The document describes the structure and function of the human ear. It discusses the three main parts of the ear - the outer, middle, and inner ear. The outer ear collects sound waves and directs them through the external auditory meatus to the tympanic membrane. Vibrations then pass through the ossicles in the middle ear and oval window to reach the fluid-filled cochlea of the inner ear. Within the cochlea, sound waves generate vibrations that stimulate hair cells and send nerve impulses to the brain for sound recognition and processing. The inner ear also contains structures like the semicircular canals that enable balance and spatial orientation.
![D.PHARM-1
HAP
PKS
[STRUCTURES AND
FUNCTIONS OF EAR]
Defination Of Ear, Structure Of Ear, Internal Parts Of Ear,Physiology Of Hearing/Mechanism
Of Hearing ,ETC.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ear-210518025533/75/Ear-1-2048.jpg)

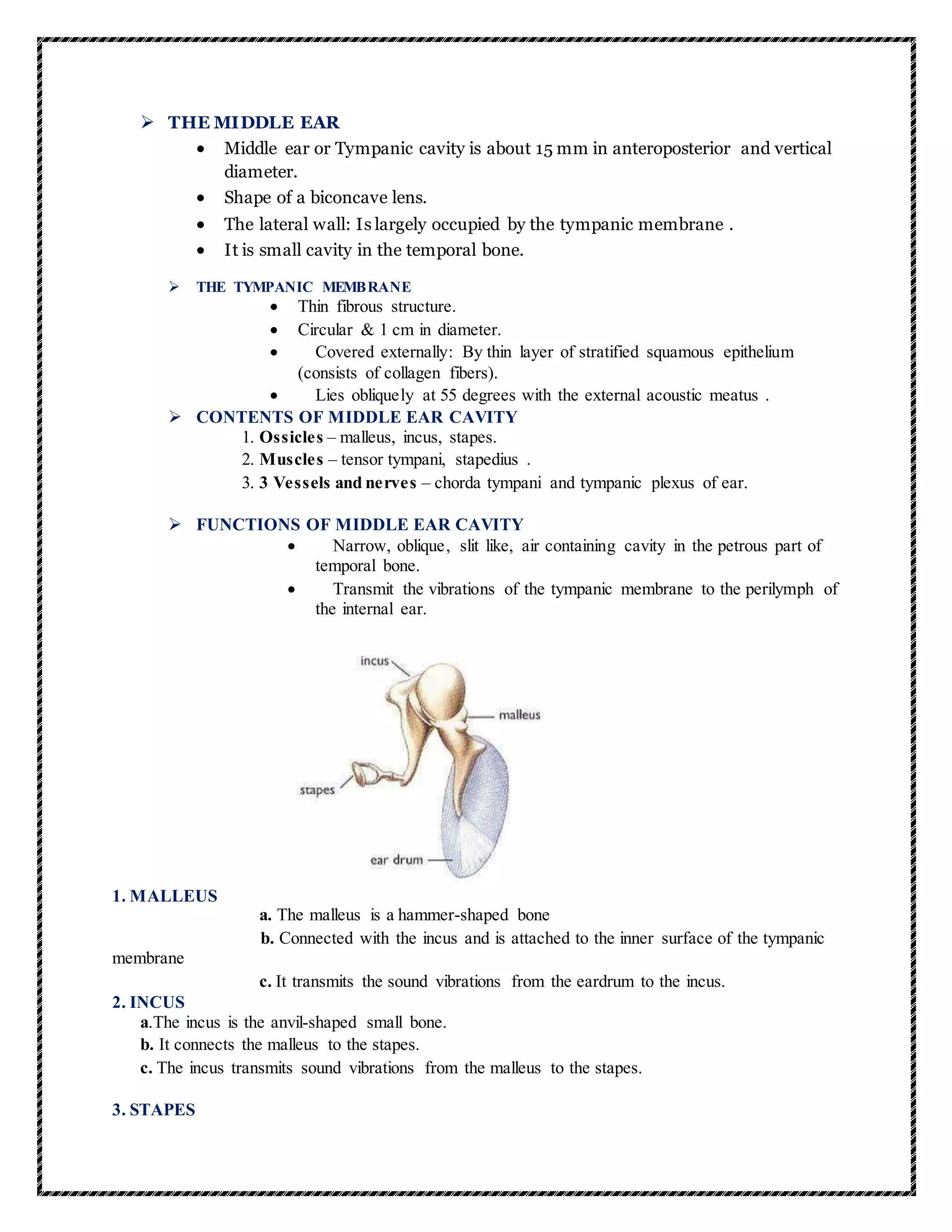
![a.The stapes is the stirrup-shaped small bone.
b. Attached to the incus laterally and to the fenestra ovalis, the "oval window", medially.
c. The oval window is adjacent to the vestibule of the inner ear.
d. The stapes is the smallest and lightest bone in the human body.
e. The stapes transmits the sound vibrations from the incus to the membrane of the inner ear
inside the fenestra ovalis.
INTERNAL EAR
The structures in the internal ear convey information to the brain about balance and
hearing.
Cochlear duct is the organ of hearing.
Semicircular ducts, utricle, and saccule are the organs of balance .
The nerve responsible for these functions is the vestibulocochlear nerve [VIII], which
divides into vestibular (balance) and cochlear (hearing) parts after entering the
internal acoustic meatus.
Cochlea – a tube shaped like a shell of a snail which consists of coiled, liquid-filled
tubes that are separated from one another by membranes. The lining of the
membranes is specialized hair cells that are sensitive to vibration. It contains the
actual organ of hearing called the organ of corti. That receives the sound waves and
transmits them to the brain.
semi-circular ducts – enable the body to maintain balance, consists of three
interconnected loop-shaped tubes at right angles to one another, these canals contain
fluid and hairlike projections that detect changes in body positions.
FUNCTION OF INTERNAL EAR
The internal ear converts the mechanical signals received from the middle ear,
which start as sound captured by the external ear, into electrical signals to transfer
information to the brain.
The internal ear also contains receptors that detect motion and position.
PHYSIOLOGY OF HEARING/MECHANISM OF HEARING
The external ear receives sound waves and directs them to the ear drum.
The ear drum vibrates in response to the sound waves and these vibrations
are transmitted through the ear ossicles (malleus, incus and stapes) to the oval
window.
The vibrations pass through the oval window on to the fluid of the cochlea,
where they generate waves in the lymphs.
The waves in the lymphs include a ripple in the basilar membrane.
These movements of the basilar movements bind the hair cells,passing
them against the tectorial membrane.
As a result, nerve impulses are generated in the aasociated afferent neurons.
These impulses are transmitted by the afferent fibres via auditory nerves to
the auditory cortex of the brain,
where the impulses are analyzed and the sound is recognized.
THE END](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ear-210518025533/75/Ear-4-2048.jpg)
