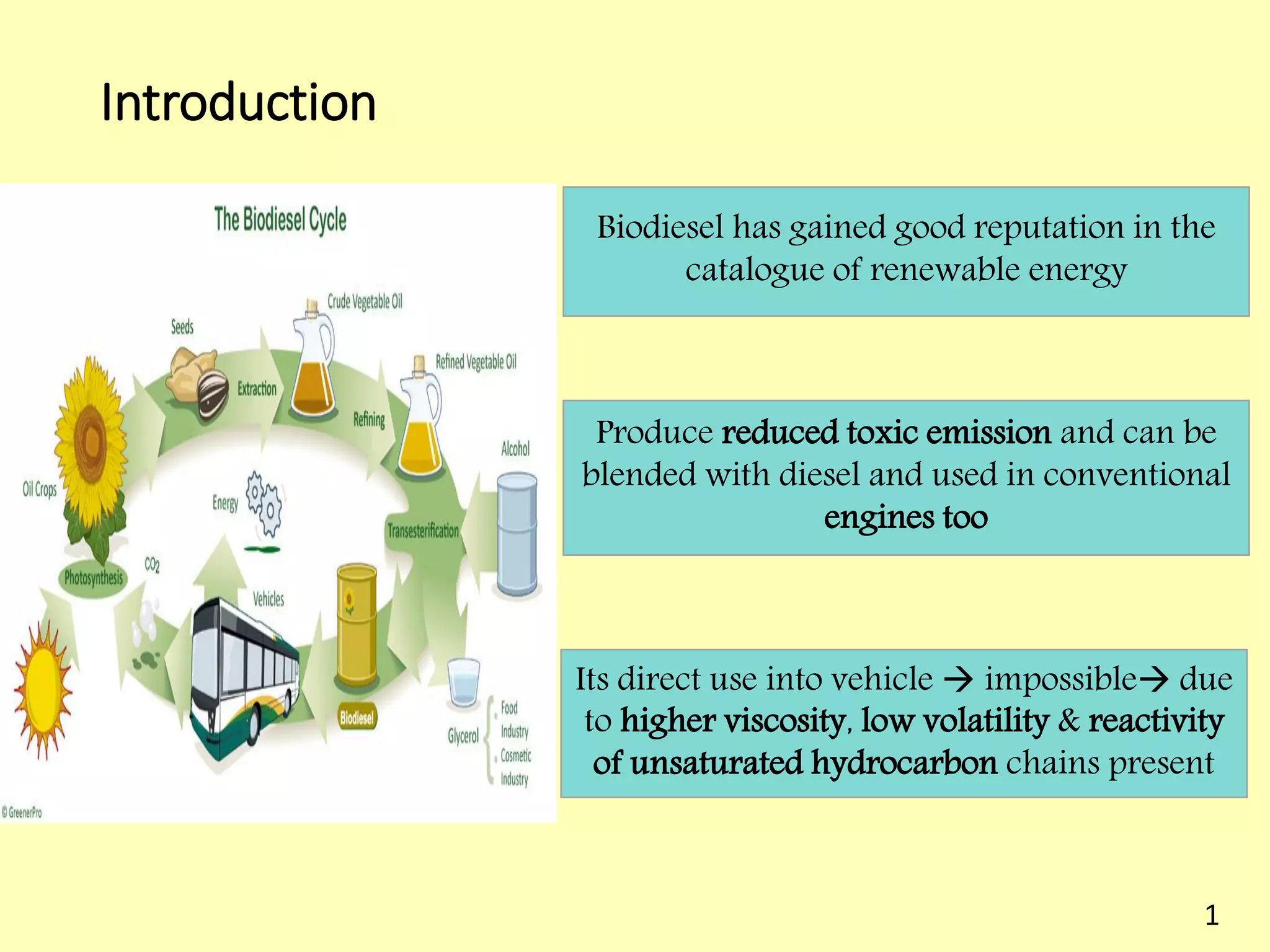
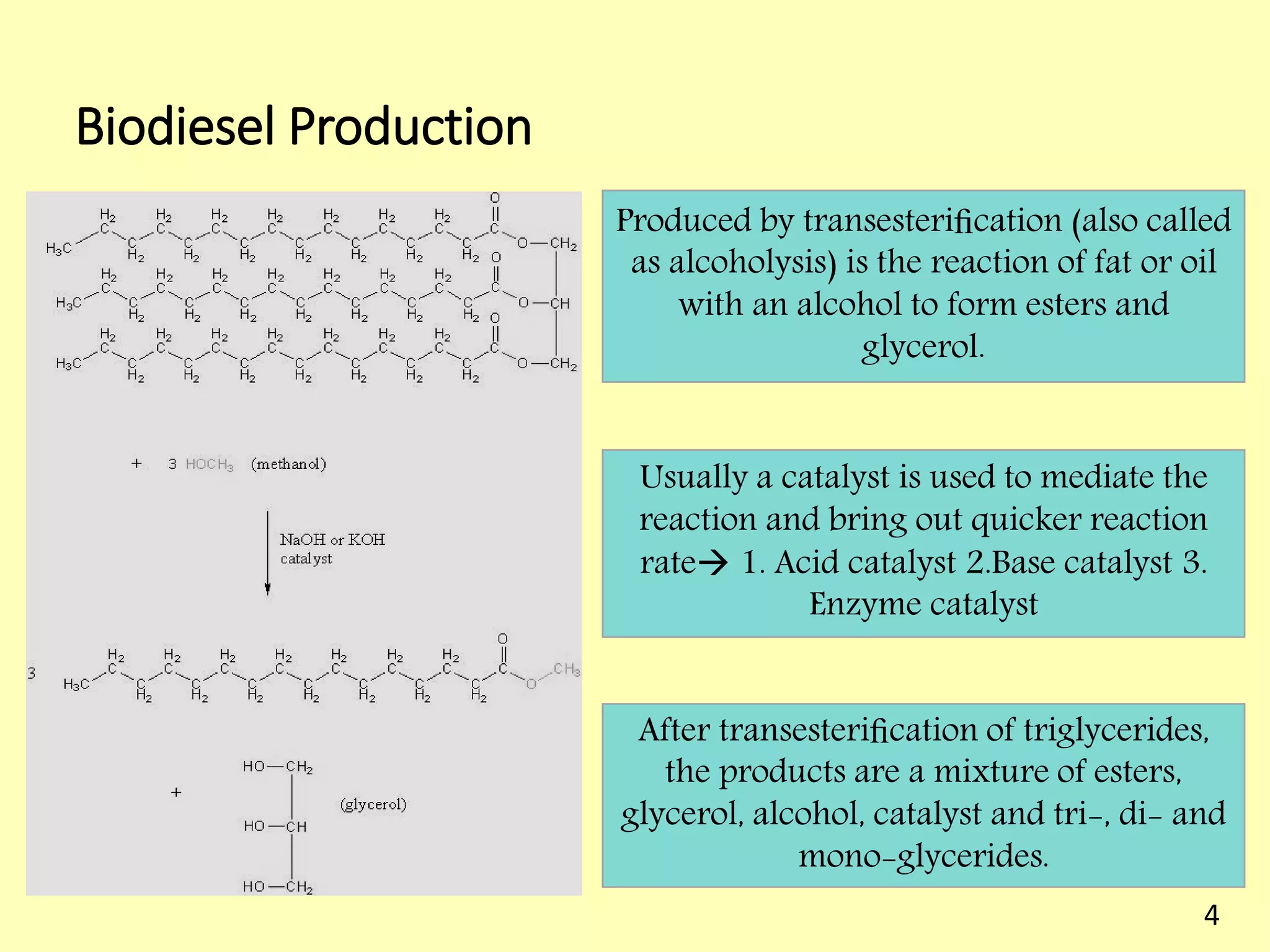
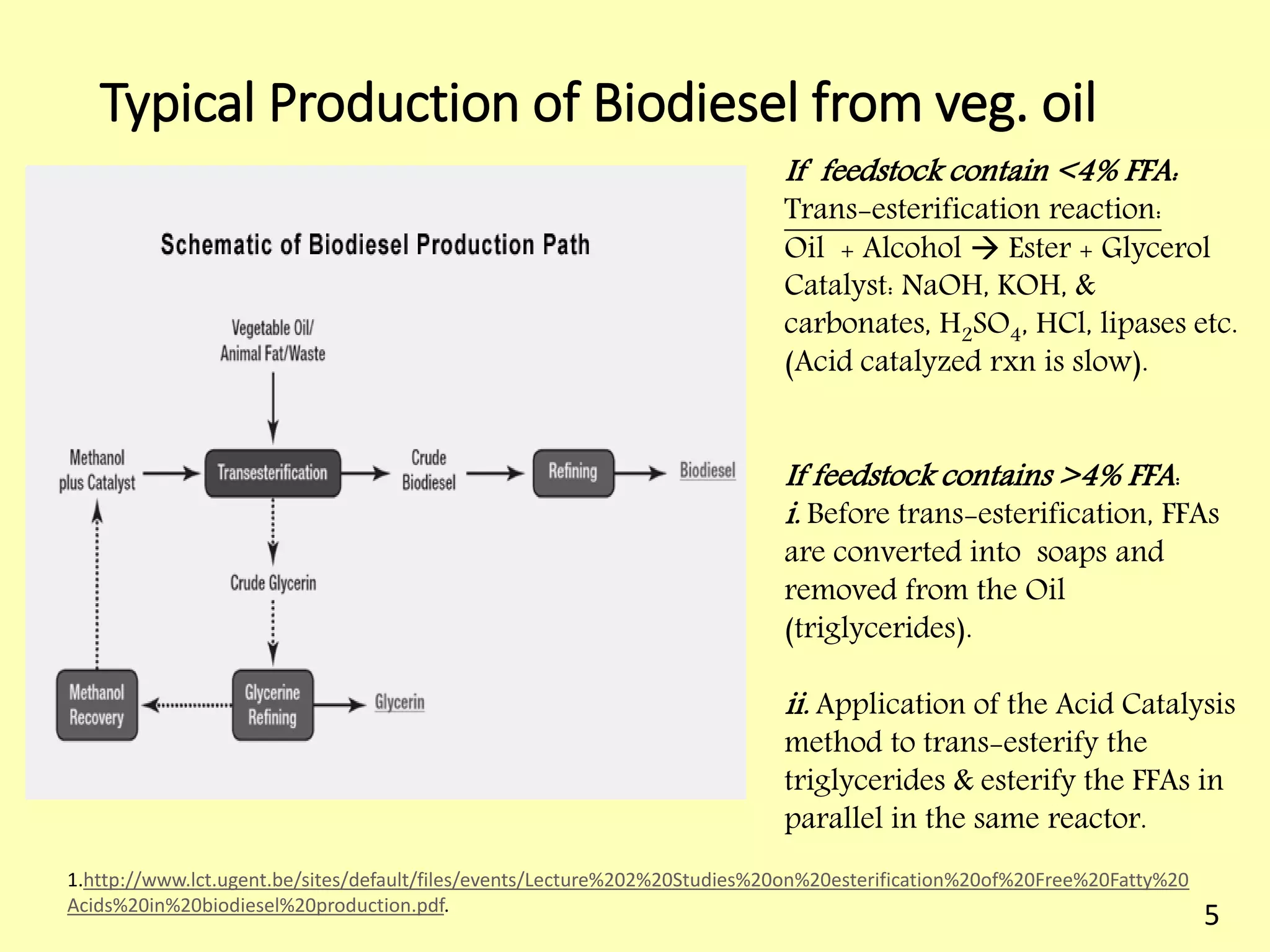
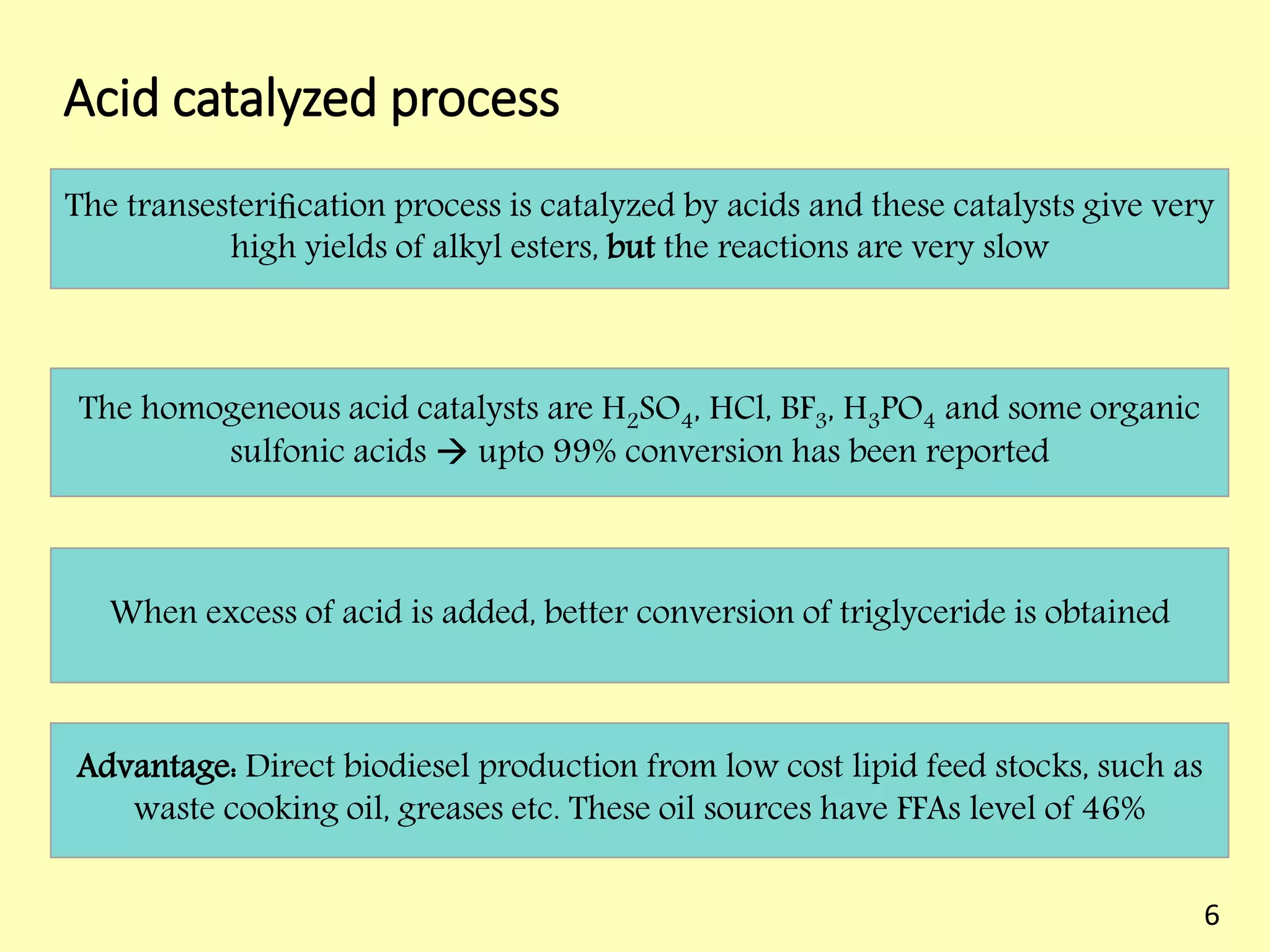
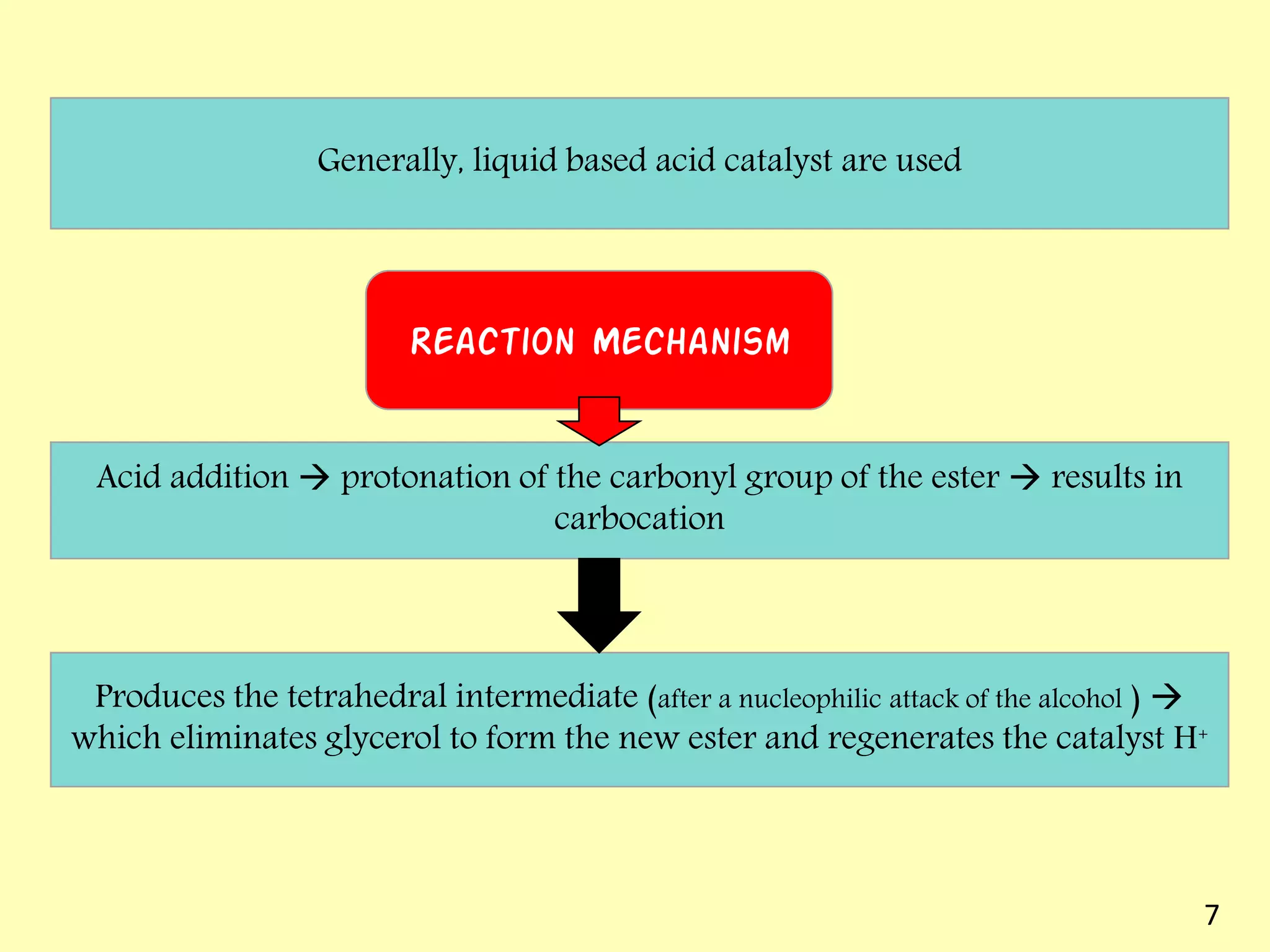
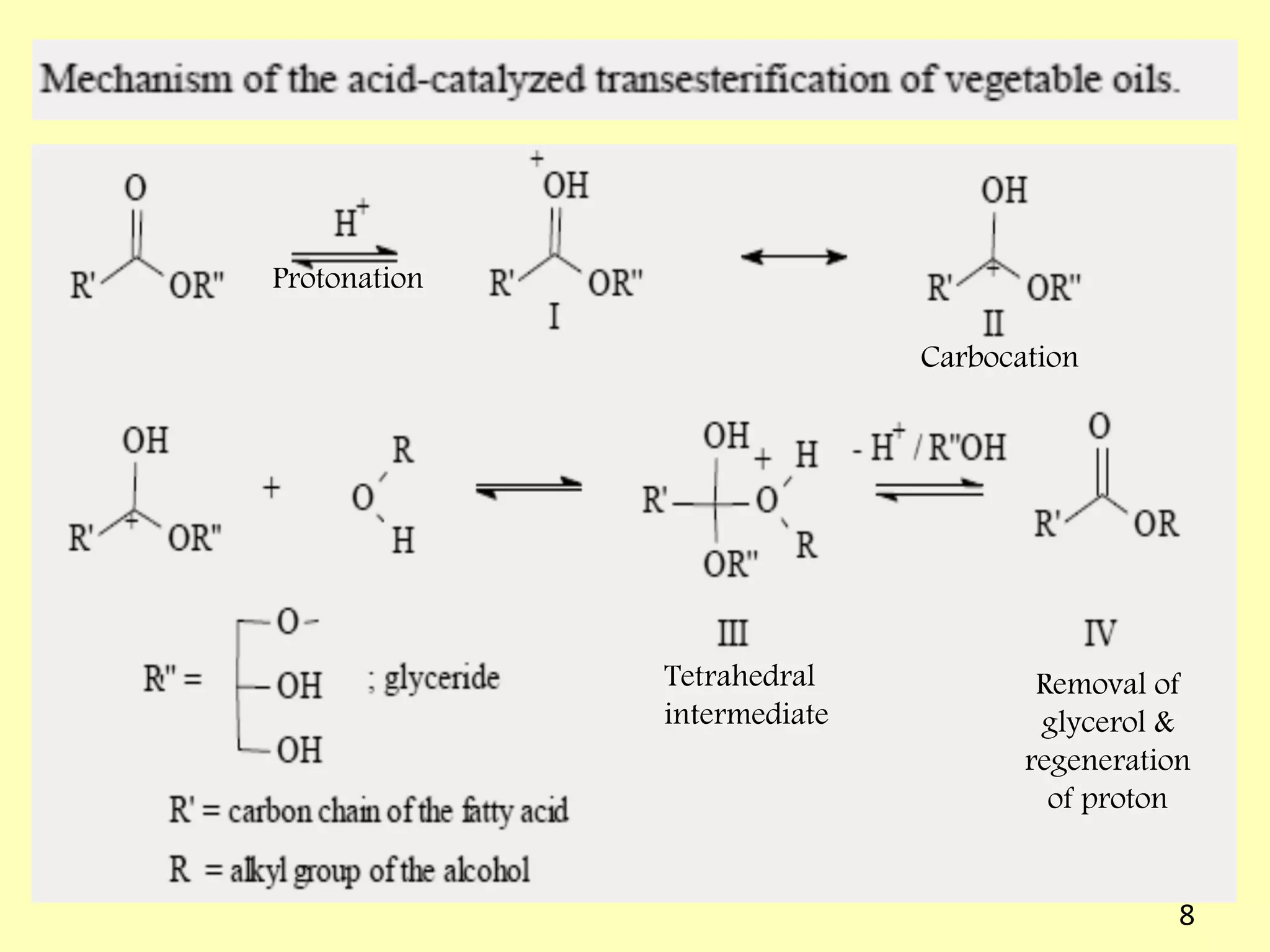
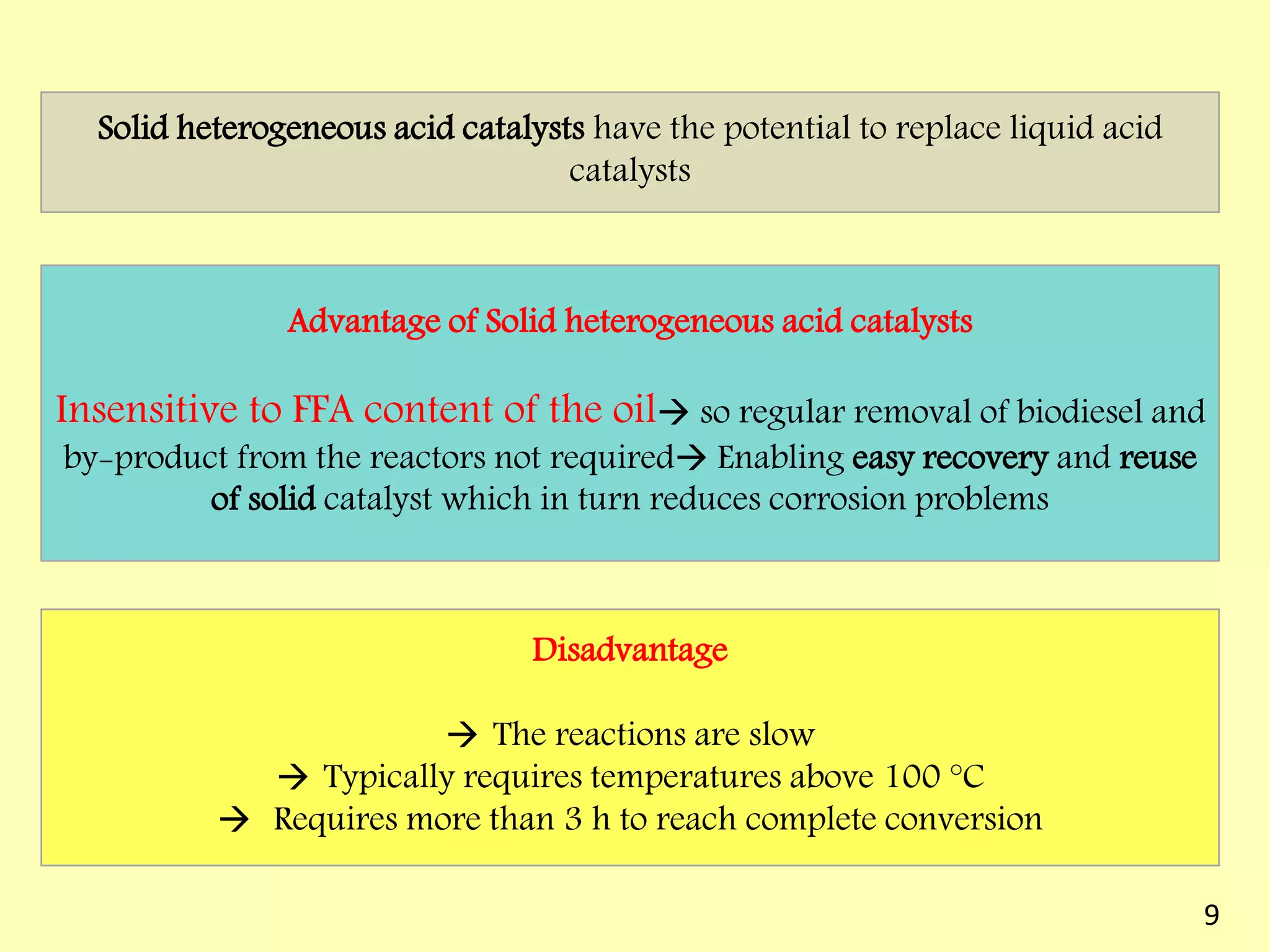
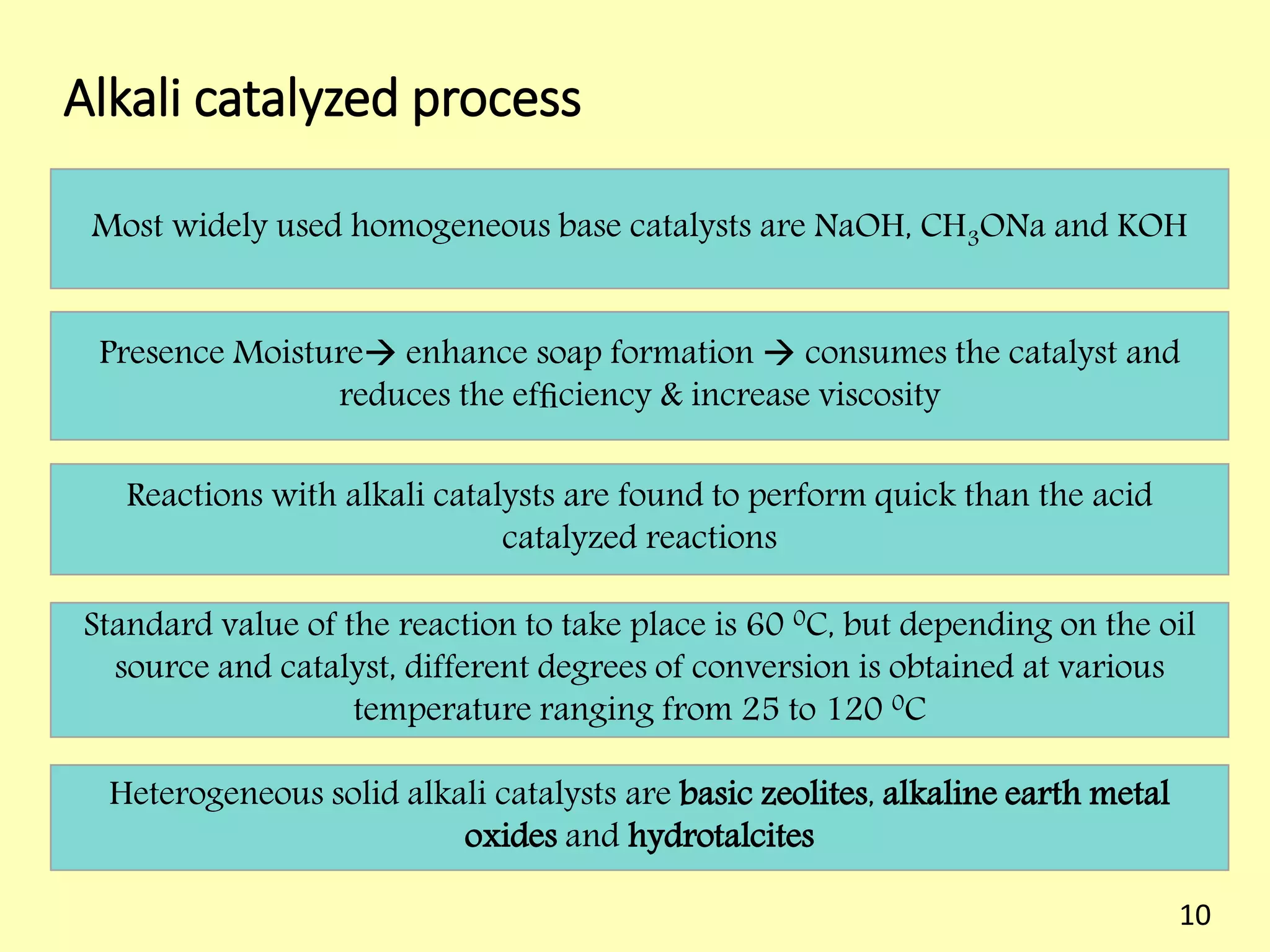
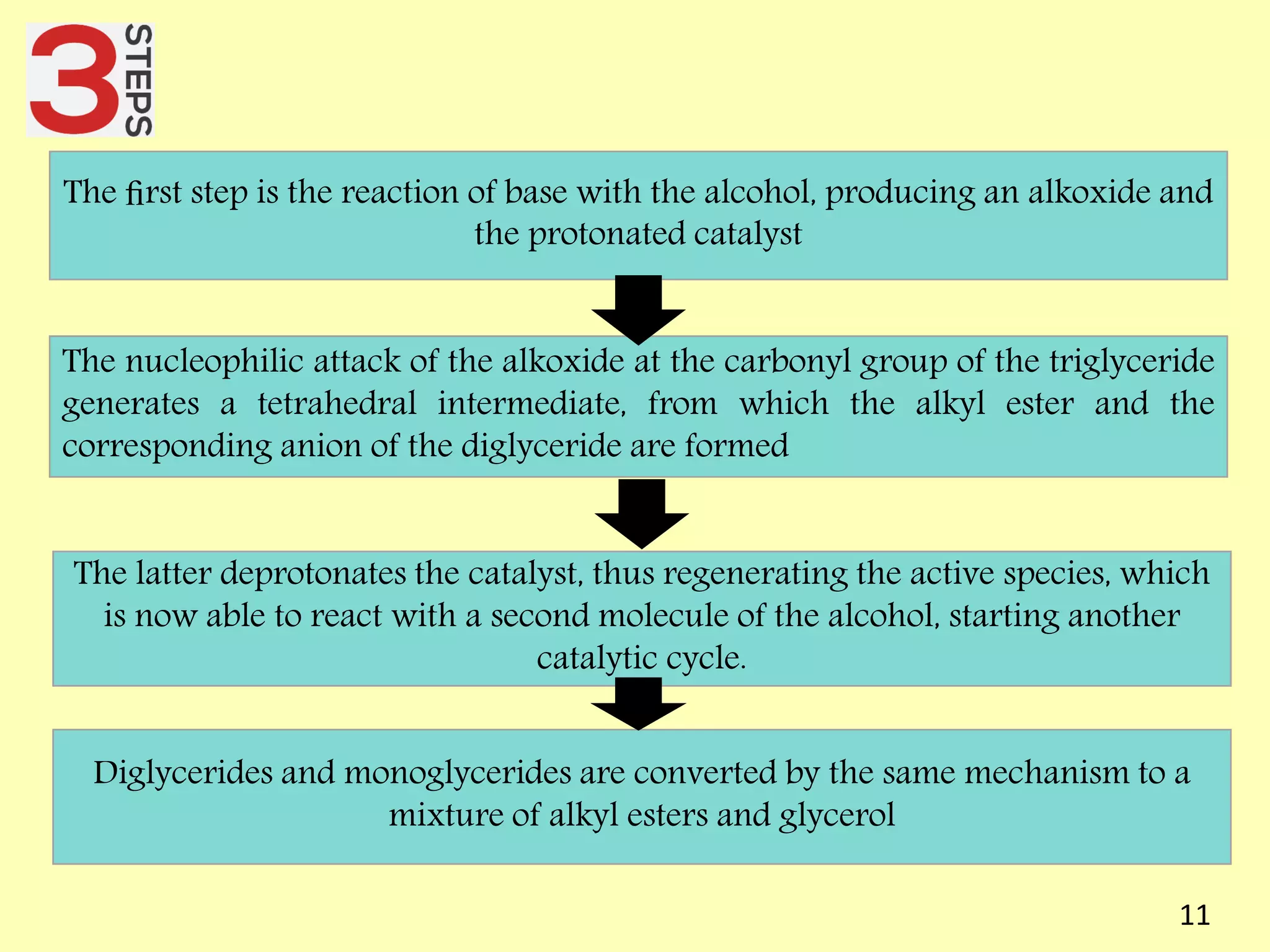
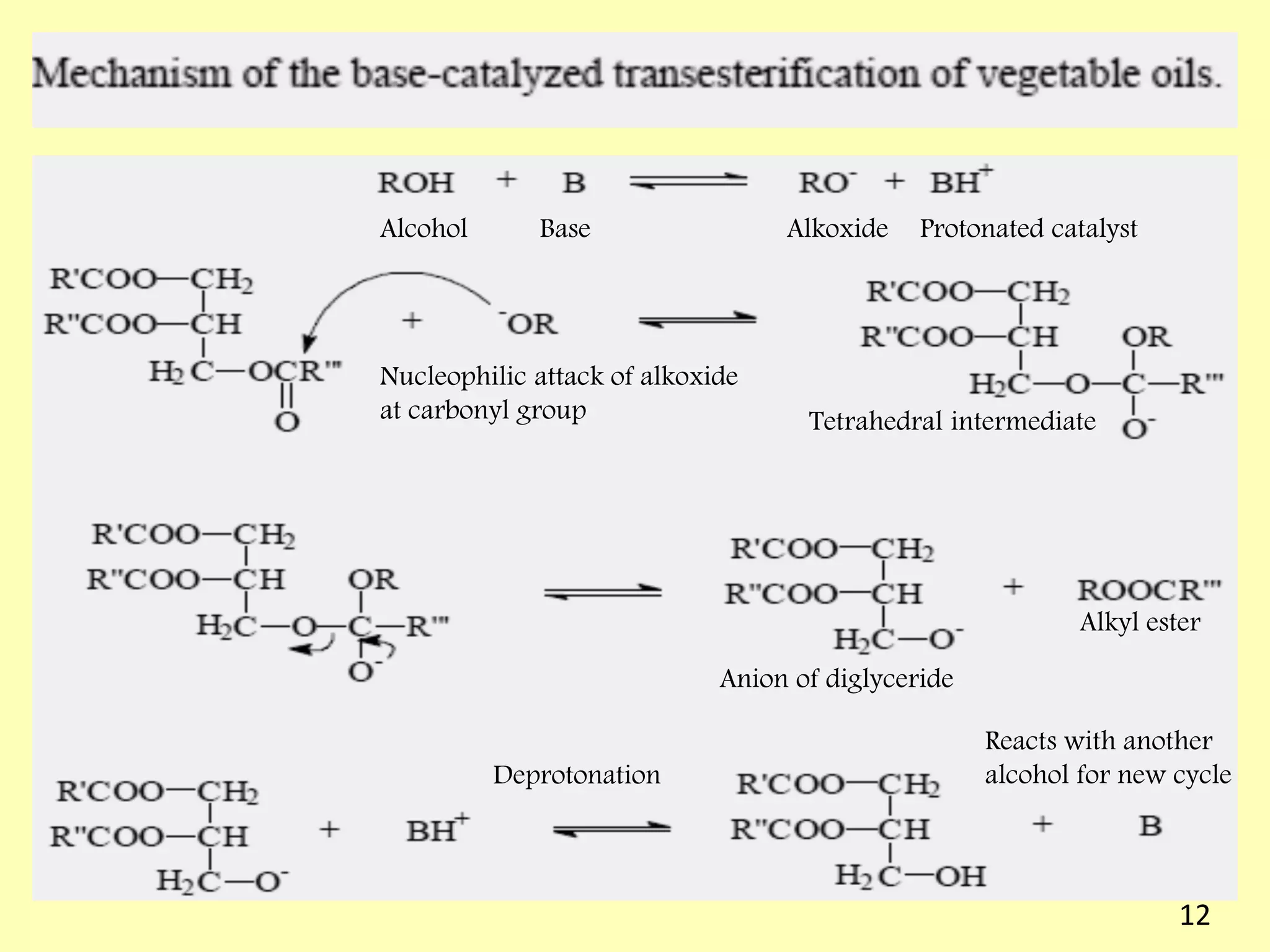
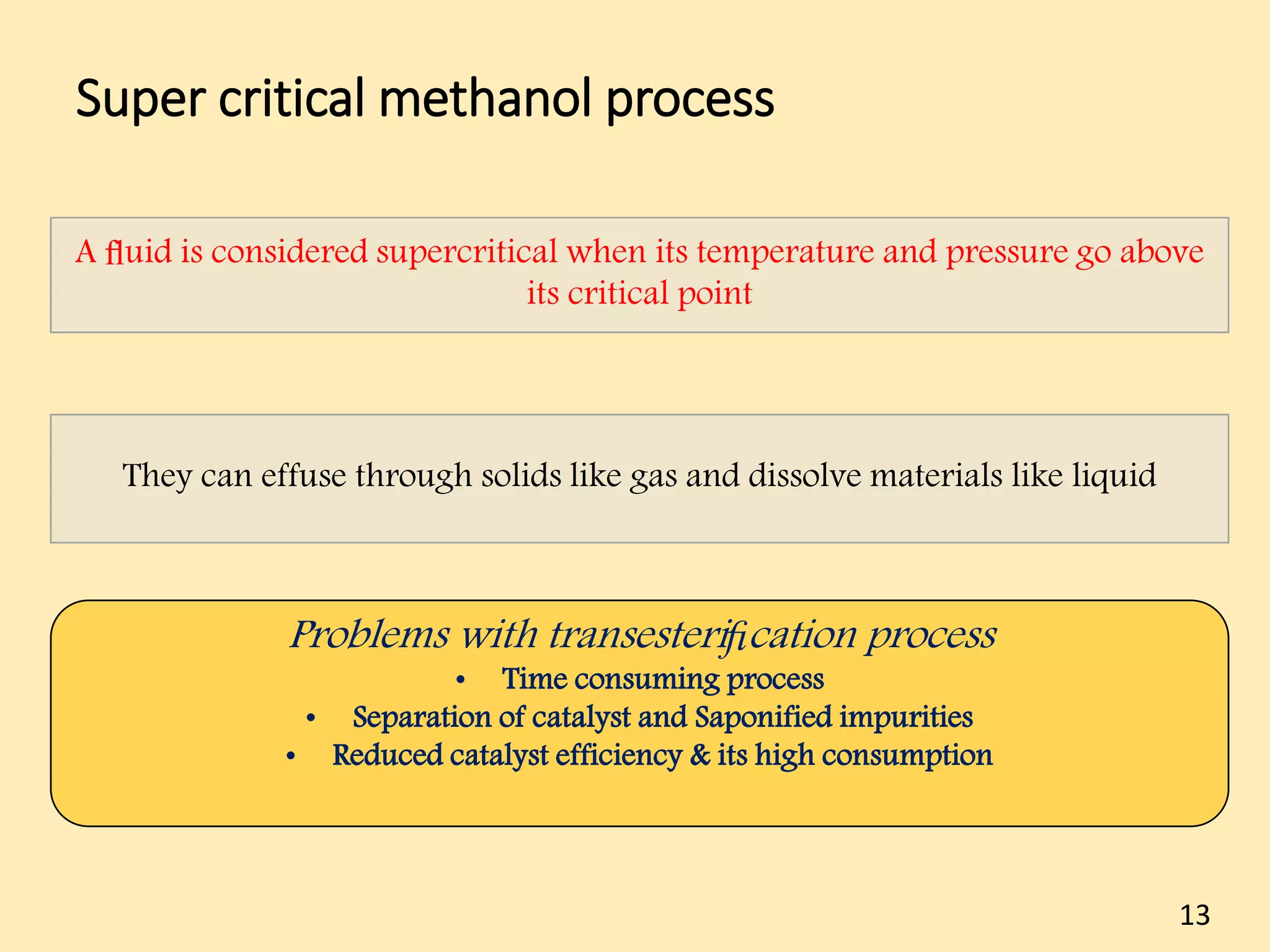
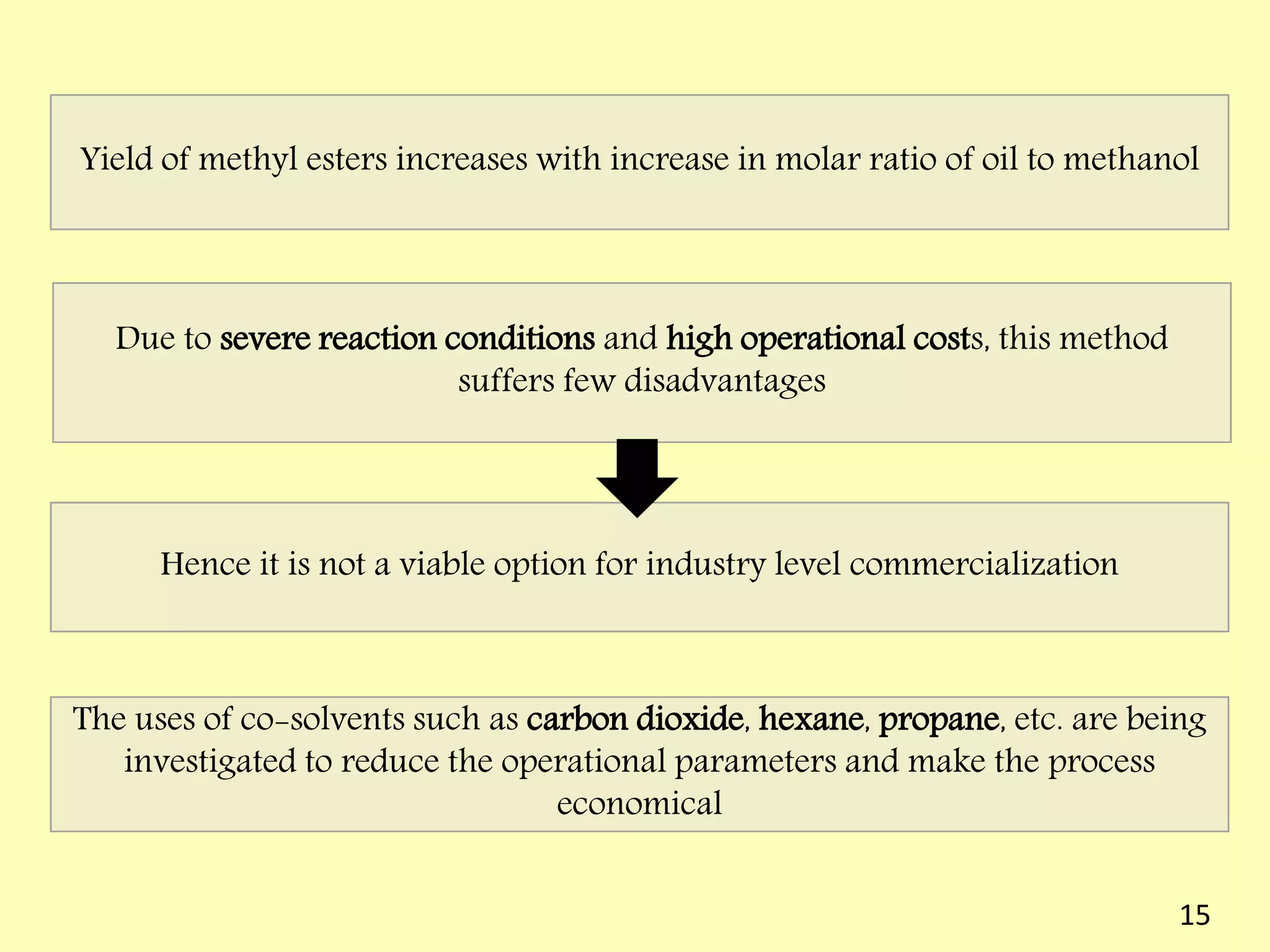
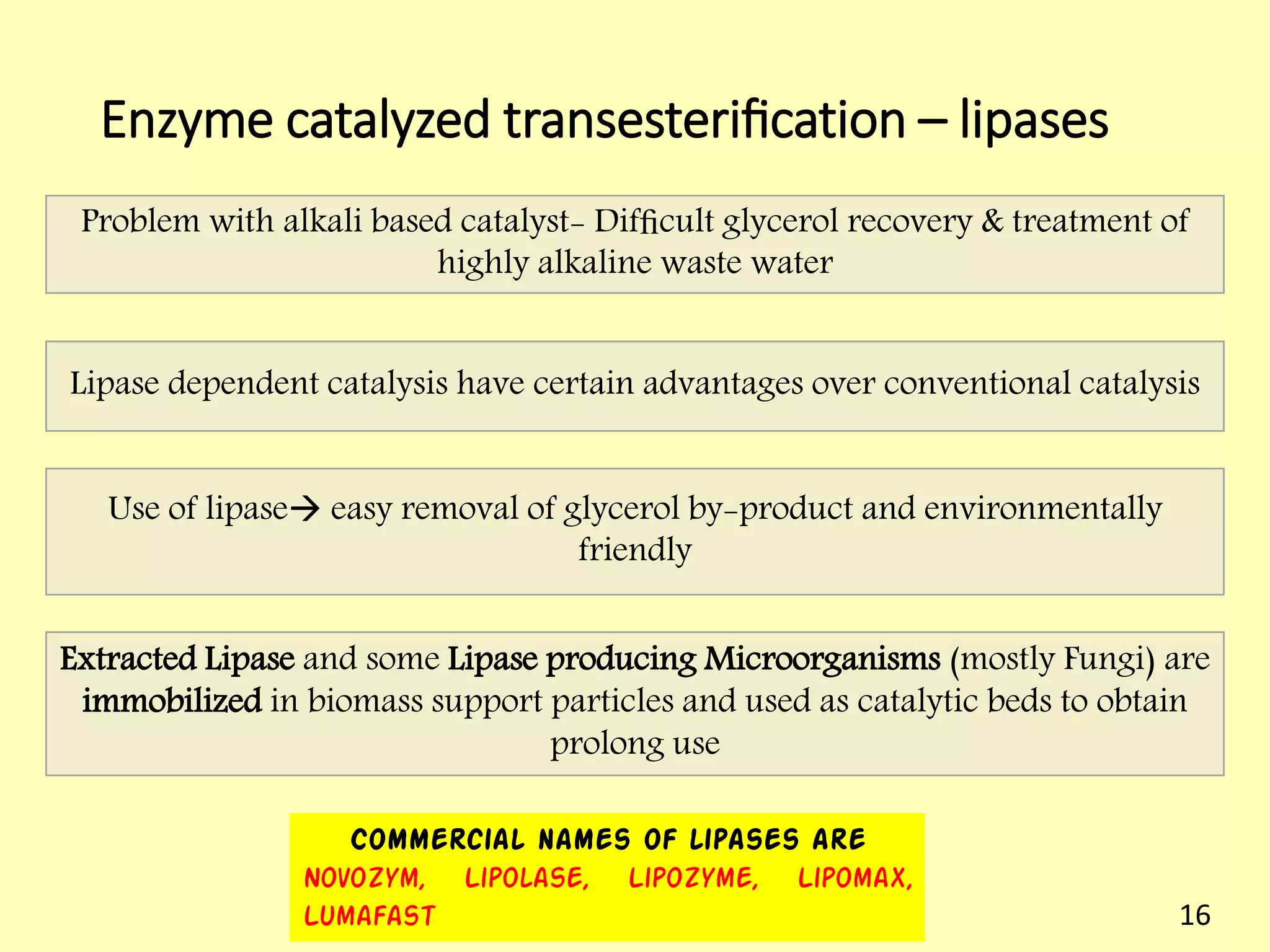
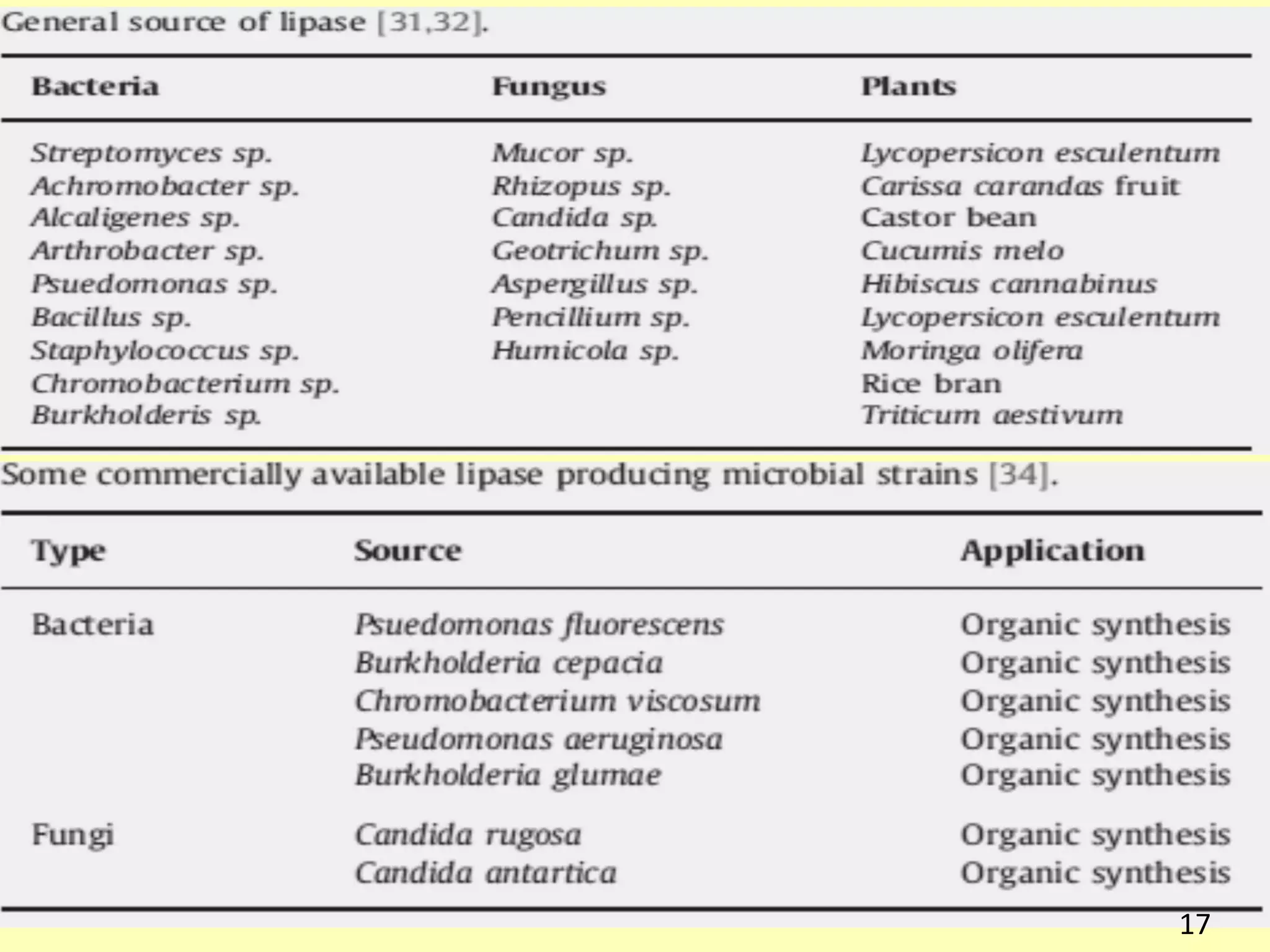
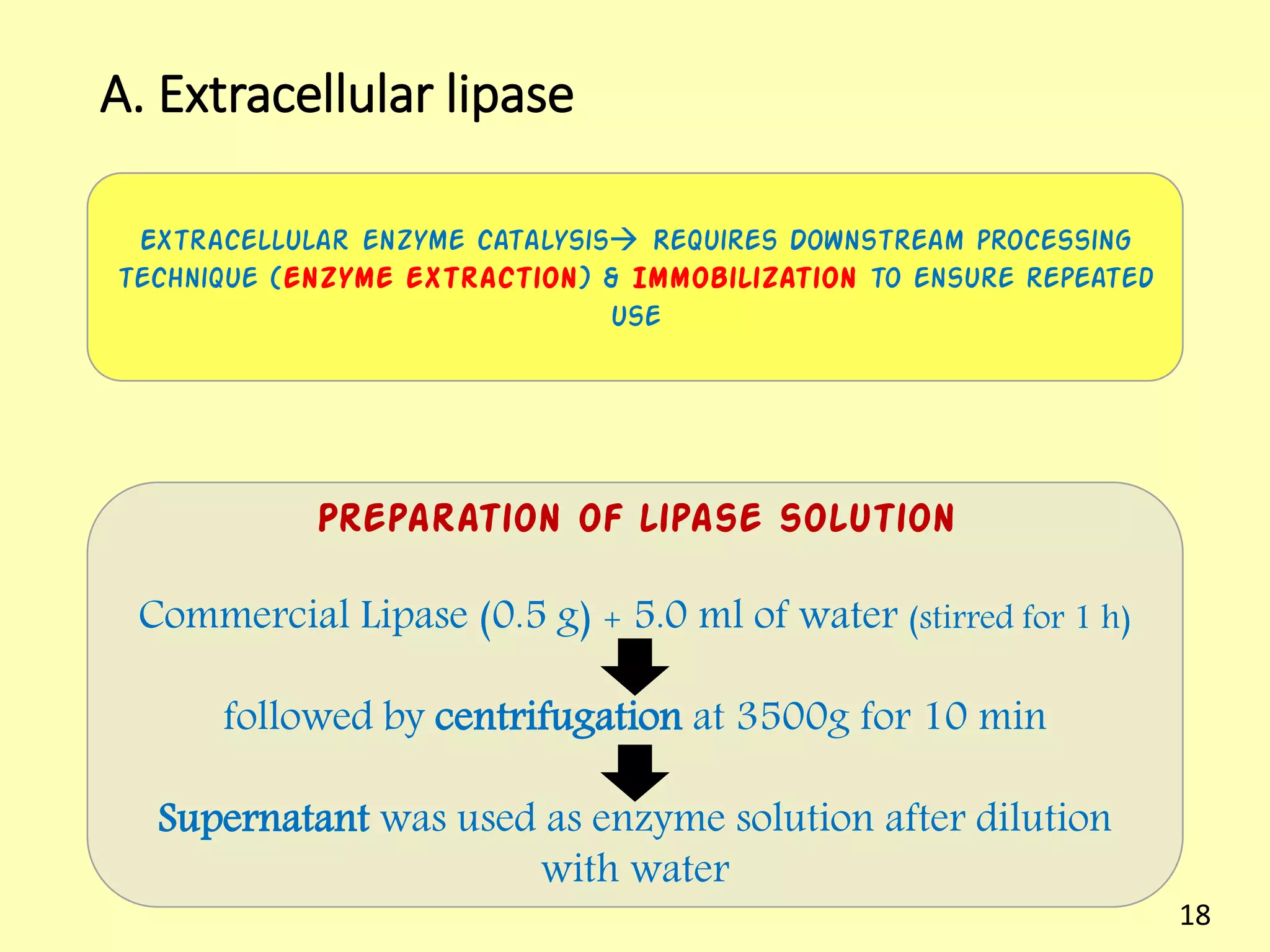
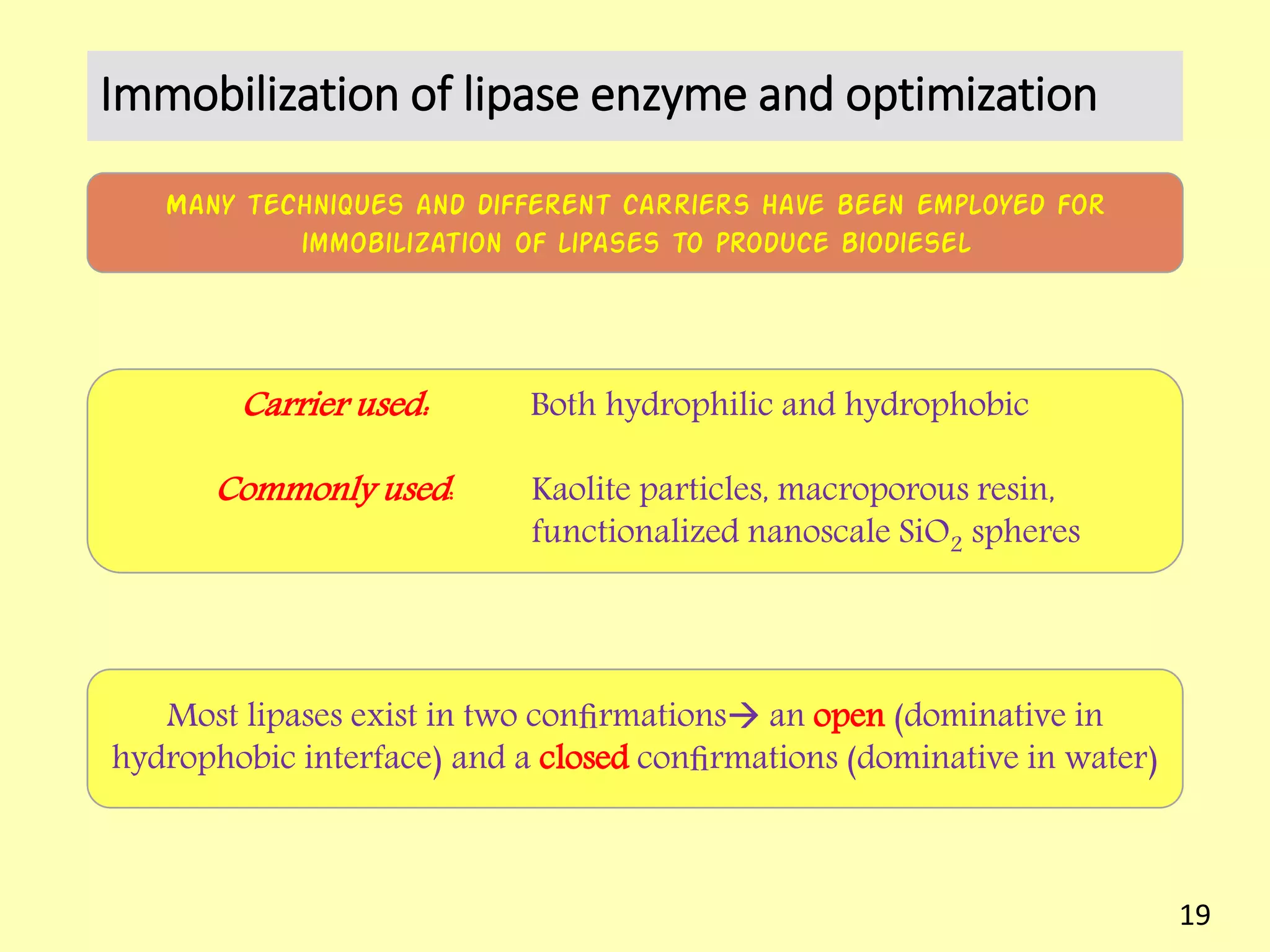
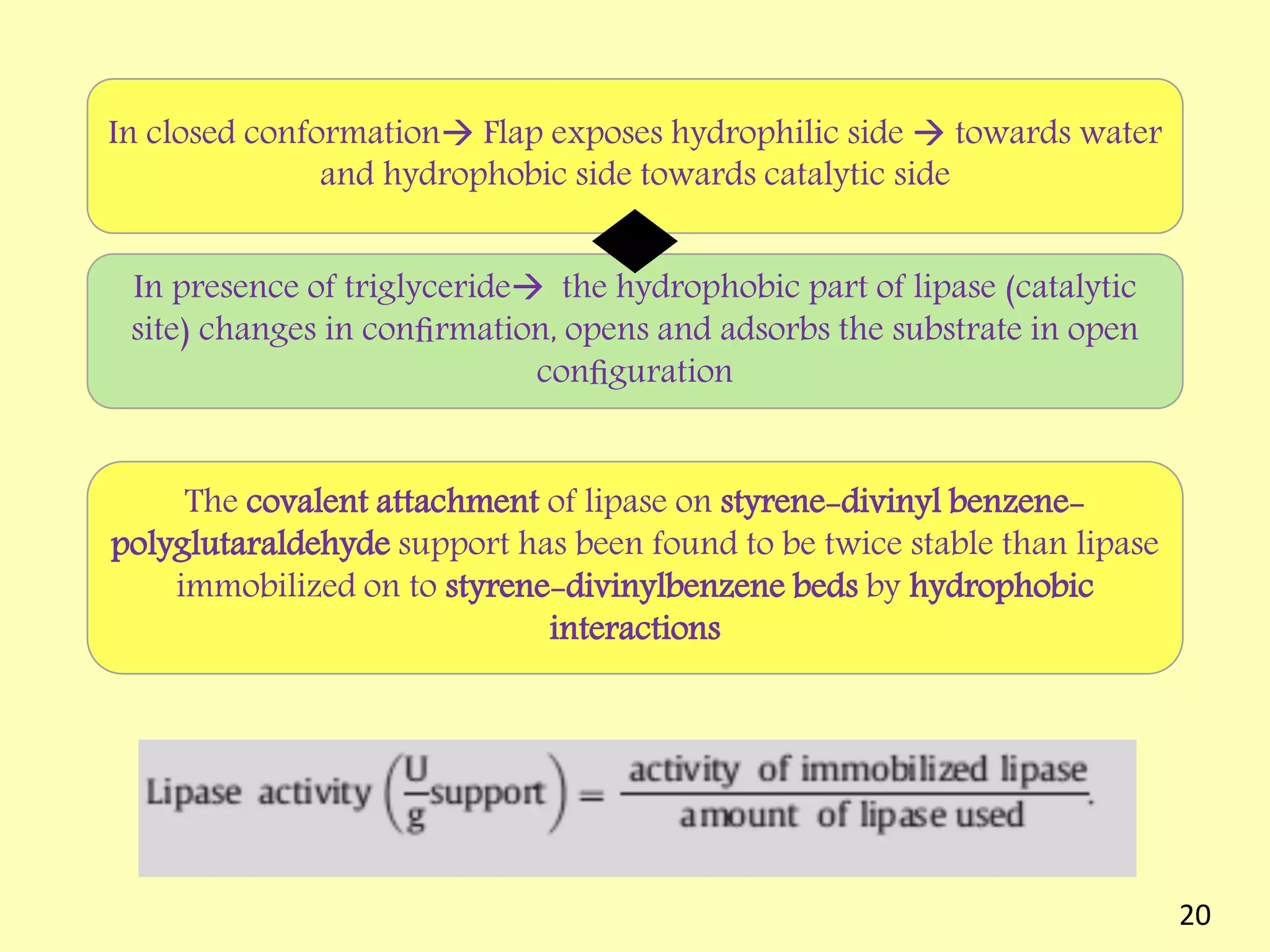
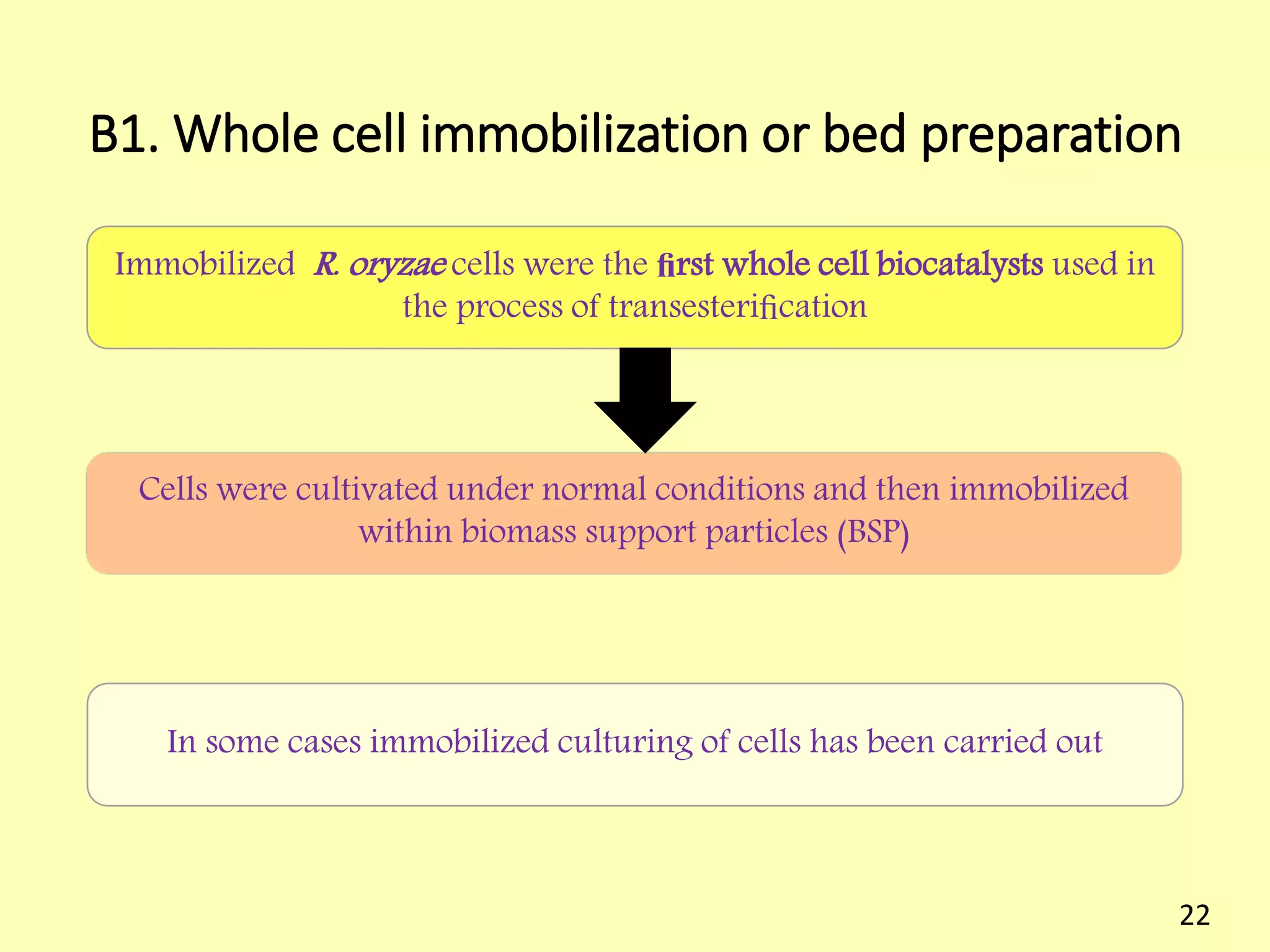
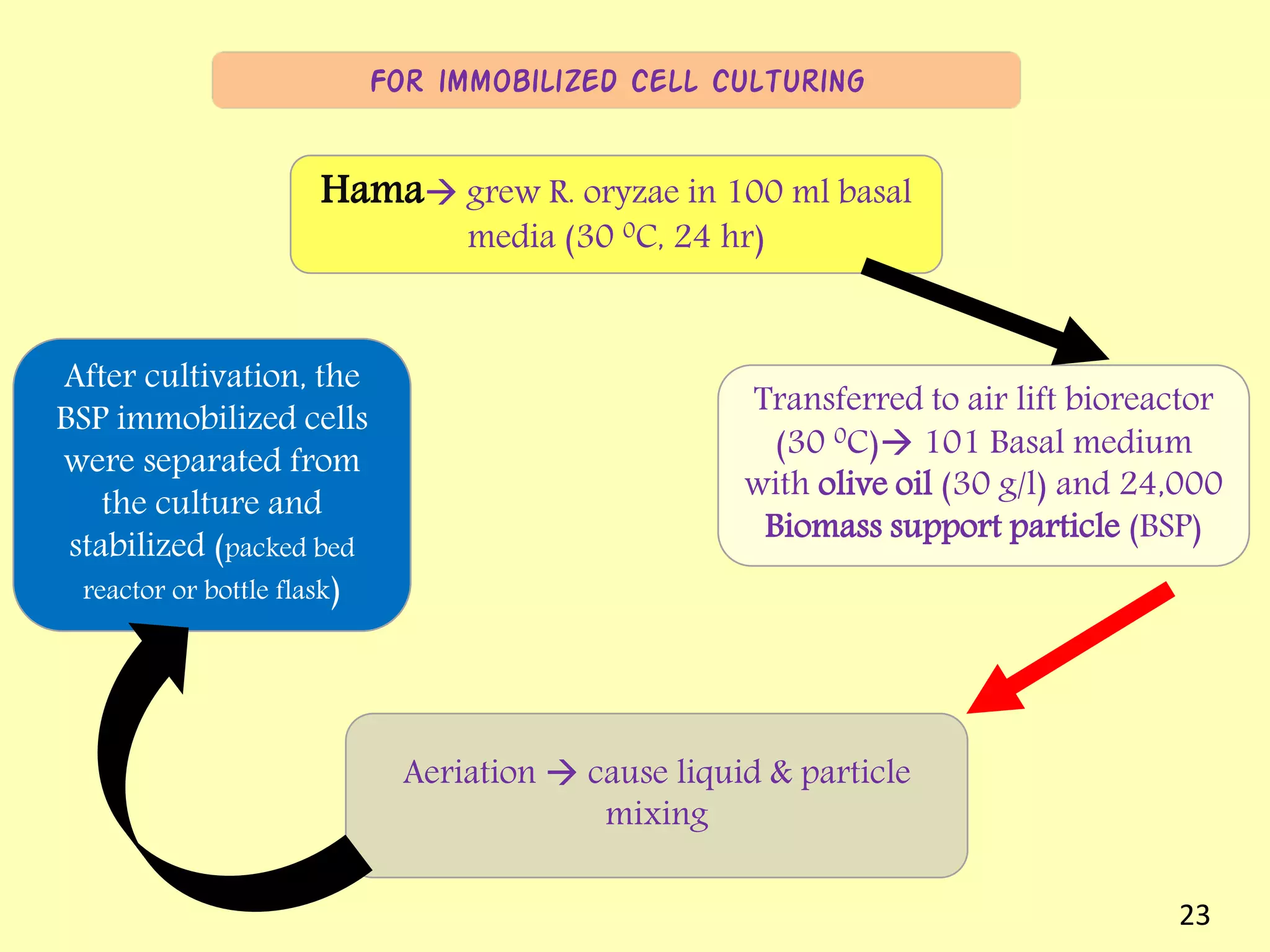
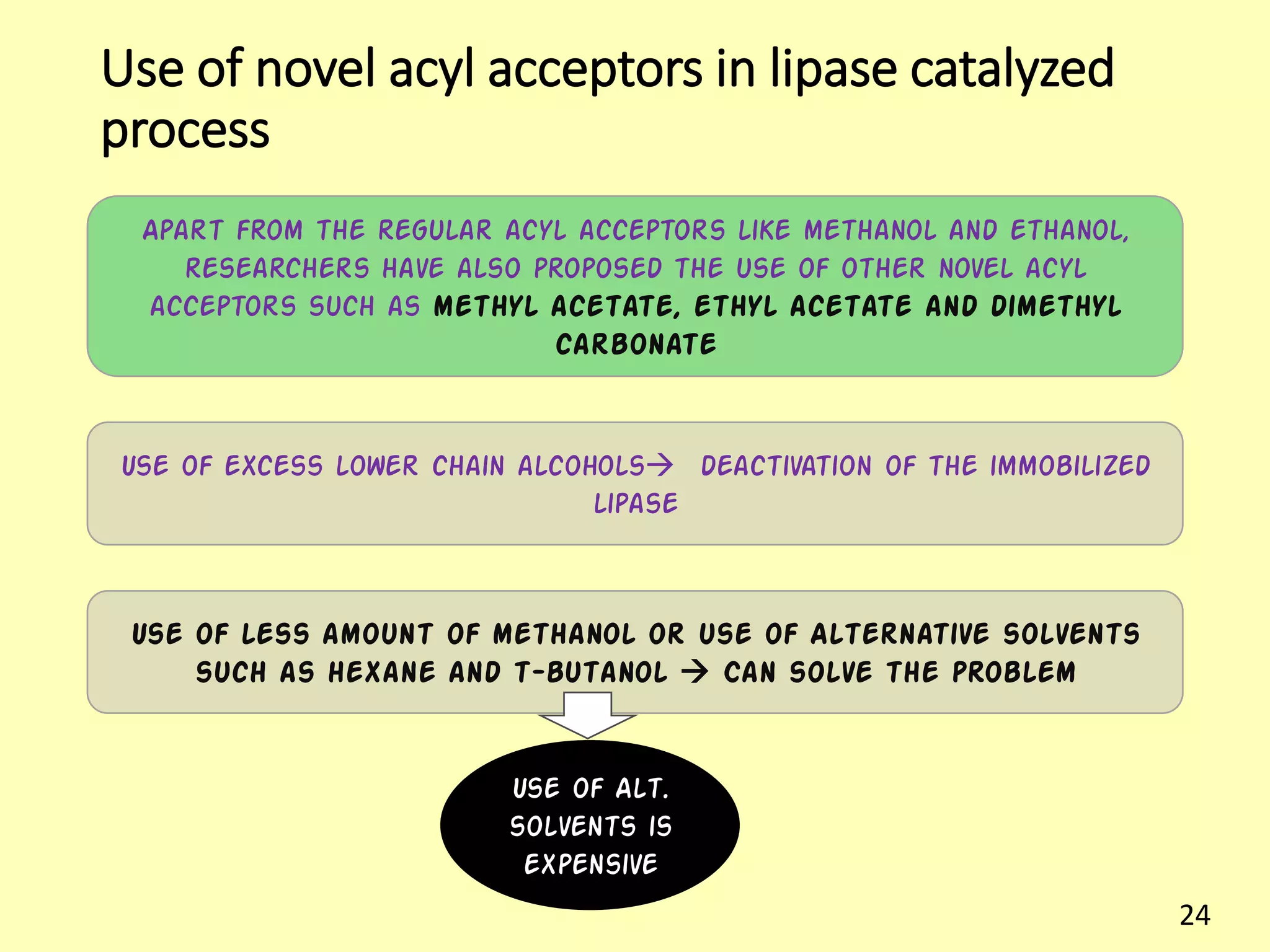
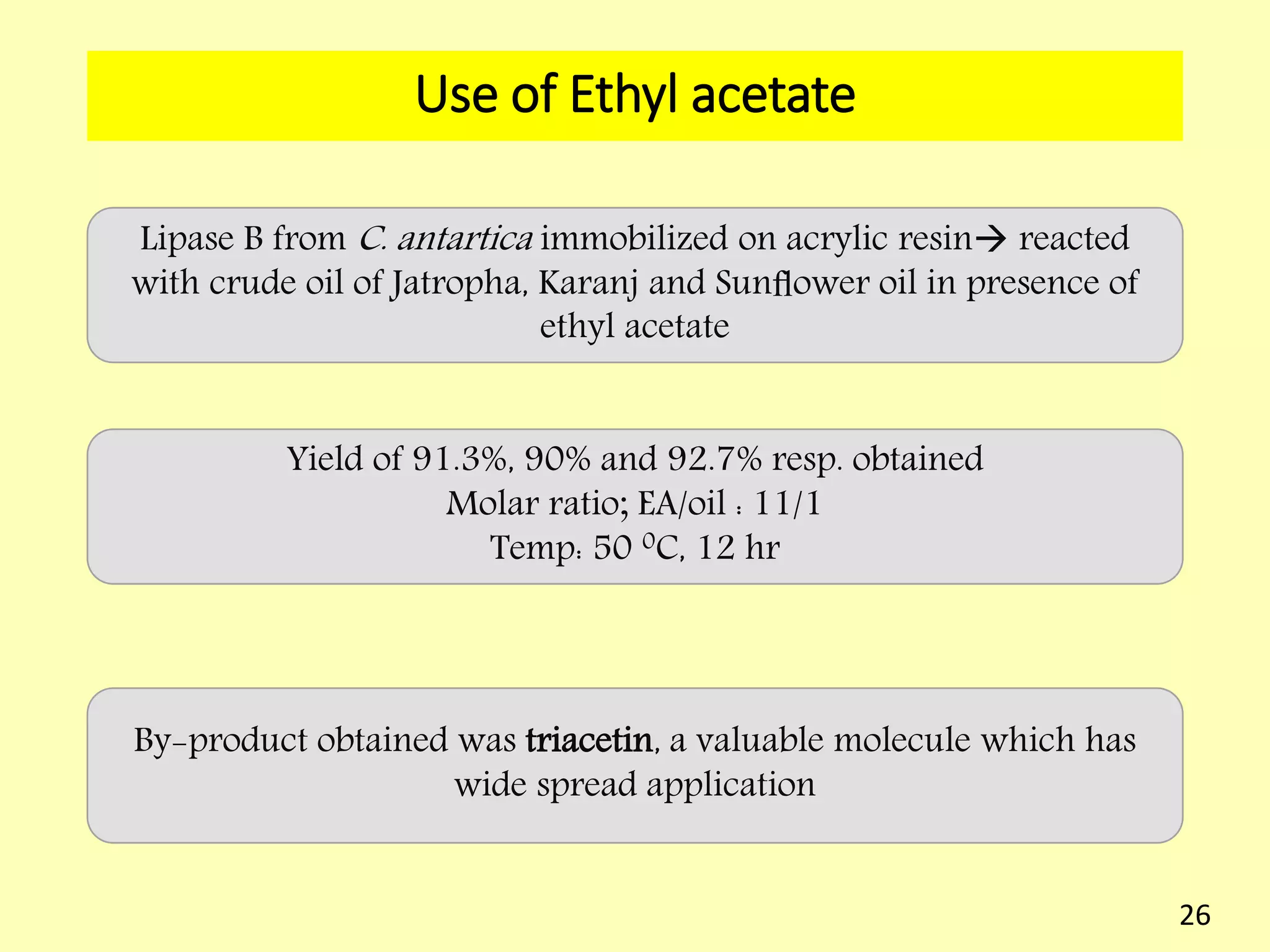
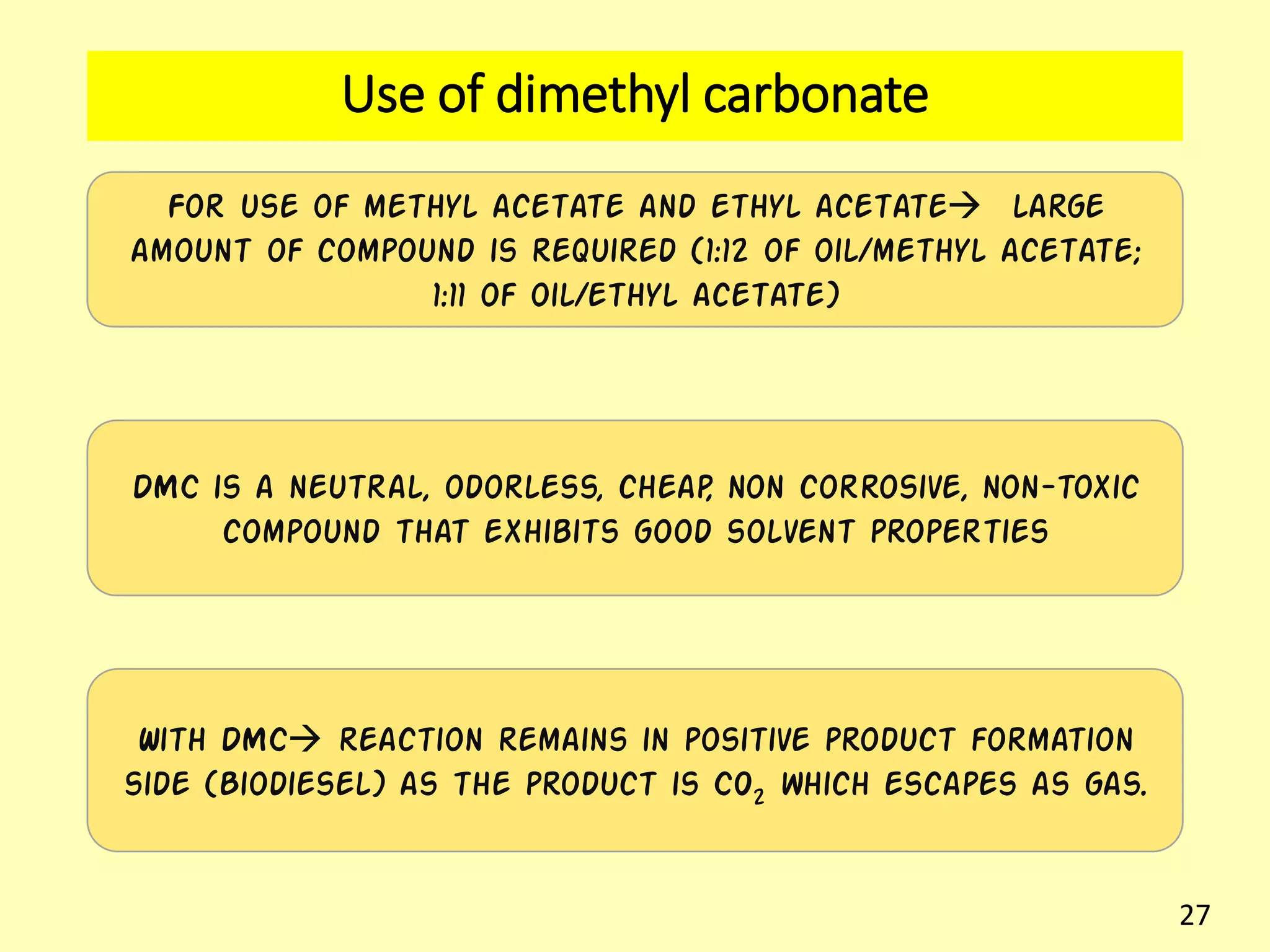
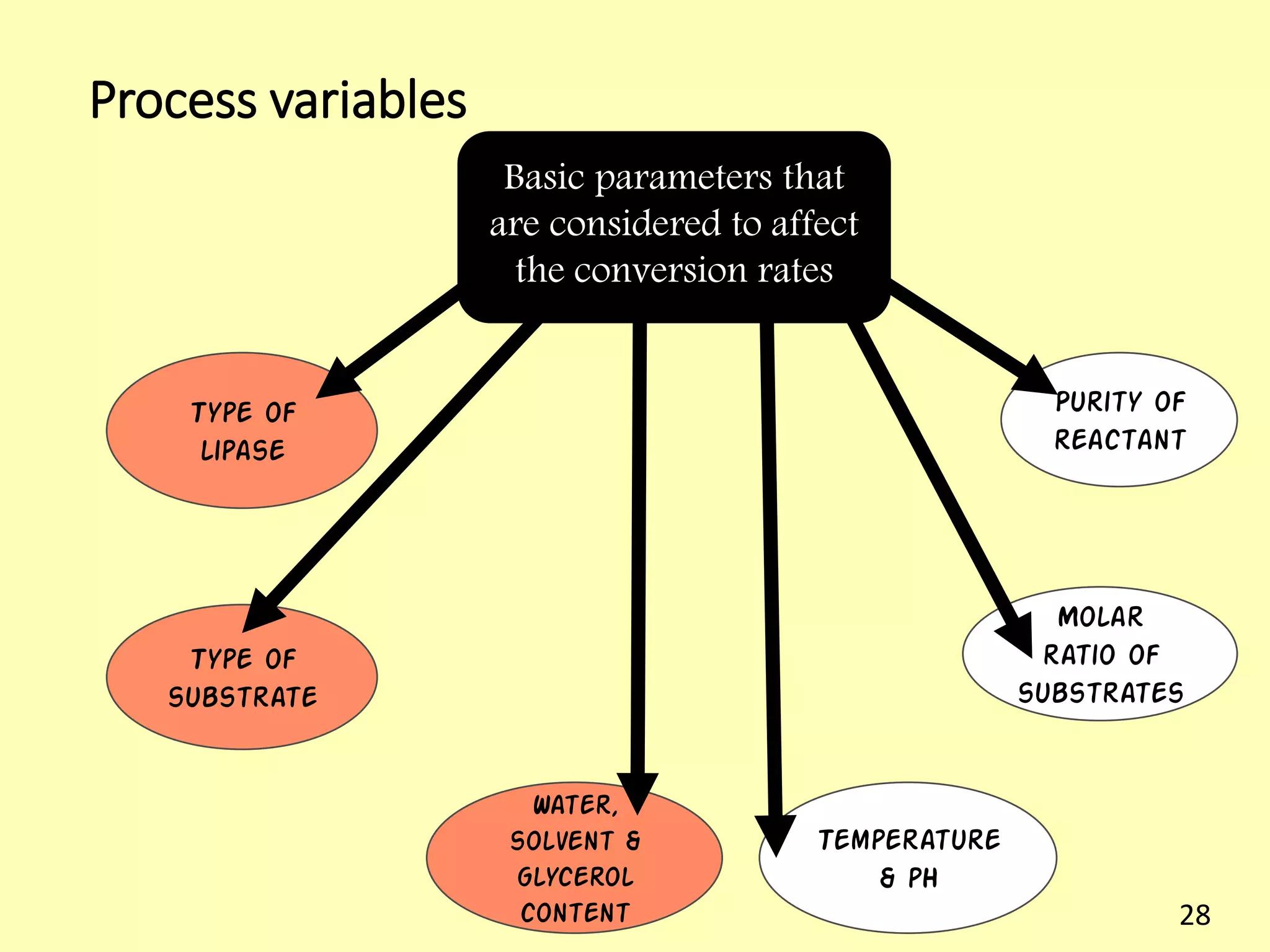
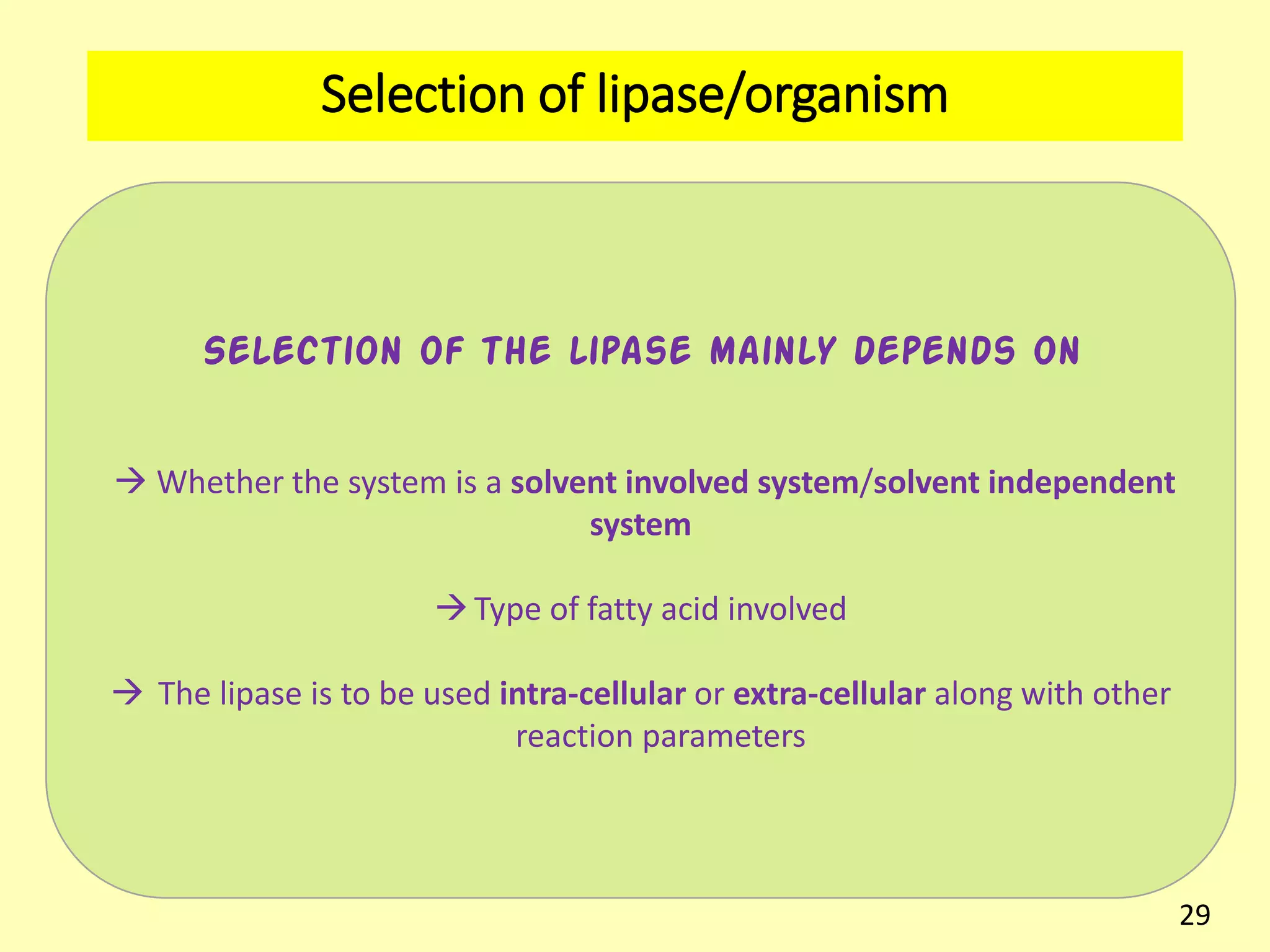
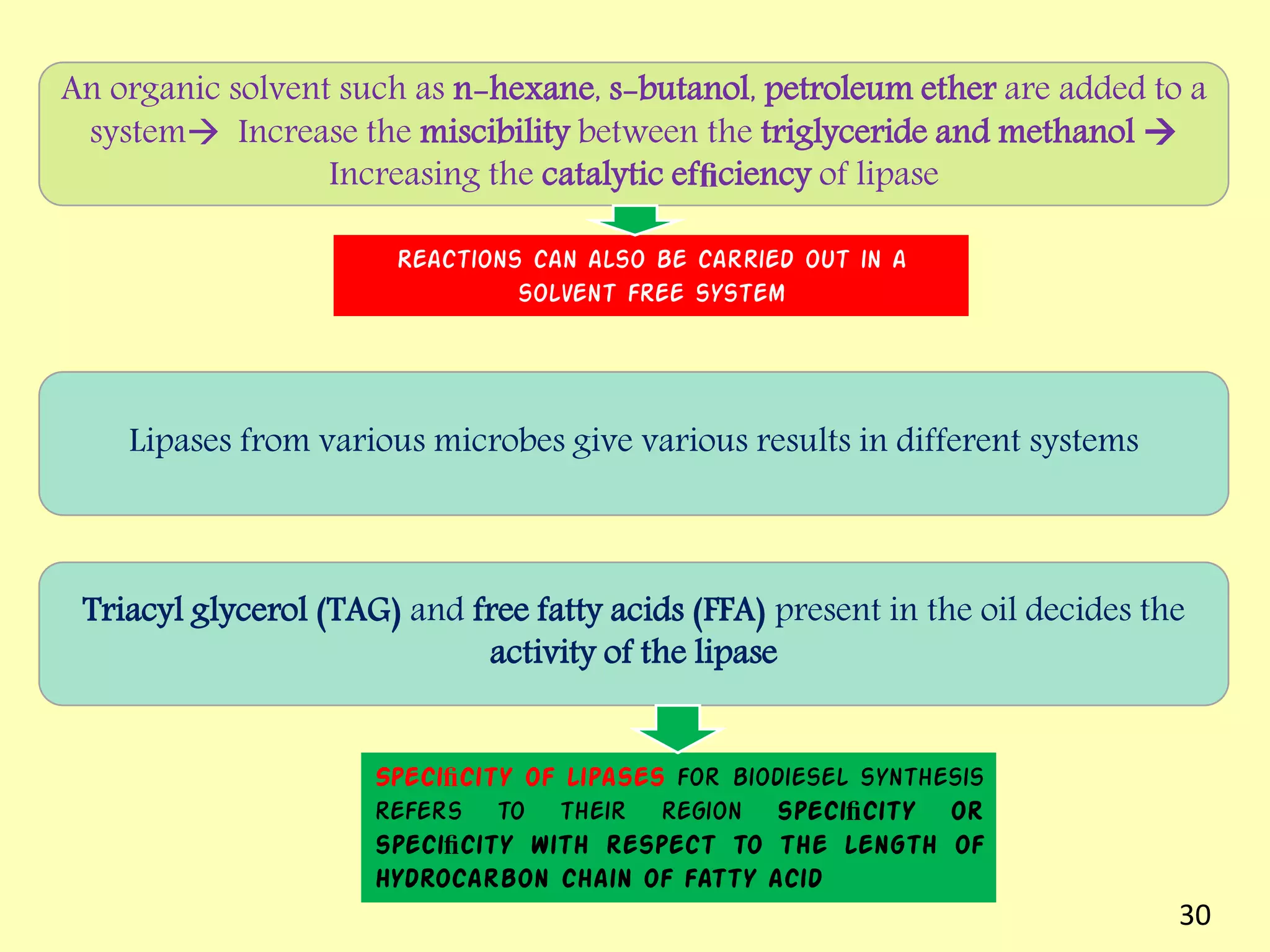
This document reviews biodiesel production methods using chemical and biological catalysts. Biodiesel can be produced via transesterification, where triglycerides from oils react with alcohol to form esters and glycerol. This reaction is catalyzed by acids, bases, or enzymes. Key process variables that affect conversion rates include the type of catalyst, substrate, temperature, solvent, molar ratios, and glycerol byproduct removal. While base catalysis is most common, acid and enzyme methods allow processing of low-quality feedstocks. Alternative acyl acceptors like methyl acetate and dimethyl carbonate also show promise. Overall, optimizing catalysts, substrates, and process conditions can improve biodiesel