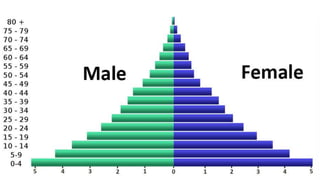
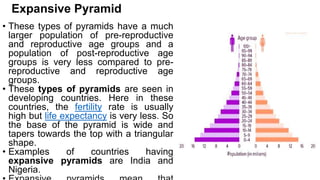
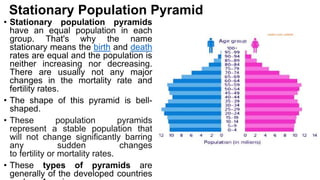
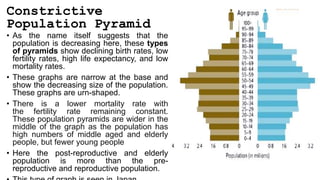
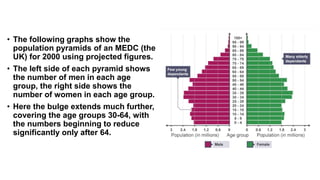
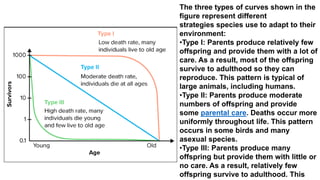
Population structure is defined by the genetic variation within populations and is influenced by evolutionary processes like recombination, mutation, genetic drift, demographic history, and natural selection. Key elements of population structure include population size, geographic distribution, age distribution, sex ratio, ethnic/racial composition, and socioeconomic factors. Understanding population structure helps policymakers address demographic challenges and meet population needs. Population pyramids graphically represent age and sex structure and can show expansive, stationary, or constrictive growth. Metapopulations are spatially structured populations that persist through a balance of local extinctions and recolonization between fragmented subpopulations.