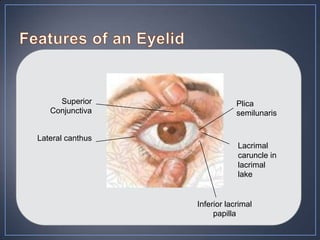
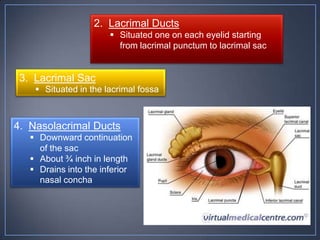
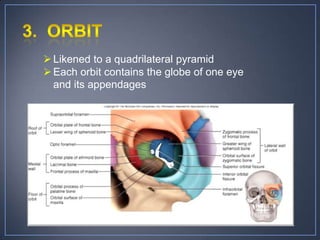
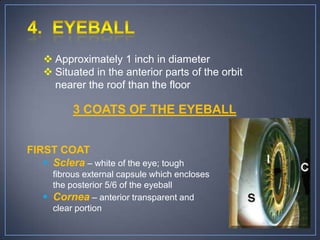
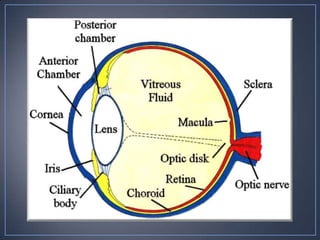
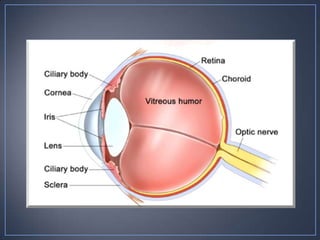
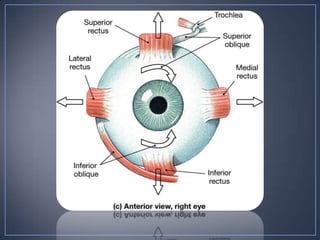
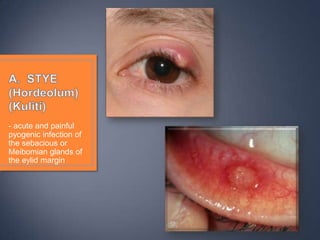
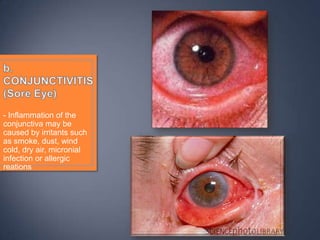
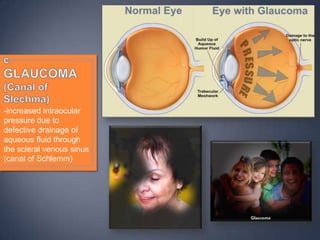
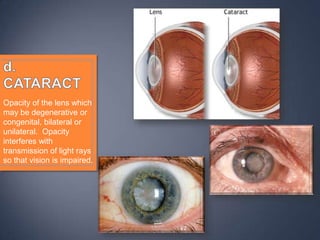
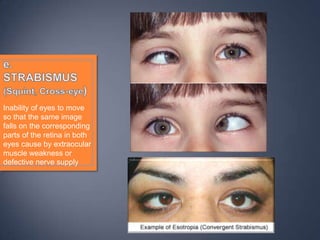
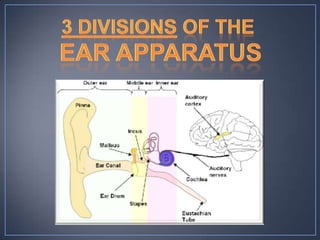
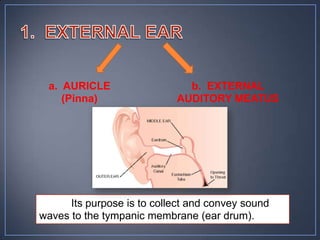
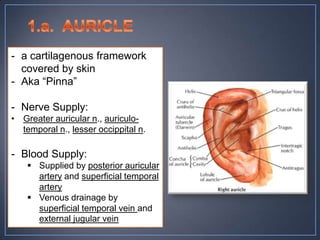
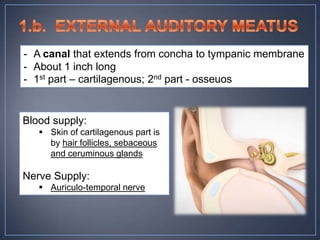
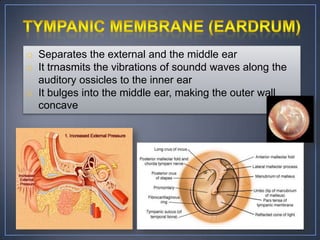
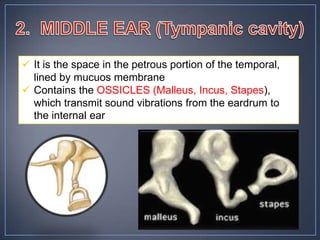
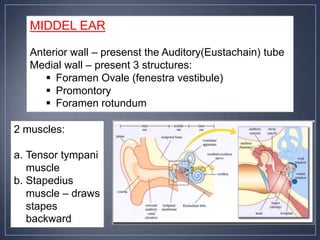
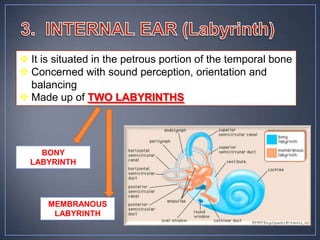
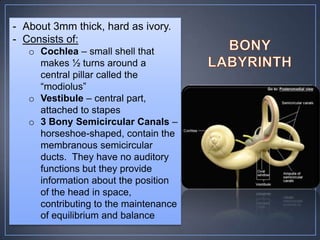
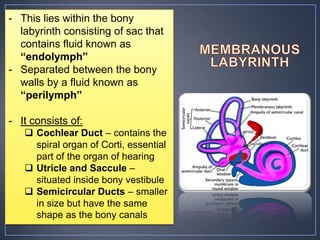
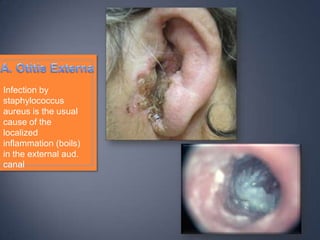
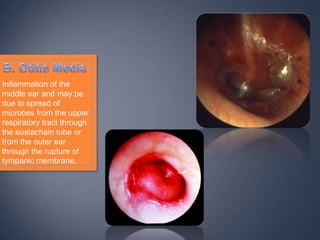
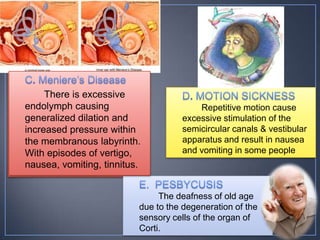
The document discusses the anatomy and physiology of the eye and ear. It describes the structures of the eye such as the coats, lacrimal apparatus, extraocular muscles, and refractive media. Common eye disorders like styes, conjunctivitis, glaucoma and strabismus are mentioned. The parts of the ear like the pinna, external auditory meatus, tympanic membrane, middle ear ossicles, inner ear bony and membranous labyrinths are outlined. Some ear diseases including otitis externa, media, Meniere's disease, and presbycusis are briefly discussed.