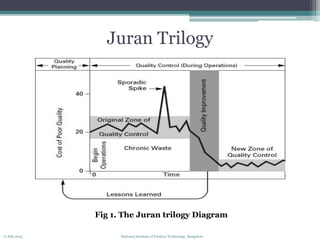
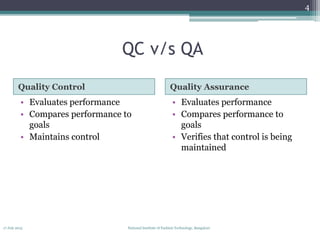
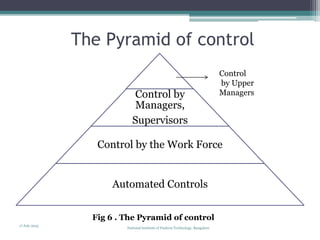
The document discusses quality control concepts and processes. It introduces common quality control frameworks like the Juran Trilogy, PDCA cycle, feedback loops, and the pyramid of control. It distinguishes between quality control and quality assurance. Planning is a key part of quality control - it involves understanding customer needs, defining control responsibilities, using tools like flow diagrams to plan inspection points, and determining who will do the planning. The overall goal of quality control processes is to maintain stability and meet customer requirements.