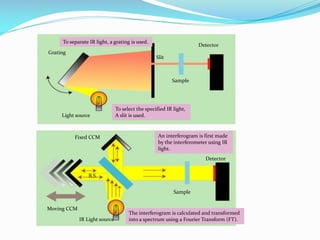
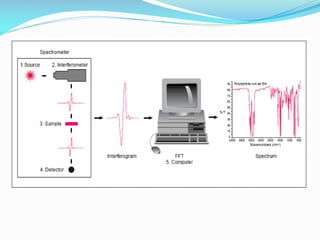
This document discusses infrared spectroscopy and Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy. It begins by defining the infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum and describing how infrared radiation is produced by molecular vibration when the applied frequency matches the natural vibration frequency. It then explains how FTIR works using an interferometer to measure all infrared frequencies simultaneously, producing a faster analysis. Key advantages of FTIR are also summarized such as speed, sensitivity, and requiring only one moving part.