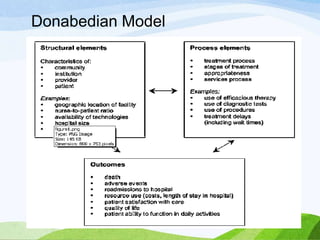
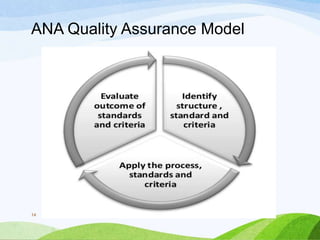
This document discusses quality assurance in healthcare. It defines quality and quality assurance, and lists their objectives. Quality is defined as the degree to which health services increase desired health outcomes consistent with current knowledge. Quality assurance aims to continuously evaluate healthcare services and their impact. The key objectives of quality assurance are to ensure quality patient care and demonstrate provider efforts to achieve best results. It also outlines various models, components, principles, approaches, factors, barriers, and the nurse's role in quality assurance.