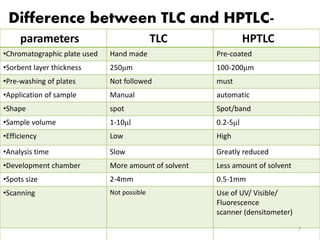
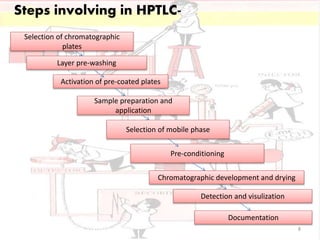
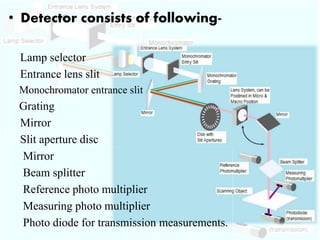
HPTLC is a sophisticated form of TLC that allows for automated, high-efficiency separation and analysis of chemical compounds. It uses plates coated with a thin layer of adsorbent like silica gel, along with solvent systems and detection methods. HPTLC provides better resolution than TLC due to smaller particle size and shorter migration distances. The presentation discusses the principle, instrumentation, steps like sample application and development, and applications of HPTLC in fields like pharmaceuticals, forensics, and environmental analysis.