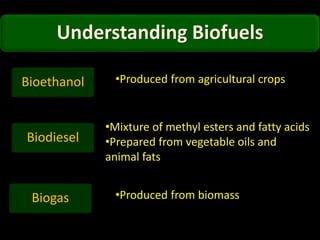
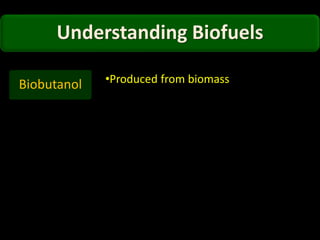
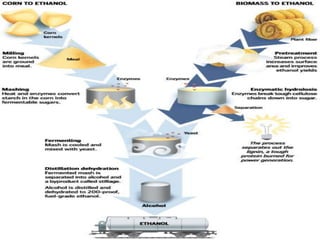
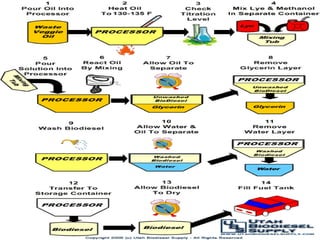
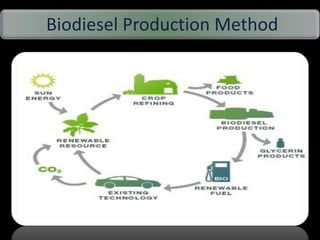
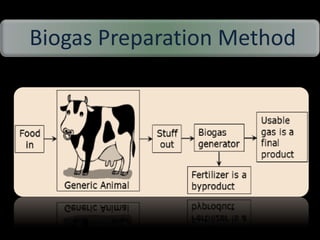
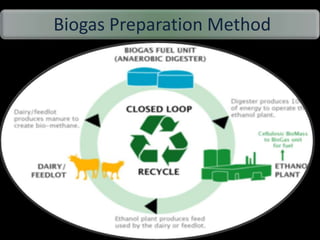
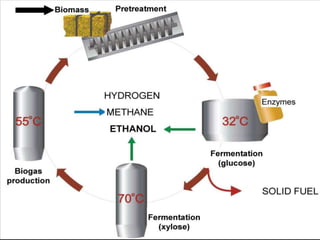
This document discusses different types of biofuels including their generation processes. It explains that biofuels are fuels derived from living organisms and biomass. There are three generations of biofuels - first from edible plant materials, second from non-edible plant parts, and third from algae. Key biofuels discussed include biodiesel, biogas, and bioethanol. Biodiesel is made through transesterification of vegetable oils. Biogas is produced through anaerobic digestion of biomass. Bioethanol is generated through fermentation of sugars from crops like corn. The document also outlines benefits and disadvantages of biofuel production.