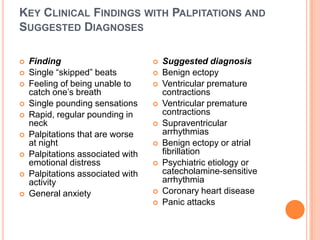
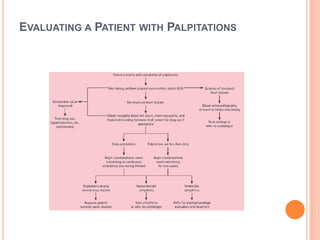
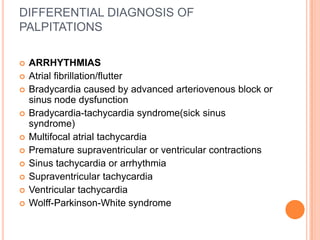
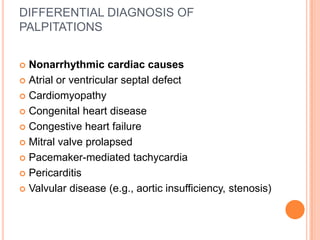
This document discusses the evaluation of a patient presenting with palpitations. It begins by defining palpitations and describing the general and systemic examination findings that should be assessed. These include vital signs, heart auscultation findings, and an ECG. It then lists key clinical findings associated with different arrhythmias and cardiovascular conditions that could cause palpitations. The document concludes by discussing the differential diagnosis of palpitations, which can be due to arrhythmias, psychiatric conditions, medications, nonarrhythmic cardiac causes, or extracardiac etiologies. A thorough history, physical exam, and testing are needed to determine the underlying cause.