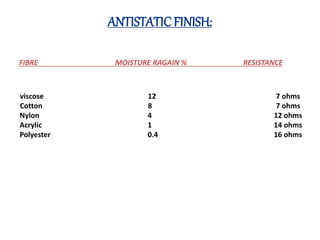
The document discusses anti-static finishes that are applied to synthetic fabrics during processing to prevent the buildup of static charge. Synthetic fabrics are not good conductors and develop static charges during spinning, weaving, and finishing. This can cause fabrics to become entangled or attract dirt. Anti-static finishes reduce the surface charge and increase conduction, using chemicals like silicone emulsions, polyethylene emulsions, and polyammonium quaternary salts. The finish can be durable or non-durable. Higher moisture regain in fibers also helps dissipate static. Common application methods are exhaustion and pad-dry-cure.