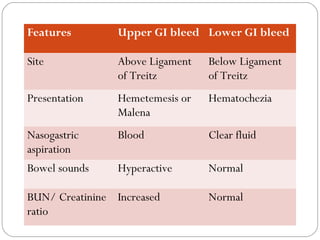
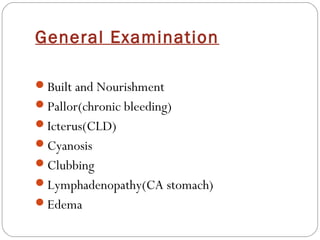
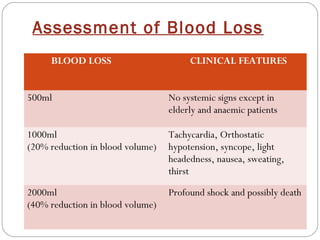
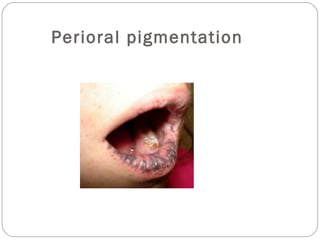
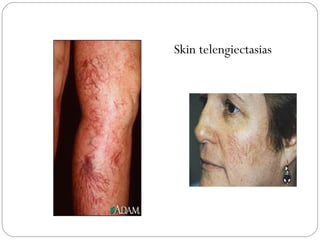
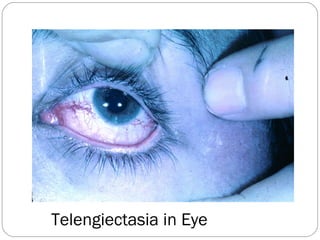
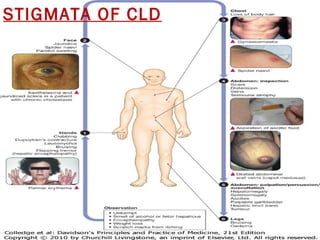
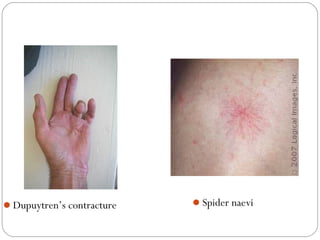
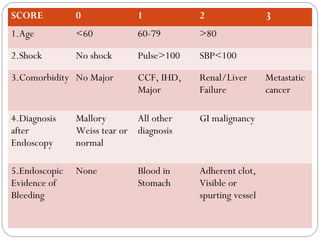
This document provides guidance on evaluating and managing a patient presenting with upper gastrointestinal bleeding. It outlines the differences between upper and lower GI bleeding and describes the relevant history, examination findings, and Rockall score for risk stratification. Key points include distinguishing symptoms of hematemesis versus hematochezia, assessing blood loss based on vital signs and volume, examining for stigmata of liver disease, and endoscopy to determine the source of bleeding and prognosis.