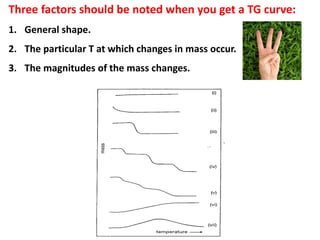
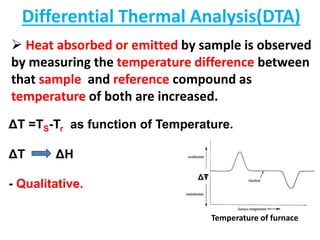
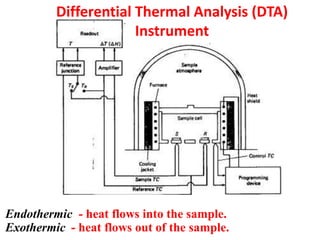
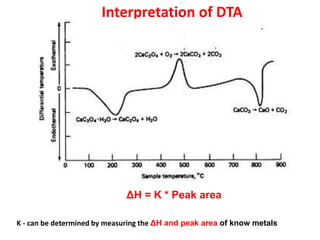
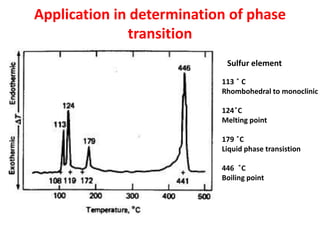
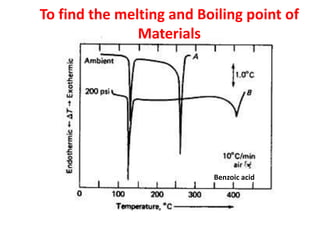
This document discusses different thermal analysis techniques including thermo gravimetric analysis (TGA), differential thermal analysis (DTA), and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). TGA measures mass changes as a function of temperature. DTA measures the temperature difference between a sample and reference as they are heated. DSC directly measures heat flows into or out of a sample during transitions. The techniques are used to study physical and chemical transitions in materials and have applications in fields like polymers, food, pharmaceuticals, and ceramics for analyzing composition, stability, phase transitions, and melting/boiling points.