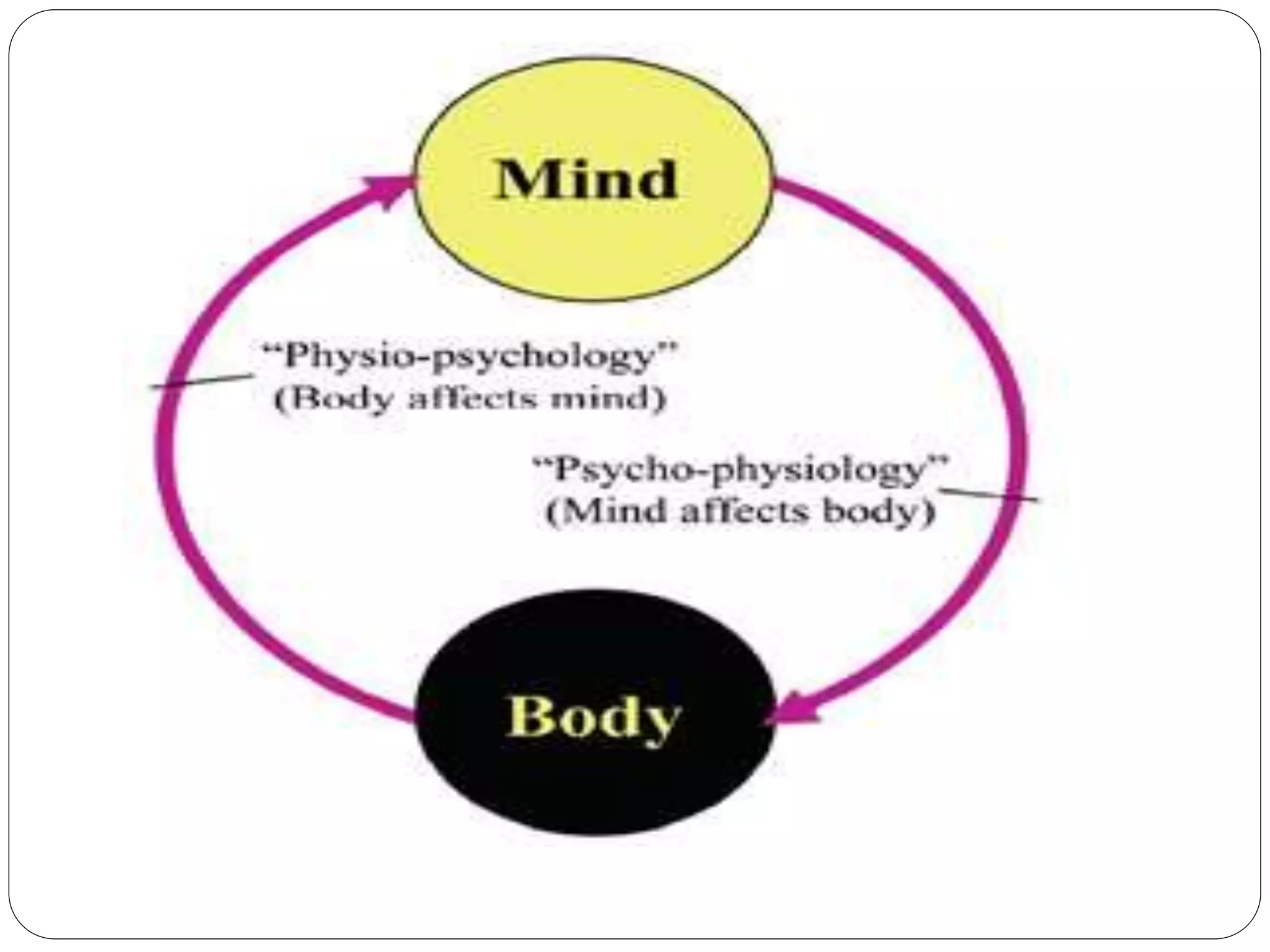
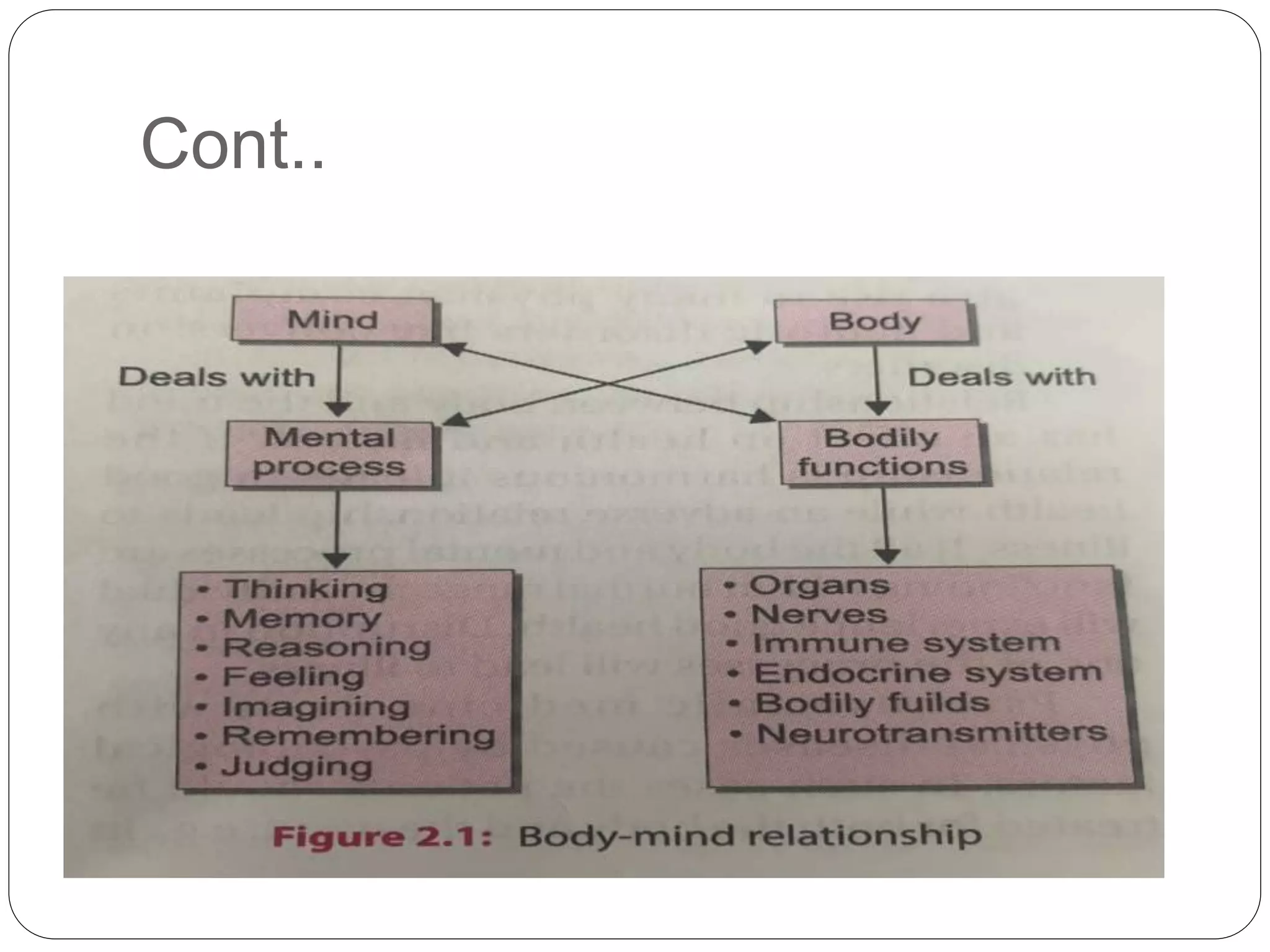
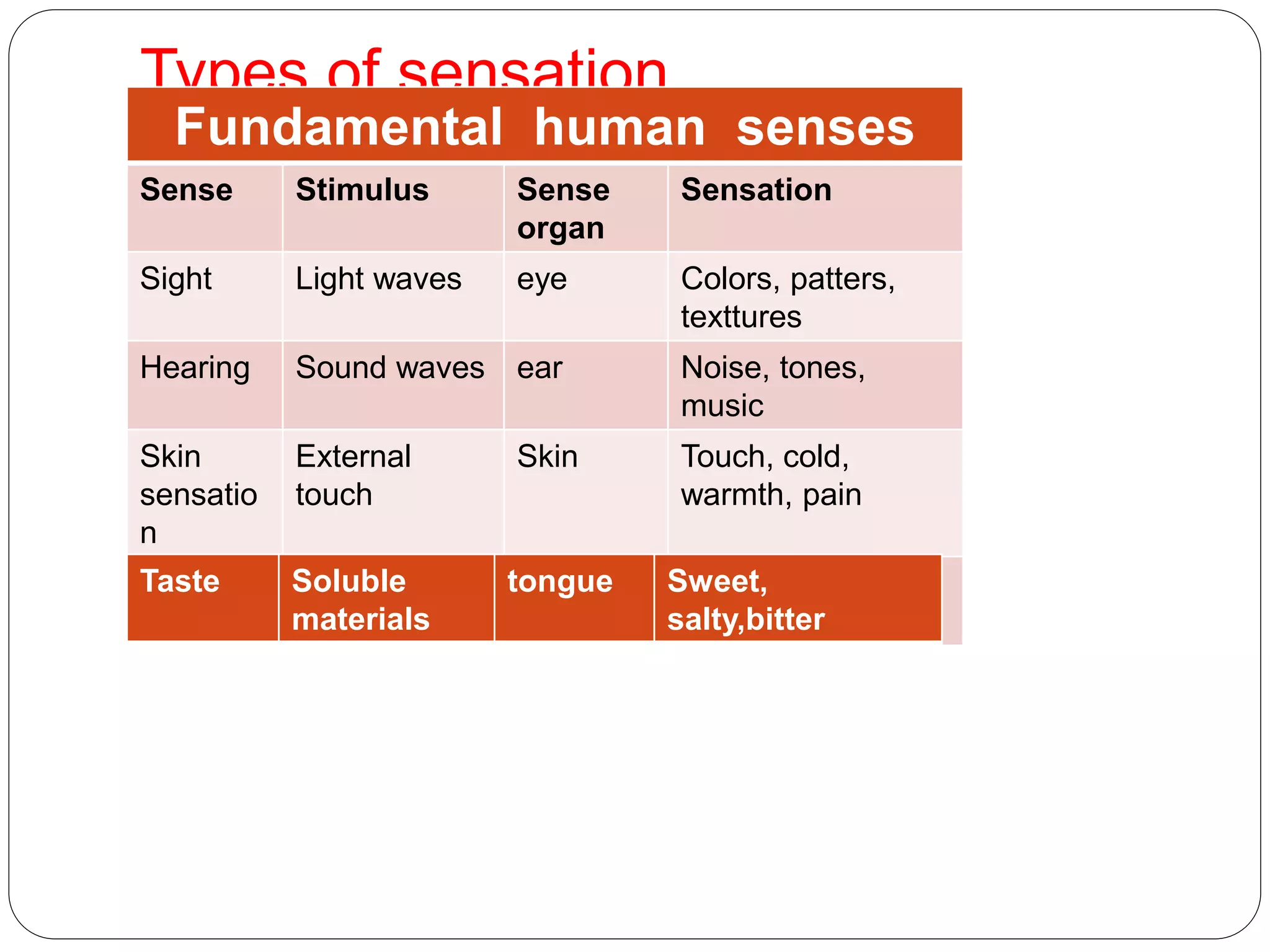
The document discusses the biological basis of behavior, including the relationship between the body and mind, genetics and inheritance of behavior, the role of the brain and nervous system in behaviors, and sensory processes. It explains how genetics, brain functioning, and sensory perception influence behaviors and mental states. The key topics covered are the mind-body connection, inheritance of traits, the brain's involvement in behaviors, and normal and abnormal sensory processing.