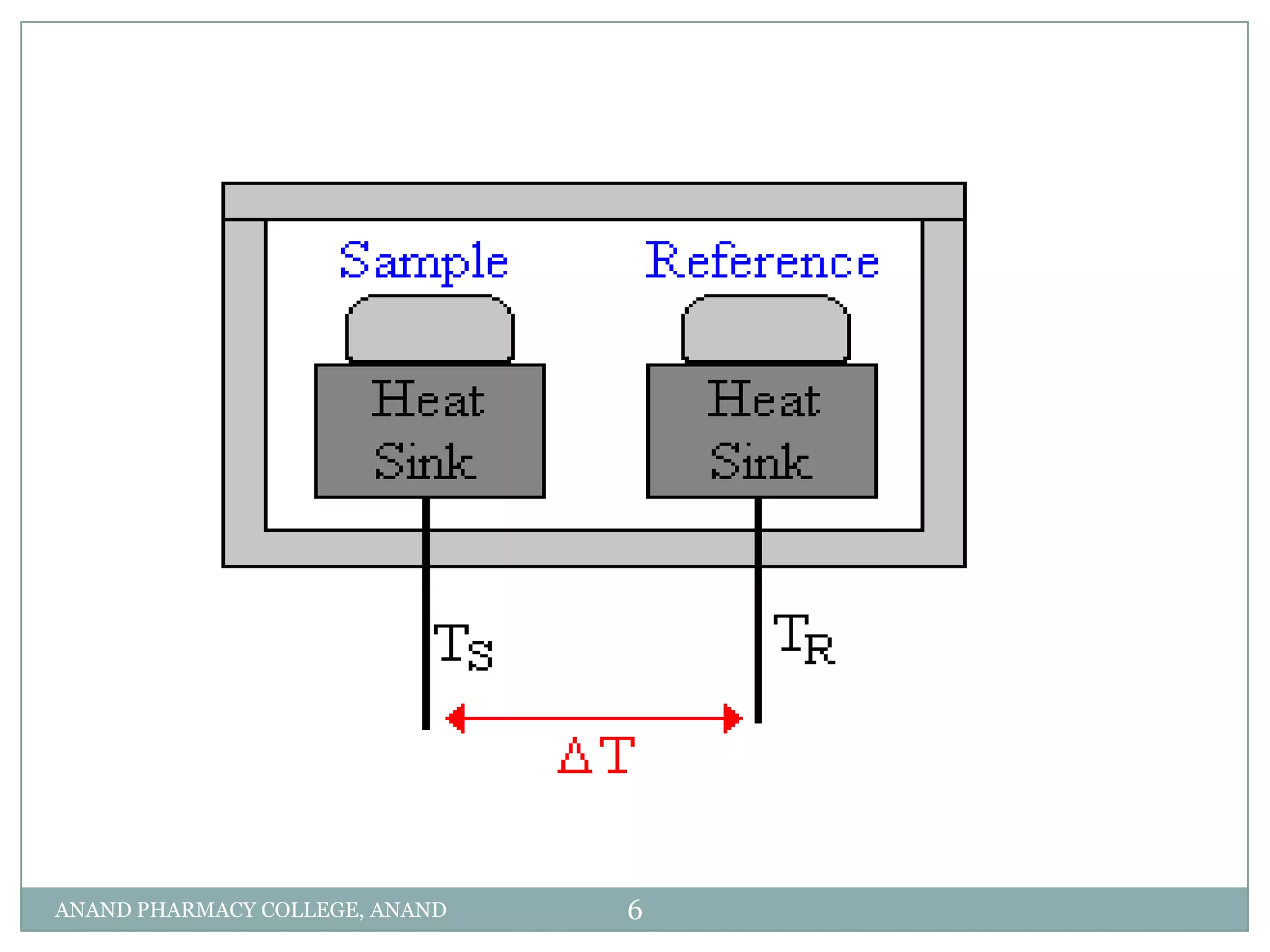
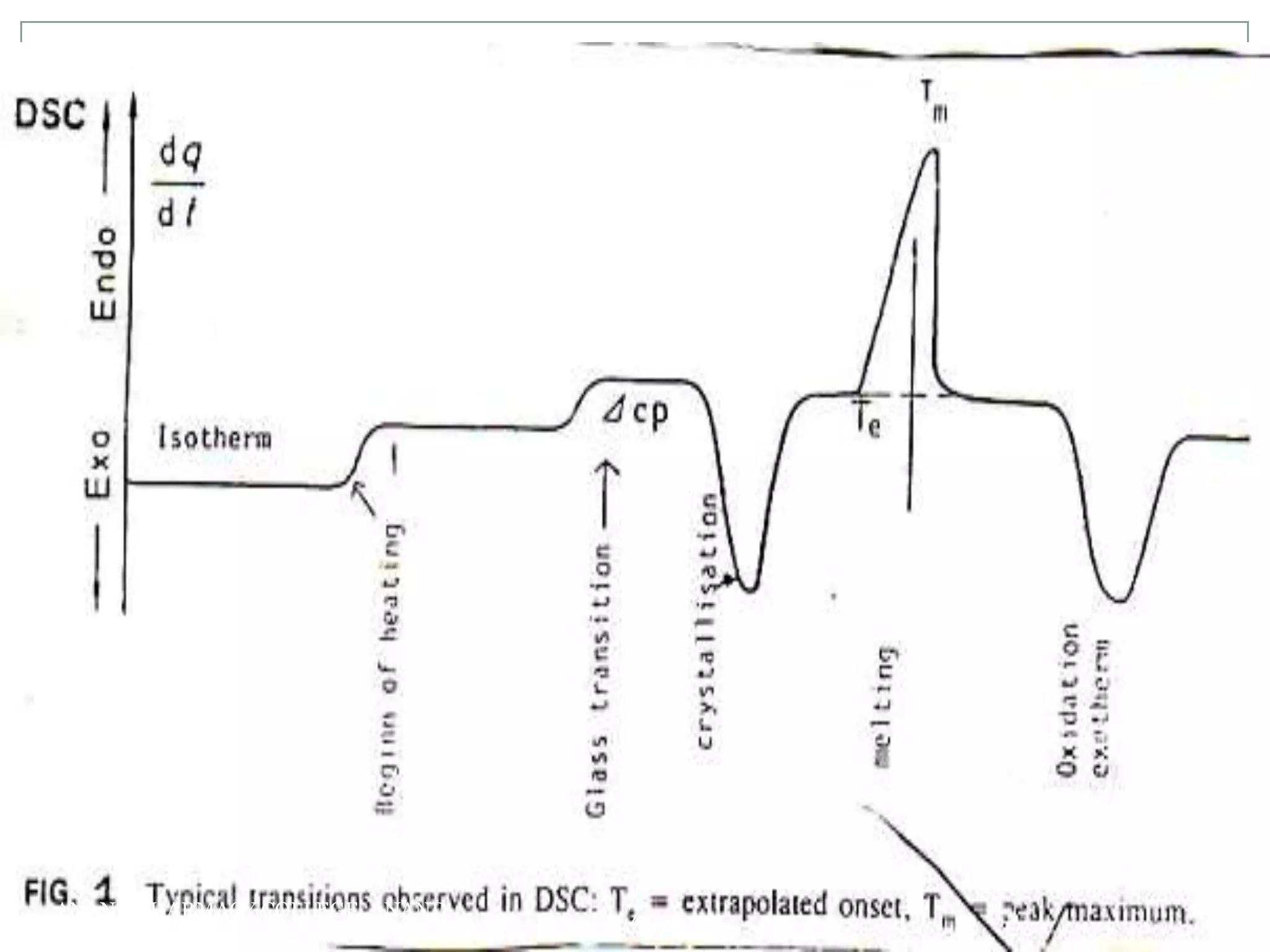
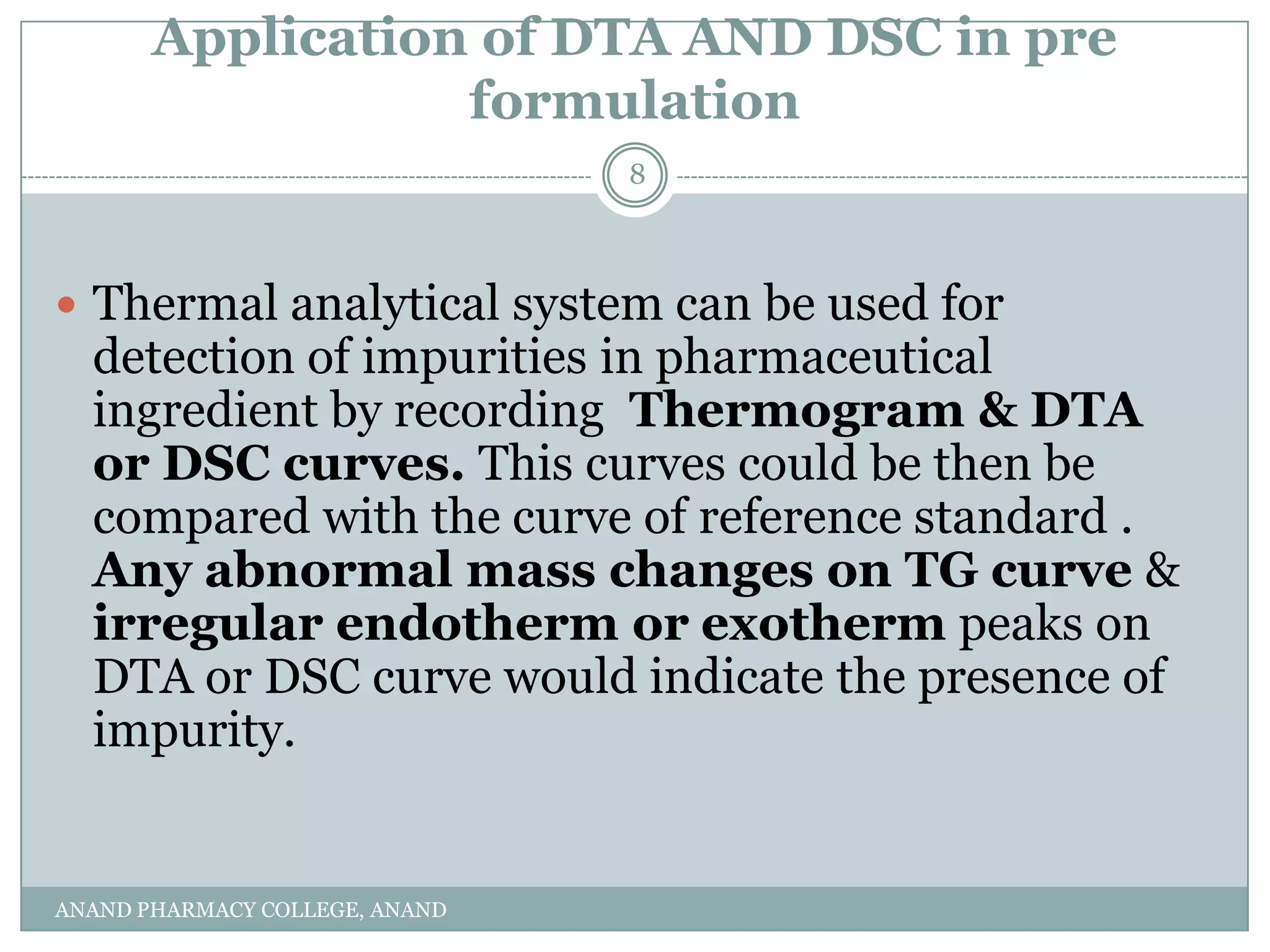
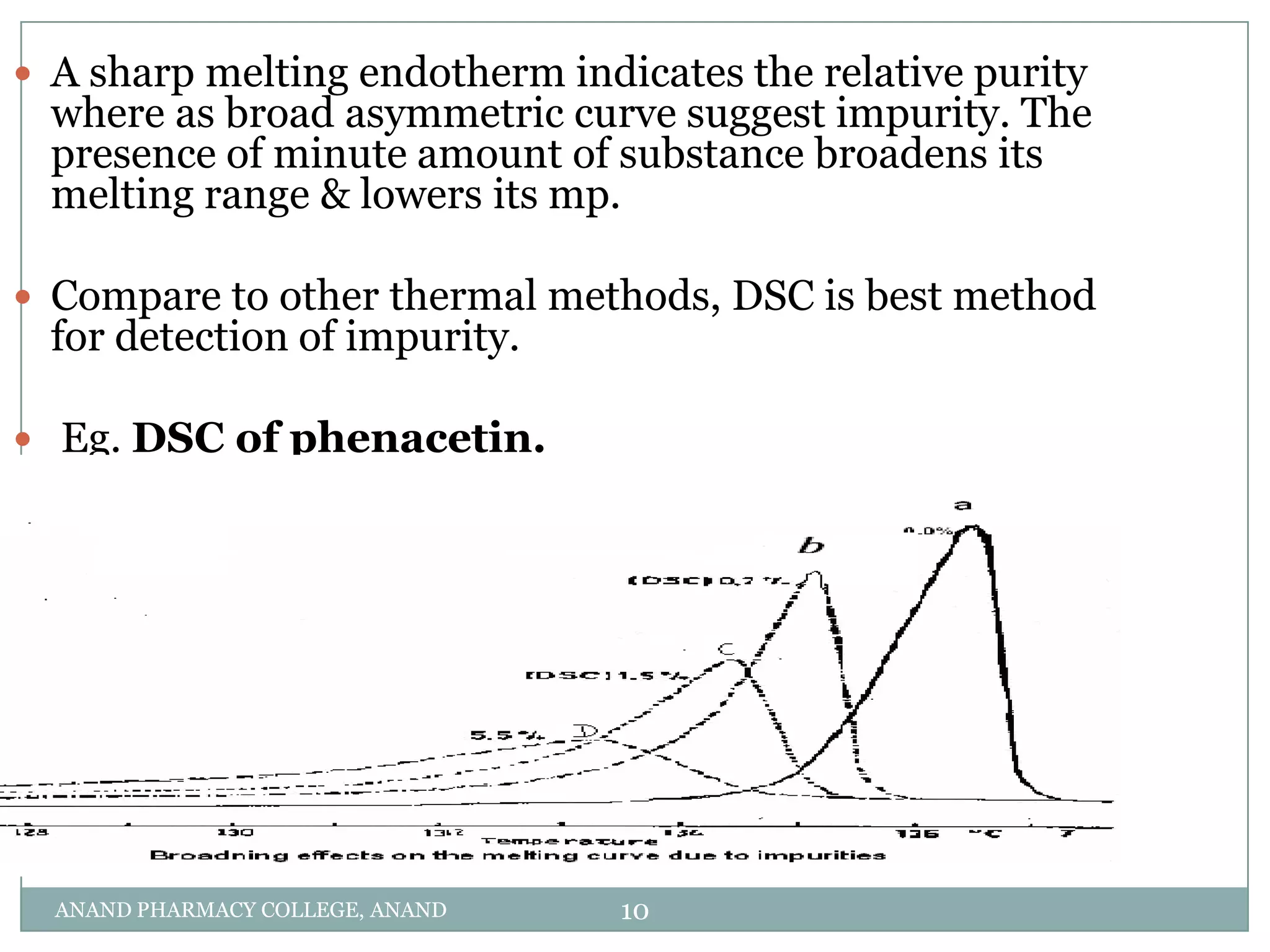
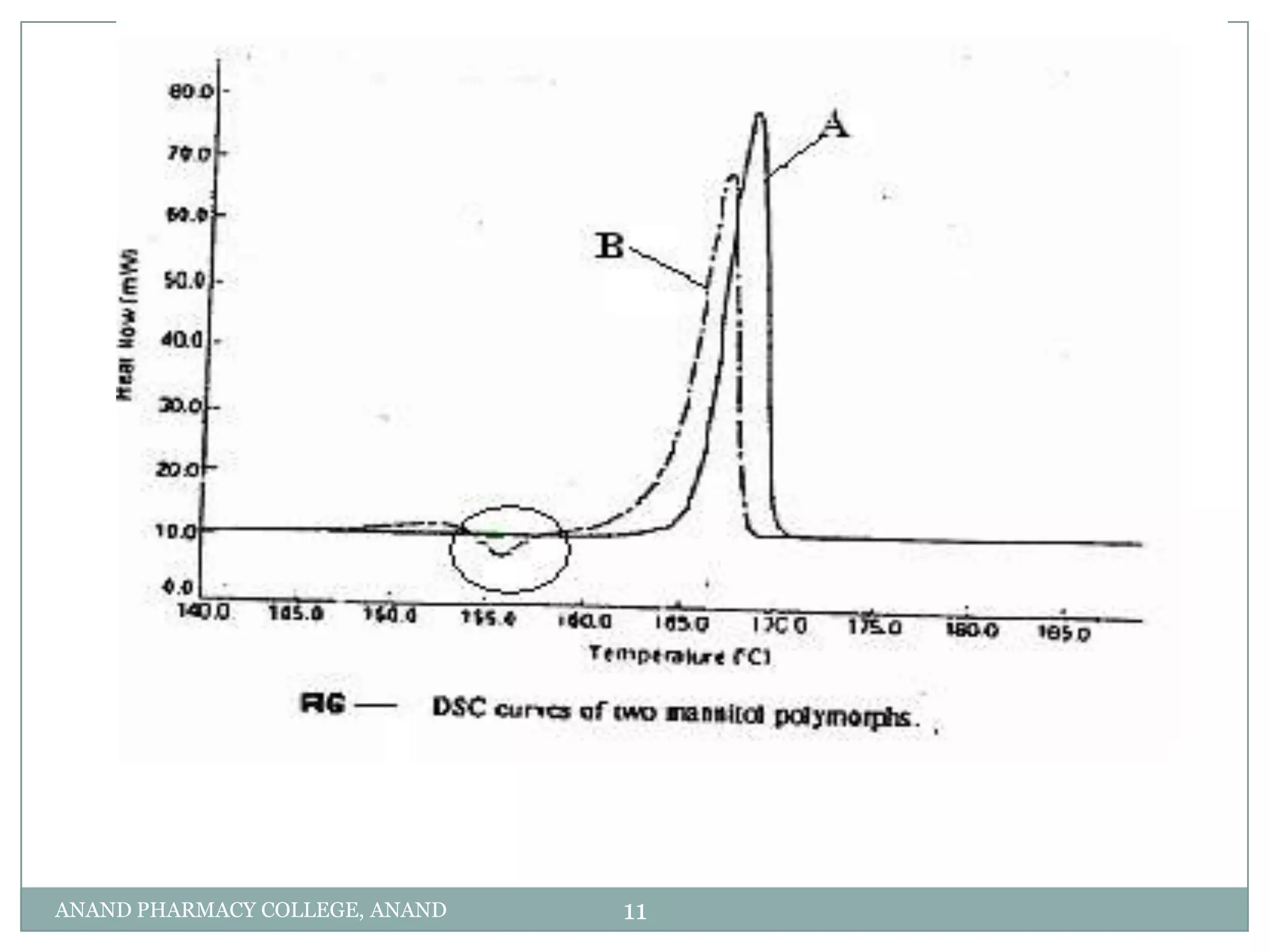
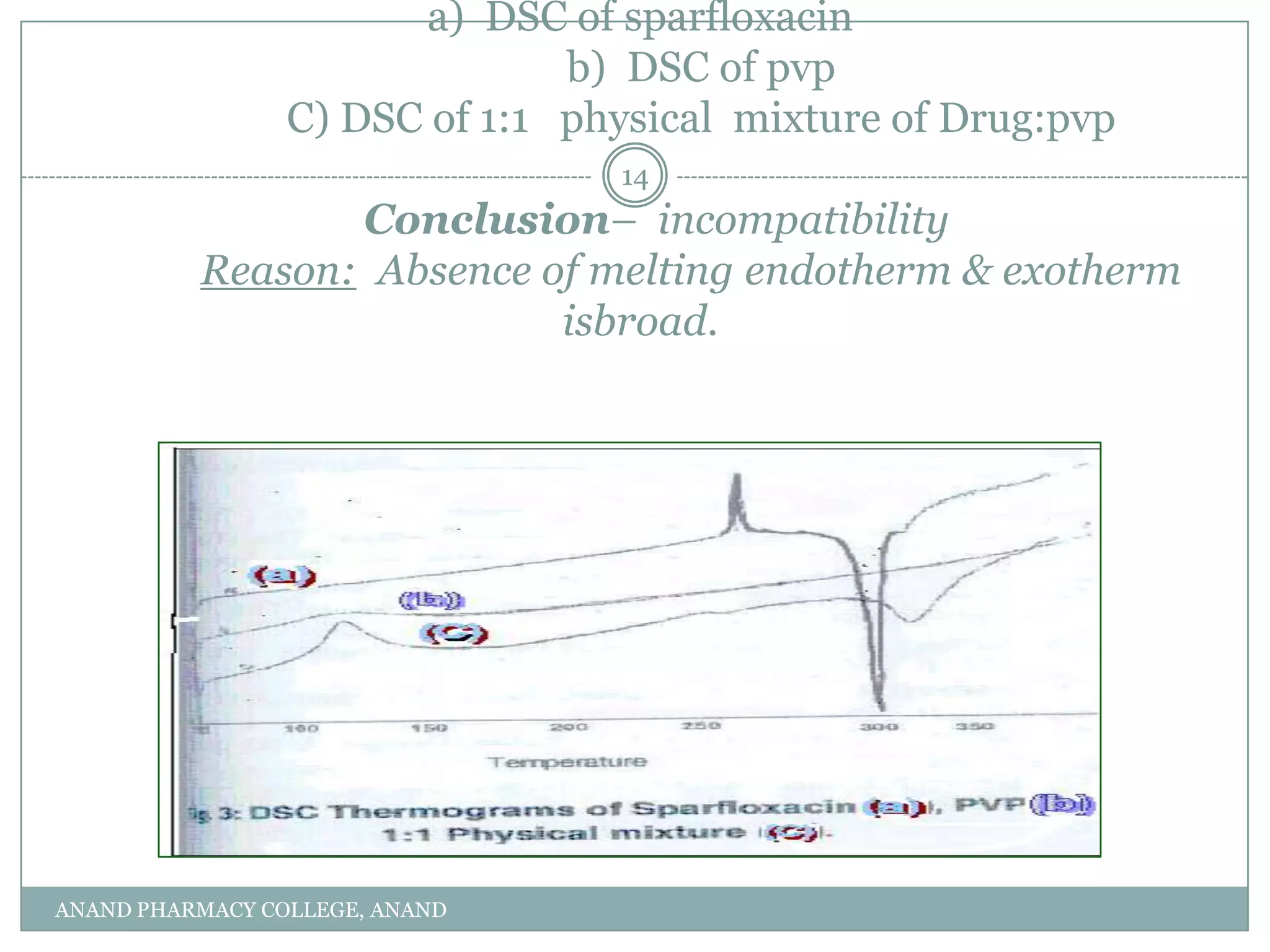
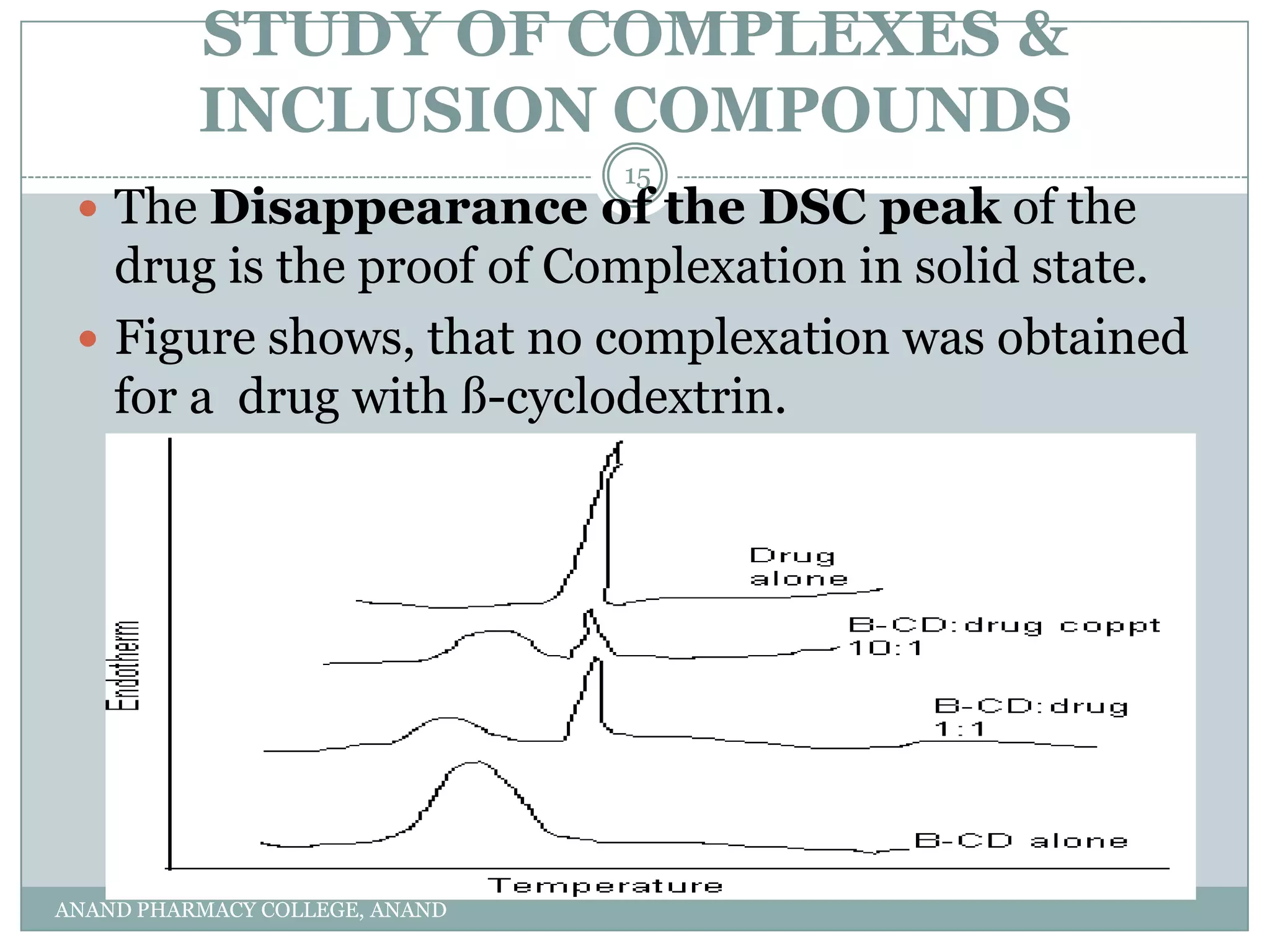
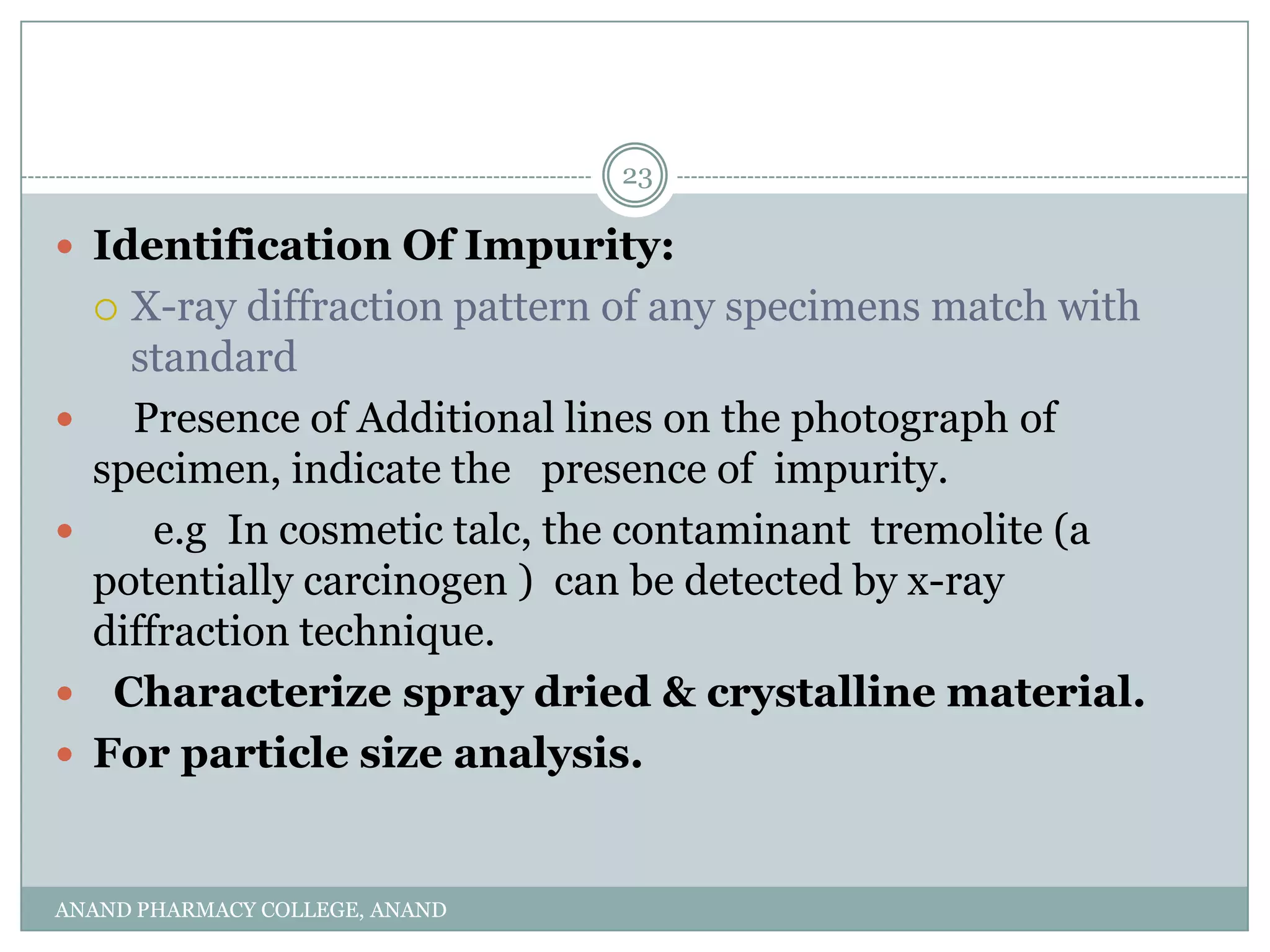
The document discusses various thermal analysis techniques used in preformulation including DSC, DTA, FTIR, and X-ray diffraction. It describes the principles of each technique and provides examples of their applications in determining impurities, polymorphism, hydrates/solvates, crystallinity, drug-excipient compatibility, and more. These techniques are valuable tools for characterization during preformulation studies.






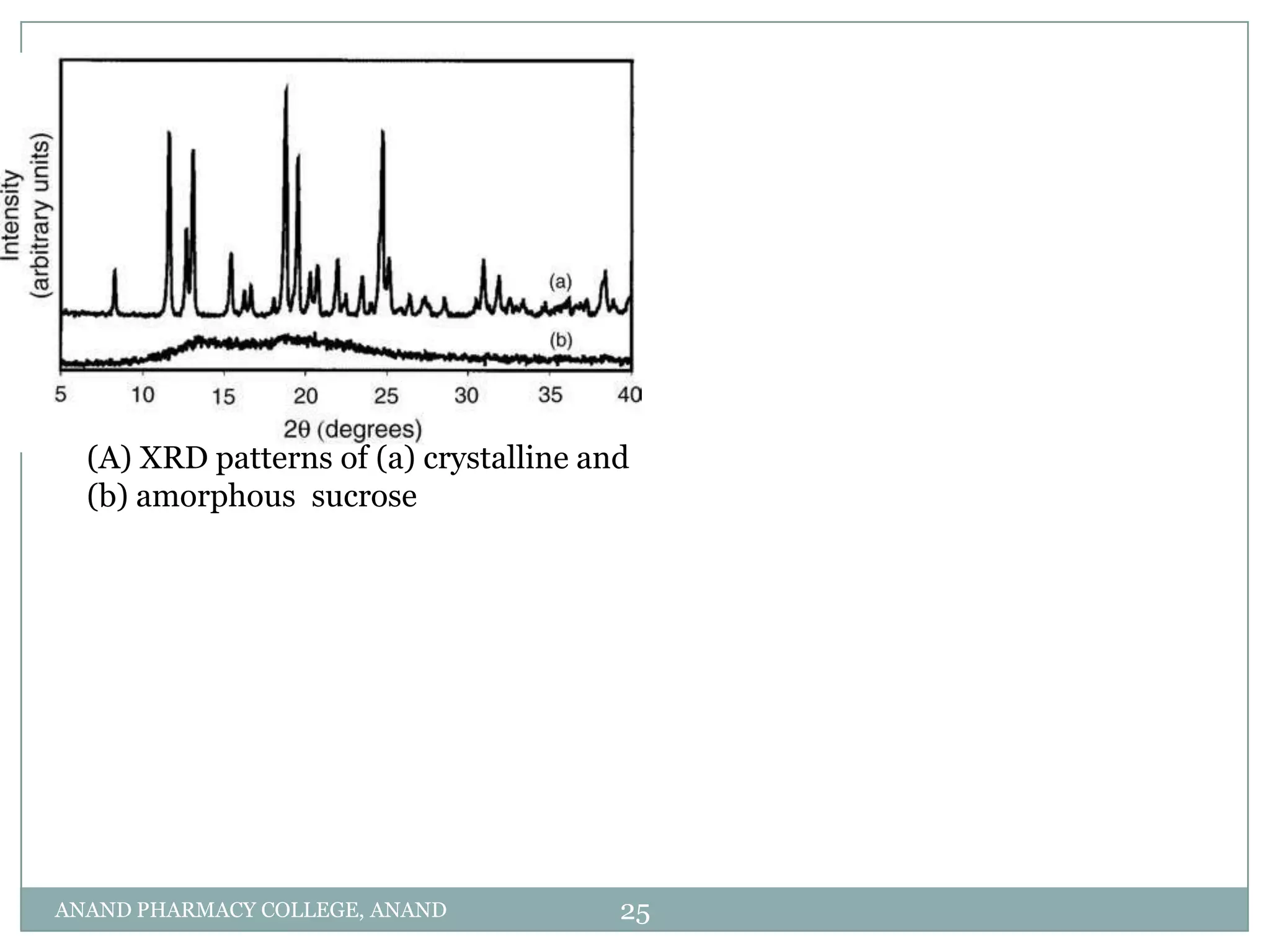

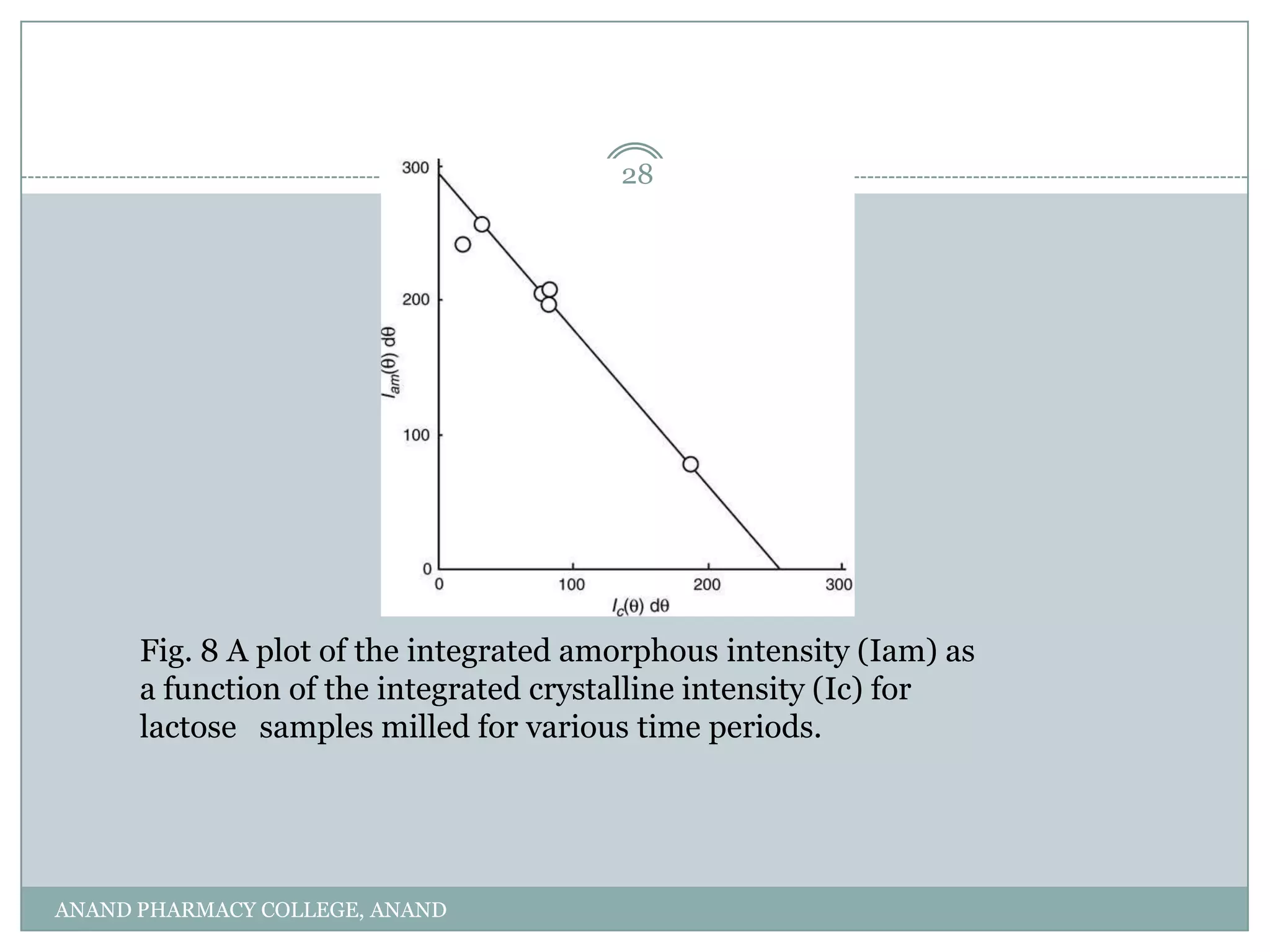
![27
X=Ic +100
Ic + qIa/p
where p and q are proportionality constants. The
values of Ia and Ic can be determined for samples of
varying degrees of crystallinity. A plot of the measured
values of Ia against those of Ic will result in a straight
line, and the intercepts on the y- and x-axes will provide
the intensity values of the 100% amorphous and
100% crystalline materials, respectively. This method
was used by Nakai et al.[17] to estimate the degree of
crystallinity of lactose that had been milled for various
time periods (Fig. 8). If the value of (q/p) is known, the
degree of crystallinity of an unknown sample can be
calculated from the experimentally determined values
of Ic and Ia.
ANAND PHARMACY COLLEGE, ANAND](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/principleandapplicationofdscdtaftirandx-raydiffraction-120318031324-phpapp02/75/Principle-and-application-of-dsc-dta-ftir-and-x-ray-diffraction-27-2048.jpg)