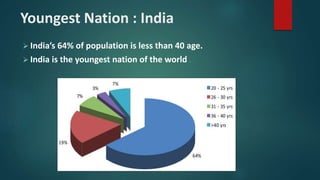
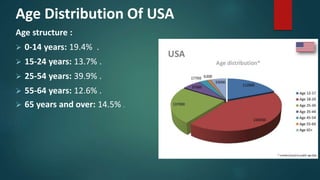
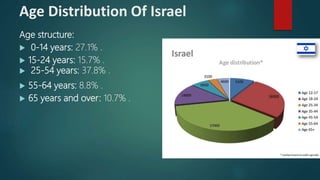
The document discusses age distributions in less developed and more developed countries. It notes that less developed countries have around one-third of their population under age 15, while more developed countries have under one-fifth under age 15. India is highlighted as having the youngest population in the world, with 64% under age 40. While a young population can provide benefits like economic growth, it also strains resources and increases challenges around education, employment, and infrastructure.