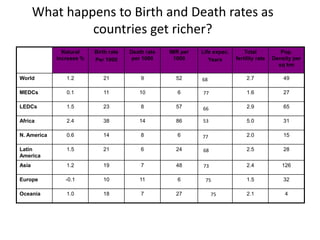
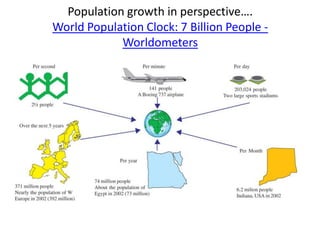
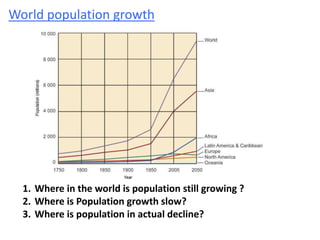
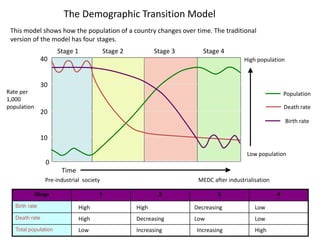
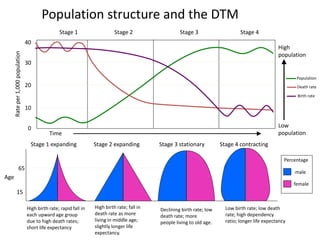
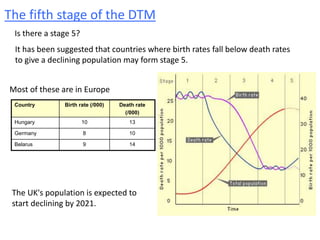
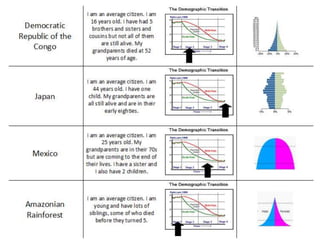
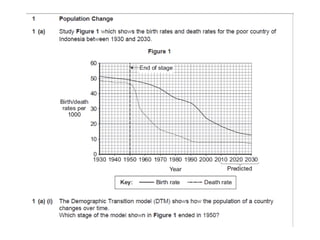
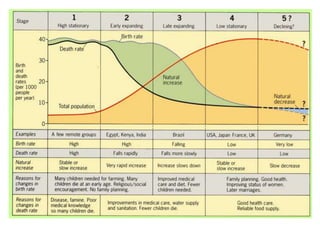
The document discusses the demographic transition model (DTM) and population trends in different parts of the world. It provides data on birth rates, death rates, population growth rates, life expectancy and total fertility rates globally and across various regions. The DTM shows how these indicators change as countries develop, typically from high birth and death rates to lower rates as countries industrialize. The model has four stages that reflect these transitions. The document also notes some countries may now be entering a fifth stage where population declines as birth rates fall below replacement levels.